Biology Notes Form 4
Biology Notes Form 4
Click Here - Free KCSE Past Papers » KNEC Past Exams » Free Downloads » KCSE Papers & Marking Schemes
Genetics
Introduction
Variations within Plant and Animal Species
Variation
Continuous and Discontinuous Variation
Continuous Variations
Discontinuous Variations
Examples include:
Structure and Properties of Chromosomes
Number of Chromosomes
Diploid Number (2n)
Chromosome Structure
Properties of Chromosomes
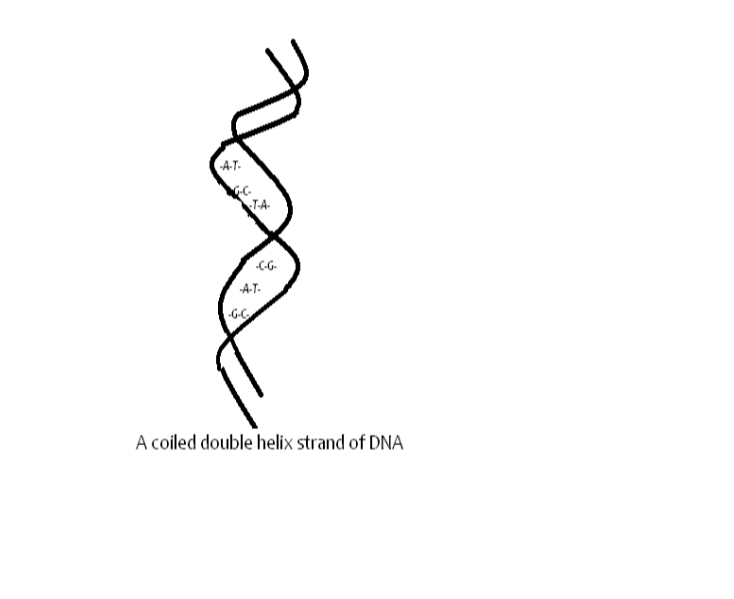
Structure of DNA
Components of DNA
Monohybrid Inheritance
Examples
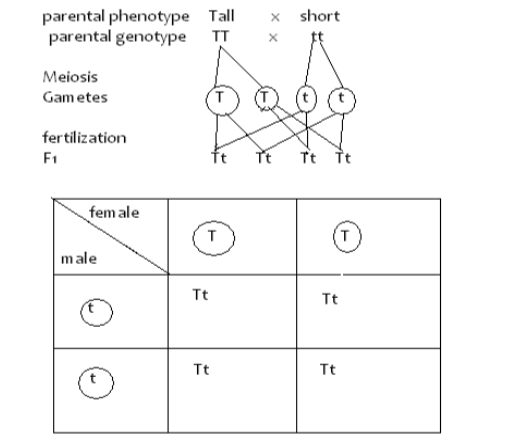
Mendel's Procedure
Results
Terms used in Genetics Genotype:
Phenotype:
Alleles:
Homozygous:
Heterozygous:
Hybrid:
Hybrid vigour or Heterosis:
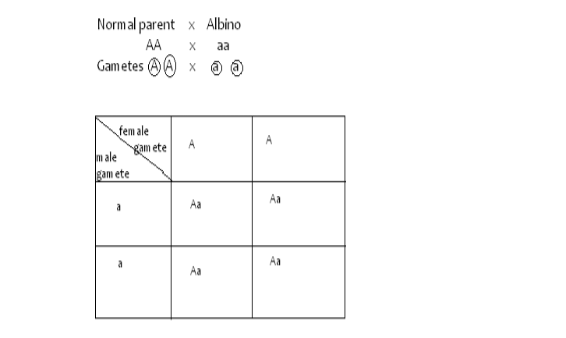
Use of Symbols
F1 genotype Tt
F1 Phenotypic ratio =All tall.
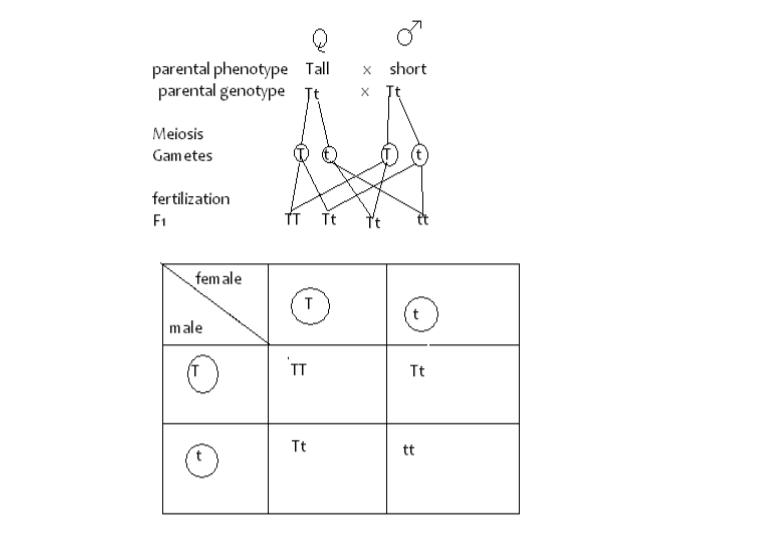
F2 Phenotypic ratio;3 Tall;1 short
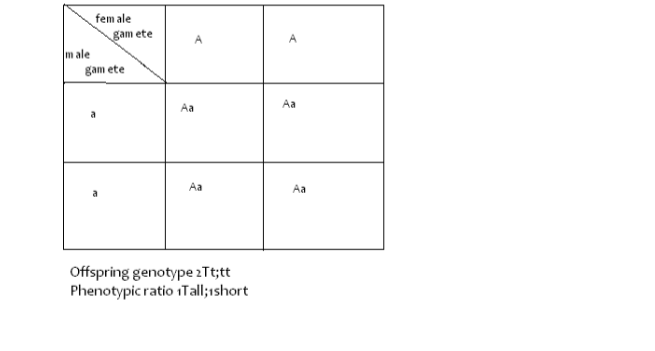
Test Cross or Back Cross
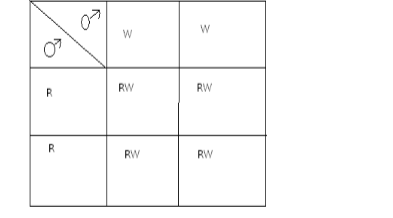
Other characters that show complete dominance in humans are:
Incomplete Dominance
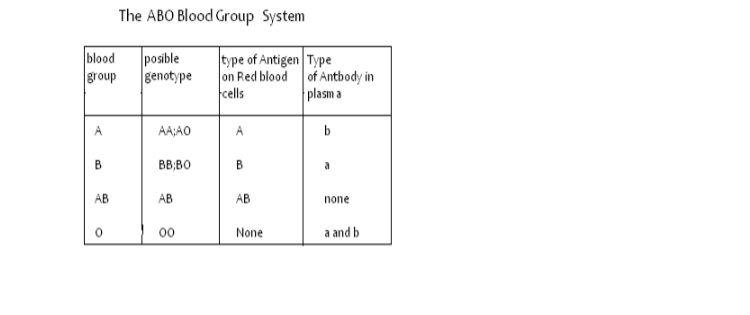
Inheritance of ABO blood groups in humans
Rhesus Factor
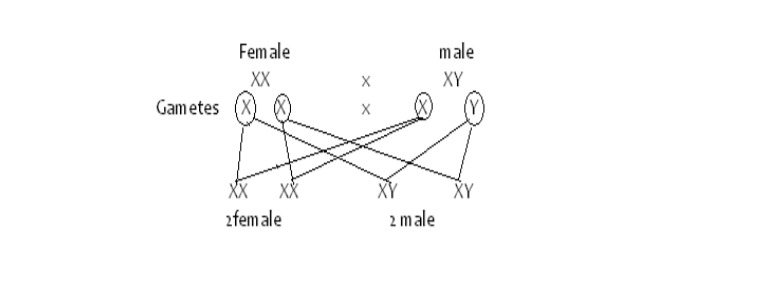
Sex Determination in Humans
Sex linked genes
In human, sex linked characters found on the X chromosome include:
Haemophilia:
Red-green colour-blindness
Genes found on y-chromosome include:
Mutations
Mutagens:
These are agents that cause mutations.
Causes and consequences of chromosomal mutations
Down's syndrome
Turner's Syndrome
Klinefelter's Syndrome
Changes in the structure of a chromosome during meiosis.
These mutations are described as follows:
Deletion:
Inversion:
Translocation:
Duplication:
Gene Mutations
Genetically inherited disorders in humans
Practical Applications of Genetics
Plant and Animal breeding
Genetic counselling
This is done through:
Genetic Engineering
Application of Genetic Engineering
Pharmaceutical industries:
Agricultural industries:
Cloning
Gene therapy
Practical Activities To demonstrate Continuous variations
Height of students
Discontinuous variations - ability to roll tongue
Demonstration of Mitosis and Meisosis
Mitosis
Meiosis
Human Finger Prints
Evolution
Meaning of Evolution and Current Concepts
The Origin of Life
Special Creation
Chemical Evolution
Evidence for Organic Evolution
Fossil Records
Limitations of the Fossil Evidence
Geographical Distribution
Comparative Embryology
Comparative Anatomy
Cell Biology
Mechanism of Evolution
Lamark’s theory
Evolution by natural selection
Darwin made the following conclusions;
Natural selection
Resistance to Drugs
Practical Activities
Comparison of Vertebrate Limbs
Comparision of Wings of bird-and insect
Education tour to Archeological site/local Museum
In Plants and Animals
Introduction
Irritability
Stimuli
>b>Response
Co-ordination
Reception
Irritability in Plants
Tropisms
Phototropism
Survival value:
Geotropism
Survival Value:
Hydrotropism
Survival Value
Chemotropism
Survival Value
Thigmotropism
Survival Value
Tactic Movements in Plants and other Organisms
Survival Value
Survival Value
Nastic Movements
Production of auxins and their effects on plant growth
Effects of Auxin on Plant Growth
Apical Dominance
Growth of adventitious roots
Parthenocarpy
Reception, Responses and Co¬ordination in Animals
Receptors
Effectors
The Nervous System
Components of the nervous system in humans
It consists of the following:
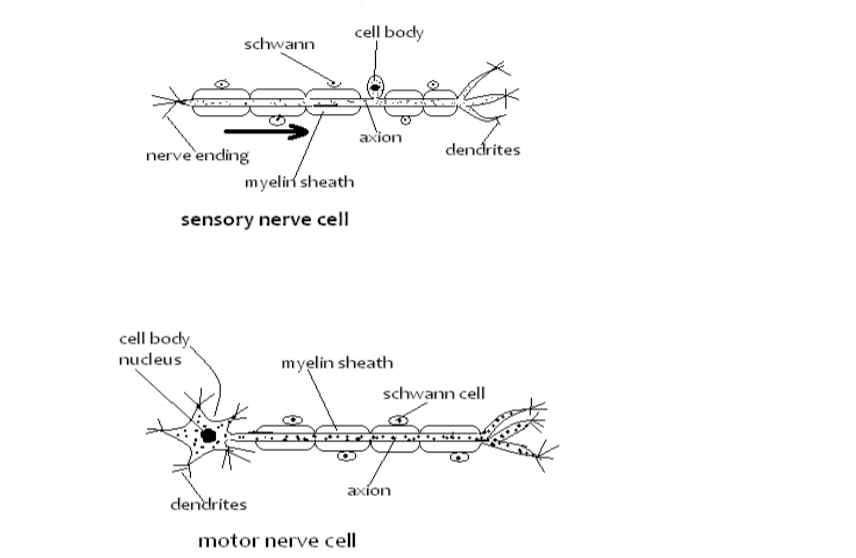
Structure and Functions of Neurons
There are three types of neurons:
Sensory neurone
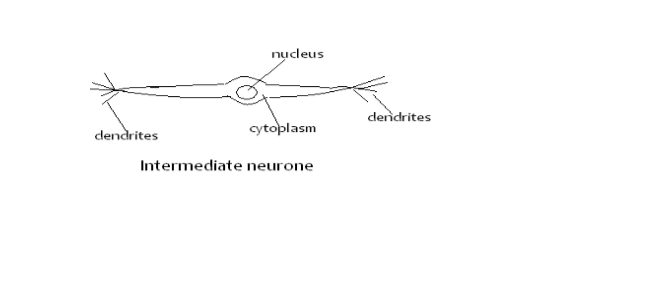
Intermediate or connector neurone
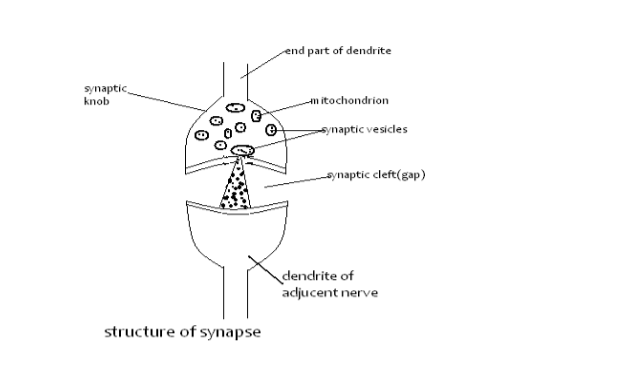
The brain consist of the following parts:
Cerebrum.
The medulla oblongata (brain stem).
The cerebellum
The hypothalamus
The pituitary gland
Optic lobes -control the sense of sight.
Olfactory lobes -control the sense of smell.
Spinal Cord
Simple And Conditioned Reflex Actions
Simple Reflex Action
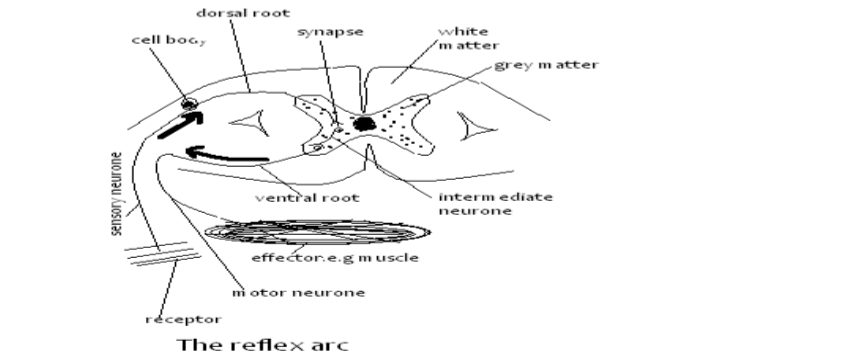
Examples of reflex action include:
Conditioned Reflexes
The Role of Endocrine System in Human Beings

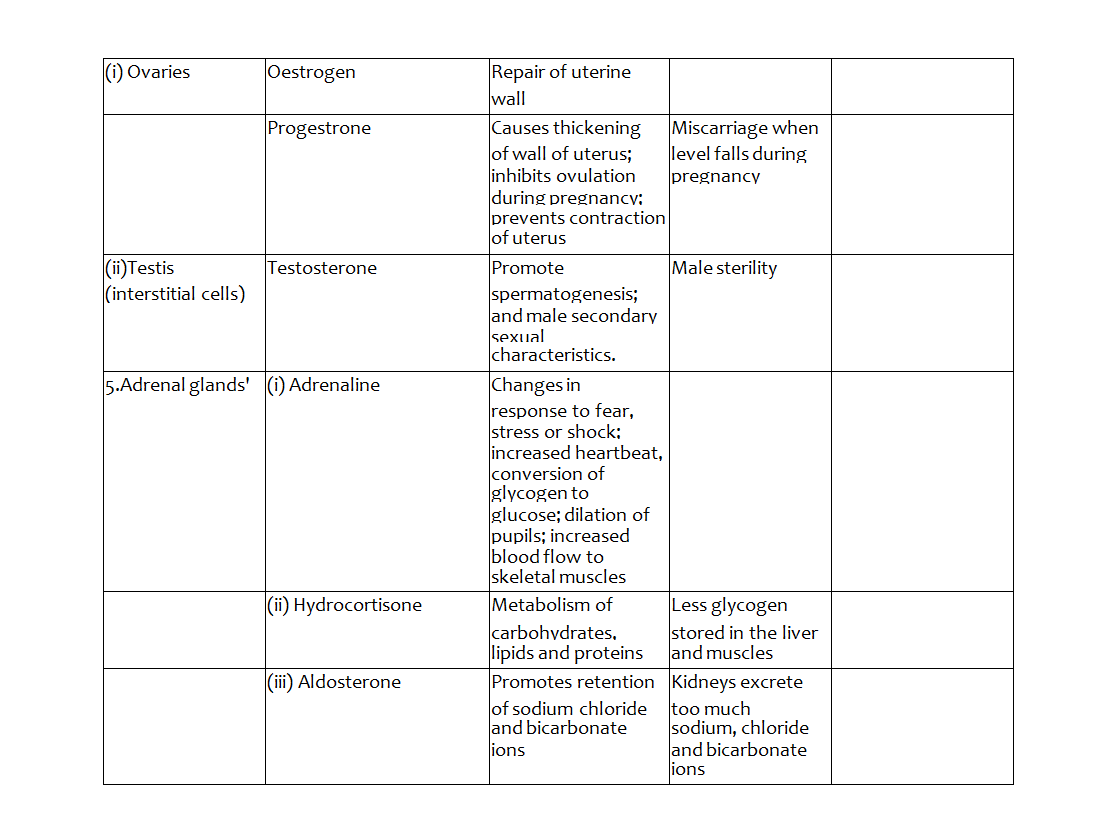
Over secretion
Under secretion
Thyroxine
Over secretion is termed hyperthyroidism this causes:
Under secretion is termed hypothyroidism:
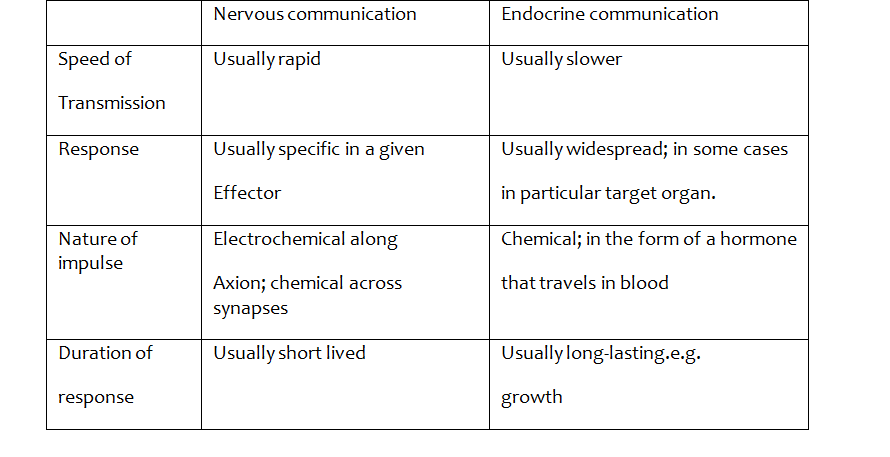
Comparison between endocrine and nervous system
Effects of drugs abuse on the human health.
Prescription drugs
Below is a list of effects of hard drugs on human health
Structure and Function of Parts of the Human Eye
Structure
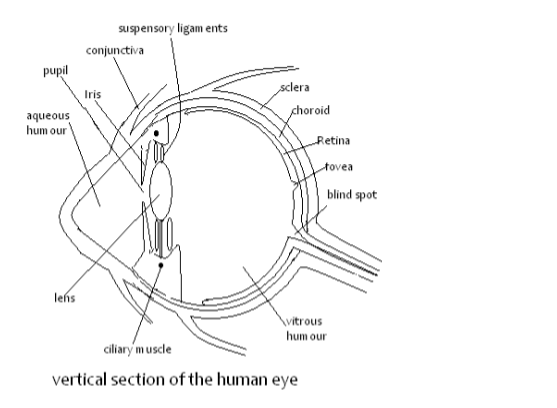
Sclerotic layer
Cornea
Choroid
Ciliary body
Suspensory ligaments
Lens
Aqueous humour
Iris
Vitreous humour
Retina
Fovea centralis
Optic nerve
Blind spot
Eye lid
Eyelashes
Conjuctiva
Accommodation
Control of light intensity entering the eye
Image formation and Interpretation
Common Eye Defects and their Correction
Short-sightedness (Myopia)
Long-sightedness (Hypermetropia)
Astigmatism
Structure and Functions of Parts of Human Ear The Mammalian Ear
The mammalian ear performs two major functions:
The ear is divided into three sections.
The Outer Ear
This consists of:
The Middle Ear
The Inner Ear
Hearing
Balance and posture
Defects of the ear
Acute labyrinthitis
Tinnitis:
Deafness.
This may be as a result of:
Otitis Media
Practical Activities
Geotropism
Phototropism
Etiolation
Young seedlings are placed in a dark box.
It is kept moist but not exposed to light.
After two weeks the seedlings are removed and observations made to note the following:
Colour of leaves is yellow.
Size of leaves is small
Length of internodes is long
Length of stem elongated long and thin.
Other seedlings that were grown in light are observed (as control) and similar measurements taken.
They are green in colour with larger leaves, shorter internodes and the stem is shorter and thicker.
Those in the dark have smaller yellow leaves, long thing stems with long internodes. (etiolated).
Experiment to Determine Distance of the Blind Spot
The Knee Jerk Experiment
Support and Movement in Plants and Animals
Necessity for support and movement
Necessity for support and movement in plants
Tissue distribution in Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous plants
Role of support tissues in young and old plant
Plants are held upright by strengthening tissues ;
Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Xylem
Plants with weak stems obtain their support in the following ways.
Support and Movement in Animals
Necessity for support and movement in animals.
Animals move from place to place:
Types and Functions of Skeletons
Exoskeleton
Functions of Exoskeleton
Endoskeleton:
Functions
External features-of Tilapia
Mammalian skeleton
The mammalian skeleton is divided into two:
The Axial Skeleton
This consists of the ;
The Skull
Sternum and ribs
The Vertebral Column
Thoracic Vertebrae
Lumbar Vertebrae
Sacral Vertebrae
Caudal Vertebrae
Appendicular Skeleton
Bones of Fore-limbs
Pectoral girdle
Humerus
Ulna and radius
Bones of hind limb
Pelvic Girdle
The Femur
Tibia and Fibula
Joints and Movement
Movable joints are of three main types:
Gliding joint
Synovial joint
Hinge joint
Types, Locations and Function of Muscles
Smooth Muscle (Involuntary Muscles)
Skeletal Muscle (striated or voluntary muscle)
Cardiac Muscle
Role of muscles in movement of the human arm
Antagonistic muscles of human forelimb
Practical Activities
To observe prepared slides of transverse section of stems of herbaceous and woody plants.
To observe wilting in young herbaceous plants.
To examine the exoskeleton in an arthropod.
To observe the external features of a finned fish.
To examine bones of the axial skeleton of a rabbit.
To observe bones of appendicular skeleton.
KCSE Revision Notes Form 1 - Form 4 All Subjects
Please insert your question in the form below. Check and ensure that your question has not been asked and answered in the enquiries appearing beneath the form.
Kenya Scholarships for Undergraduate Students » Kenya Scholarships for Postgraduate Students » Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyan Students » Kenya Undergraduate Scholarships » Full Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyans » Kenya Postgraduate Scholarships » Scholarships & Grants » Undergraduate Scholarships » Universities in Kenya » Kenya Universities and Colleges Central Placement Service (KUCCPS) » Colleges in Kenya » KASNEB Registration & Results » Secondary Schools Scholarships in Kenya » Undergraduate & Graduate Scholarships for Kenyans
Scholarships for African Students » Undergraduate Scholarships » African Women Scholarships & Grants » Developing Countries Scholarships » Erasmus Mundus Scholarships for Developing Countries » Fellowship Programs » Funding Grants for NGOs » Government Scholarships » LLM Scholarships » MBA Scholarships » PhD and Masters by Research Scholarships » Public Health Scholarships - MPH Scholarships » Refugees Scholarships » Research Grants » Scholarships and Grants
Scholarships in Australia » Scholarships in Belgium » Scholarships in Canada » Scholarships in Germany » Scholarships in Italy » Scholarships in Japan » Scholarships in Korea » Scholarships in Netherlands » Scholarships in UK » Scholarships in USA
aa Biology Questions and Answers
10th Grade Biology Questions and Answers
10th Grade Biology Test
11th Ncert Biology
12th Class Biology Book Free Download
2017 Biology Hsc Answers
9th Grade Biology Study Guide
A Level Biology Biological Molecules Questions
A Level Biology Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Biology Notes Edexcel
A Level Biology Notes Xtremepapers
A Level Biology Questions and Answers
A Level Biology Questions and Answers (Pdf)
A Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
A Level Biology Questions by Topic - Kidney Questions With Markschemes
A Level Biology Revision
A Level Biology Revision Edexcel
A Level Biology Revision Guide
A Level Biology Revision Notes
A Level Biology Revision Notes Pdf
A Level Biology Textbook Pdf
A Level Biology Year 1 / as Aqa Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Edexcel Notes - a* Biology
Aerobic Respiration in Plants
All Biology Essays
All Biology Essays Form 1
All Biology Essays Form 2
All Biology Essays Form 3
All Biology Essays Form 4
Anaerobic Respiration Equation
Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers
Animal Cell Questions and Answers
Animal Cell Quiz
Animal Cell Quiz Labeling
Ap Bio Quizzes
Ap Biology Essay Questions and Answers
As Level Biology Notes
Bbc Bitesize Biology Ks3
Biology 101
Biology 12th
Biology 12th Class Notes Pdf
Biology 2019 Syllabus
Biology Book 3 Klb
Biology Book 3 Notes
Biology Book for Class 11
Biology Book Pdf Free Download
Biology Cell Structure Test
Biology Class 12 Ncert Solutions
Biology Class 12 Pdf
Biology Communication Syllabus
Biology Diagrams for Class 12 - Biology Diagram Software - Biology Diagrams for Class-10 - Biology Diagrams for Class 11 - Biology Diagrams for Class 9 - Biology Diagrams to Label - Biology Diagram of Female Reproductive System - Biology Diagrams Pdf - Biology Diagrams in Form 1 - Biology Diagrams in Form 2 - Biology Diagrams in Form 3 - Biology Diagrams in Form 4 - Kcse Biology Diagrams -biology Revision Tips
Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Biology Essay Questions and Answers 2018
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 1
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 4
Biology Essays and Answers
Biology Essays and Answers Form 1
Biology Essays and Answers Form 2
Biology Essays and Answers Form 3
Biology Essays and Answers Form 4
Biology Essays Kcse
Biology Essays Kcse Form 1
Biology Essays Kcse Form 2
Biology Essays Kcse Form 3
Biology Essays Kcse Form 4
Biology Essays Pdf
Biology Exam 2 Test
Biology Exam Form Four
Biology Exam Form One
Biology Exam Form Three
Biology Exam Form Two
Biology Exam Practice Test
Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Exam Study Guide
Biology Excretion Notes
Biology Exercise Form 4 With Answers
Biology Final Exam Answer Key
Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2016
Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2017
Biology Final Exam Answers 2018
Biology Final Exam Answers 2019
Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers
Biology Form 1 & 2 and Answers
Biology Form 1 Chapter 1
Biology Form 1 Diagrams
Biology Form 1 Notes
Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 1 Past Papers
Biology Form 1 Questions
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 1
Biology Form 1 Revision Questions
Biology Form 1 Syllabus
Biology Form 2 Chapter 1
Biology Form 2 Chapter 2
Biology Form 2 Diagrams
Biology Form 2 Notes
Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 2 Past Papers
Biology Form 2 Pdf
Biology Form 2 Questions
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2
Biology Form 2 Revision Notes
Biology Form 2 Syllabus
Biology Form 3 Chapter 3
Biology Form 3 Classification
Biology Form 3 Diagrams
Biology Form 3 Ecology
Biology Form 3 Notes
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 3 Past Papers
Biology Form 3 Questions
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Term 3
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers+pdf
Biology Form 3 Revision Notes
Biology Form 3 Syllabus
Biology Form 3 Topics
Biology Form 4 All Chapter
Biology Form 4 Chapter 4
Biology Form 4 Diagrams
Biology Form 4 Notes
Biology Form 4 Notes All Chapter Pdf
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 1
Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Past Papers
Biology Form 4 Questions
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 4
Biology Form 4 Syllabus
Biology Form 4 Textbook Pdf
Biology Form Four Notes Pdf
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form One
Biology Form One Exam
Biology Form One Notes Pdf
Biology Form One Questions
Biology Form One Questions and Answers
Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form One Term Three Test
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Three Reproduction
Biology Form Three Reproduction.
Biology Form Three-questions and Answers
Biology Form Two Diagrams
Biology Form Two Notes Pdf
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form2
Biology Form2 Textbook
Biology Grade 10 Exam Papers
Biology Hsc Pdf
Biology Human Reproduction Video
Biology Kcse 2017
Biology Kcse 2017 Paper 1
Biology Kcse Questions
Biology Made Familiar
Biology Mcq for Class 11
Biology Mcq for Class 12
Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams
Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams Pdf
Biology Mcq for Neet Pdf
Biology Mcq With Answers Pdf
Biology Mcqs for Class 12 Pdf
Biology Mid Familia Form One
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cxc
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf
Biology Notes
Biology Notes for High School Students
Biology Notes for Igcse 2014
Biology Notes Form 1
Biology Notes Form 1 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 2
Biology Notes Form 2 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 3
Biology Notes Form 3 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 4
Biology Notes Form 4 Chapter 2
Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf
Biology Notes Form One Pdf
Biology Notes Form Three
Biology Notes Form Two
Biology Objective Answer
Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Pdf
Biology Paper 1
Biology Paper 1 Notes
Biology Paper 1 Questions
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Paper 1 Topics
Biology Paper 2 2017
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Paper 2 Revision
Biology Paper 2018
Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Paper 4 Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Paper One Questions and Answers
Biology Past Papers 2017
Biology Past Papers Form 3
Biology Practical Book Class 12 Pdf
Biology Practical Exam
Biology Practicals Questions and Answers
Biology Practice Test 9th Grade
Biology Practice Test Answers
Biology Practice Test Questions and Answers
Biology Question and Answers Note
Biology Questions
Biology Questions and Answers
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 3
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 4
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Biology Questions and Answers on Cells
Biology Questions and Answers Online
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Questions for High School
Biology Questions for High School Students With Answers
Biology Questions Multiple Choice
Biology Questions Quizlet
Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher
Biology Quiz for Class 9
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 12
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for High School
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions for Class 12
Biology Quiz Questions for College Students
Biology Quiz With Answers
Biology Quiz With Answers Pdf
Biology Revision
Biology Revision a Level
Biology Revision Notes Form 1
Biology Revision Notes Form 2
Biology Revision Notes Form 3
Biology Revision Notes Form 4
Biology Revision Notes Igcse
Biology Revision Questions
Biology Study Guide
Biology Study Guide - Biology Questions and Answers
Biology Study Guide Answer Key
Biology Study Guide Answers
Biology Study Guide Ib
Biology Study Guide Pdf
Biology Study Notes
Biology Syllabus in Kenya
Biology Test Questions and Answers
Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Topics Form One
Biology Unit 1 Quiz
Biology | Revision Science
Cell Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Cell Biology Exam Questions Pdf
Cell Biology Mcq With Answers
Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions Pdf
Cell Biology Previous Question Papers
Cell Biology Question Bank
Cell Biology Question Bank Pdf
Cell Biology Question Paper Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf in Hindi
Cell Biology Short Answer Questions
Cell Biology Test Bank Questions
Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers
Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Mcq Pdf
Cell Organelles Labeling Quiz
Cell Organelles Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Cell Questions and Answers
Cell Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Questions Quizlet
Cell Structure and Function Pdf
Cell Structure and Function Pdf Class 11
Cell Structure and Function Quiz Answers
Cell Structure and Function Test Answer Key
Cell Structure and Function Test Pdf
Cells
Cells Questions
Cellular Organization Pdf
Chemical Equation for Aerobic Respiration
Chemistry Form 1 Questions and Answers
Chemistry Form 2 Exams
Chemistry Form 2 Questions and Answers
Chemistry Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Chemistry Form 3 Questions and Answers
Chemistry Form 3 Revision Questions
Chemistry Form 4 Questions and Answers
Chemistry Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Chemistry Kcse Questions and Answer
Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Chemistry Paper 3 Question and Answer
Cie a Level Biology Notes 2016
Cie a Level Biology Notes Pdf
Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 Mcqs
College Biology Practice Test
College Biology Quiz
College Biology Quiz Chapter 1
College Biology Quizlet
College Biology Study Guide
College Biology Study Guide Pdf
College Biology Test Questions and Answers
Complete Biology for Cambridge Igcse Revision Guide Pdf
Cytology Mcqs With Answers Pdf
Difficult Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Animals
Download Form Three Biology Notes
Download Klb Biology Book 2
Easy Biology Questions
Easy Cell Questions
Edexcel a Level Biology B
Edexcel a Level Biology Notes Pdf
Edexcel a Level Biology Salters Nuffield
Edexcel A2 Biology Notes
Edexcel as Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel Biology A2 Revision Notes Pdf
Edexcel Biology Unit 2 Revision Notes
Edexcel Gcse Science Revision Guide Pdf
Energy Questions Science Bowl
Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Answers
Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Download Free
Exam Notes for Biology 101
Excretion Question and Answer Form 4 Work
Excretion Questions and Answers
Excretory System Questions and Answers Pdf
Excretory System Structure
F3 Biology Test Paper
Form 1 Biology Exam
Form 1 Biology Notes
Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 1 Biology Syllabus
Form 1 Mathematics Questions and Answers
Form 1 Mathematics Test Paper Pdf
Form 1 Revision Papers
Form 2 Biology Exam
Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers >
Form 2 Biology Syllabus
Form 2 Mathematics Questions and Answers
Form 3 Biology Book
Form 3 Biology Exam
Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 3 Chemistry Exam Paper
Form 3 Chemistry Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 3 English Exam Paper
Form 3 History Exam Paper
Form 3 Maths Exam Paper
Form 4 Biology Exam
Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers
Form Four Biology Book
Form Four Biology Revision Questions
Form Four Biology Syllabus
Form Four Biology Topics
Form One Biology Book
Form One Biology Questions
Form One Biology Revision Questions
Form One Biology Syllabus
Form One Biology Topics
Form One Geography Questions and Answers
Form One Notes of Biology
Form One Past Papers
Form Three Biology Book
Form Three Biology Notes
Form Three Biology Revision Questions
Form Three Biology Syllabus
Form Three Biology Topics
Form Three Cre Notes Pdf
Form Two Biology Book
Form Two Biology Examination
Form Two Biology Notes
Form Two Biology Revision Questions
Form Two Biology Syllabus
Form Two Biology Topics
Form Two Chemistry Cat
Form Two Chemistry Past Papers
Form Two Chemistry Questions and Answers
Form Two Chemistry Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Two Notes
Free a-level Biology Revision App | Pass Your Biology Exams
Free Biology Form 1 Notes
Free Biology Form 2 Notes
Free Biology Form 3 Notes
Free Biology Form 4 Notes
Free College Biology Practice Test
Free Kcse Revision Notes
Fun Biology Questions
Funny Biology Questions and Answers
Funny Biology Quotes
Funny Science Questions
Funny Science Questions to Ask
Gas Exchange Exam Questions
Gas Exchange Practice Test
Gas Exchange Quiz
Gcse Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Gcse Biology Past Papers
Gcse Biology Revision
Gcse Biology Revision Notes
Gcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf
Gcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf 9-1
Gcse Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Gcse Biology Textbook Pdf
Gcse Biology Topics - Pass My Exams: Easy Exam Revision Notes
General Biology Practice Test With Answers
General Biology Quiz
General Biology Test Questions and Answers
General Knowledge in Biology Human Body
General Science Mcq for Ssc
General Science Mcqs With Answers Pdf
General Science Notes Pdf
Geography Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Geography Form 1 Revision Questions
Geography Form 3 Questions
Good Biology Questions to Ask
Gre Biology Practice Test
Gre Biology Subject Test Pdf
Hard Biology Quiz Questions
Hard Science Questions and Answers
Hard Science Questions to Ask Your Teacher
High School Biology Final Exam Doc
High School Biology Final Exam Pdf
High School Biology Final Exam Questions
High School Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers
High School Biology Practice Test
High School Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
How Does the Excretory System Work
How Many Chromosomes Do Gametes Have
How Many Copies of Each Gene Do Gametes Have
How Much Genetic Information Is Found in a Gamete
How to Study Biology: 5 Study Techniques to Master Biology
Hsc Biology 2018
Hsc Biology 2019
Ial Biology Notes
Ib Biology Question Bank by Topic
Igcse Biology Alternative to Practical Revision
Igcse Biology Notes 2017 Pdf
Igcse Biology Notes Edexcel
Igcse Biology Paper 6 Notes
Igcse Biology Revision Guide
Igcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf
Igcse Biology Revision Worksheets
Igcse Biology Znotes
Igcse Notes Chemistry
Igcse Physics Revision Notes Pdf
Interesting Biology Questions
Interesting Questions to Ask About Biology
Interesting Science Questions and Answers
Intro to Biology Quiz
K.c.s.e Mathematics Paper 1 2017
Kcse 2015 Biology Paper 3
Kcse 2016 Biology Paper 1
Kcse 2016 Biology Paper 2
Kcse 2017 Biology Paper 2
Kcse 2017 Papers
Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Kcse Biology Essays
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 1
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 2
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 3
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 4
Kcse Biology Notes
Kcse Biology Notes Pdf
Kcse Biology Paper 1
Kcse Biology Paper 1 2017
Kcse Biology Paper 1 2017 Pdf
Kcse Biology Paper 2
Kcse Biology Paper 2 2013
Kcse Biology Paper 2 2015
Kcse Biology Paper 2 2017
Kcse Biology Paper 3 2016
Kcse Biology Paper 3 Past Papers
Kcse Biology Past Papers and Answers
Kcse Biology Practical Past Papers
Kcse Biology Practicals
Kcse Biology Questions and Answers
Kcse Chemistry Notes
Kcse Chemistry Paper 1 2013
Kcse Chemistry Paper 1 2016
Kcse Chemistry Paper 2 2014
Kcse Chemistry Paper 2 2016
Kcse Chemistry Past Papers
Kcse Chemistry Past Papers and Answers
Kcse Chemistry Practical
Kcse Cre Past Papers and Answers
Kcse English Paper 3 2016
Kcse Essays
Kcse Made Familiar Chemistry
Kcse Made Familiar Geography
Kcse Made Familiar Kiswahili
Kcse Made Familiar Mathematics Pdf
Kcse Mathematics Paper 1 2016
Kcse Mathematics Past Papers Pdf
Kcse Mock Papers Pdf
Kcse Past Papers
Kcse Past Papers 2012
Kcse Past Papers 2013
Kcse Past Papers 2014 Pdf
Kcse Past Papers 2017
Kcse Past Papers Biology
Kcse Past Papers Chemistry
Kcse Revision Question
Kcse Revision Question for Biology
Kcse Syllabus Pdf
Kenya Secondary School Chemistry Syllabus
Kenya Secondary School Syllabus Pdf
Klb Biology Book 2
Klb Biology Book 2 Notes
Klb Biology Book 2 Pdf
Klb Biology Book 3 Pdf
Klb Biology Form 1
Klb Biology Form 1 Notes
Klb Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf
Klb Biology Form 1 Pdf
Klb Biology Form 2 Book
Klb Biology Form 2 Notes
Klb Biology Form 2 Pdf
Klb Biology Form 3 Notes
Klb Biology Form 3 Pdf
Klb Biology Form 4 Notes
Klb Biology Form 4 Pdf
Klb Biology Form One
Klb Geography Form 3
Knec Biology Syllabus
Kusoma Biology Notes
Kusoma Biology Notes Pdf
Kusoma.com Past Papers
Made Familiar Biology Pdf
Made Familiar Mathematics
Mathematics Form 3 Questions and Answers
Mathematics Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Mcq on Cell Biology Class 9
Mcqs About Gaseous Exchange
Middle School Science Bowl Biology Questions
More Than 1800 Biology Questions and Answers to Help You Study
Most Tested Questions in Form 1 Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form 2 Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form 3 Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form 4 Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form Four Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form One Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form Three Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form Two Biology and Their Answers
Multiple Choice Questions on Biology
Multiple Choice Questions on Cell Structure and Function
O Level Biology Practical Experiments
Orm Three Biology Notes
Page Navigation
Past Paper Questions by Topic Biology
Pdf Biology Form 3
Physics Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Form One Questions and Answers
Physics Questions and Answers Pdf for Competitive Exams
Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz
Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz for 5th Grade
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Grade 8
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Pdf
Plant Cell
Plant Cell Pdf Download
Plant Cell Questions and Answers
Plant Cell Test Questions
Practical Biology Experiments Pdf
Practical Biology Question and Answer Pdf
Preliminary Biology
Questions About Cells Biology
Questions and Answers on Gaseous Exchange
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 1
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 2
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 4
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Four
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Three
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Two
Questions Based to Introduction to Biology
Questions on Cell Structure and Function
Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Humans
Questions to Ask in Biology Class
Questions to Confuse Your Science Teacher
Respiration and Gas Exchange Worksheet
Respiration Notes My Elim Form Two
Revision Papers
Revision Quiz for Biology for Form Three
Science Bowl Biology Study Guide
Science Bowl Questions Biology
Science Bowl Questions Chemistry
Science Bowl Questions Earth Science
Science Bowl Questions Math
Science Bowl Questions Middle School
Science Bowl Questions Physics
Science Quiz for Class 9 Biology
Science Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10
Science Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Pdf
Science Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Pdf
Simple Scientific Questions
Smart Questions to Ask a Physics Teacher
Smart Questions to Ask a Science Teacher
Snab Biology Revision Notes
The Animal Cell Quiz Answers
The Excretory System Answer Key
The Excretory System Worksheet Answers
The Plant Cell Quiz Answer Key
Tricky Biology Questions and Answers
Tricky Science Questions for Adults
Tricky Science Quiz Questions
Two Biology Revision Questions
Types of Respiration
What Are Gametes
What Are Gametes in Biology
What Are Gametes in Plants
What Are Gametes in Punnett Squares
What Are Gametes Quizlet
What Are the Types of Gametes
Working of Excretory System
Year 11 Biology
Znotes as Biology
"Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form 2
"Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form 3
"Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form 4
"Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form Four
"Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form One
"Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form Three
"Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form Two
1 a a KCSE Past Papers
10th Grade Biology Questions and Answers
10th Grade Biology Test
11th Ncert Biology
12th Class Biology Book Free Download
2014 KCSE Marking Schemes
2014 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2015
2015 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4
2016 KCSE Papers
2016 KCSE Prediction Questions
2017 Biology Hsc Answers
2017 KCSE Prediction Questions
2018 Biology KCSE Leakage
2018 Biology KCSE Questions
2018 KCSE Busineness Studies
2018 KCSE Exam
2018 KCSE Leakage
2018 KCSE Prediction Questions
2018 KCSE Questions
2019 Biology KCSE Leakage
2019 Biology KCSE Questions
2019 KCSE Leakage
2019 KCSE Questions
9th Grade Biology Study Guide
A a a Biology Notes
a a a Biology Notes!
a a a BiologyNotes!
A a KCSE Past Papers
A Biblical View of Social Justice
A Level Biology Biological Molecules Questions
A Level Biology Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Biology Notes Edexcel
A Level Biology Notes Xtremepapers
A Level Biology Past Papers
A Level Biology Questions and Answers
a Level Biology Questions and Answers
A Level Biology Questions and Answers (Pdf)
A Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
A Level Biology Questions by Topic Kidney Questions With Markschemes
A Level Biology Revision
A Level Biology Revision Edexcel
A Level Biology Revision Guide
A Level Biology Revision Notes
A Level Biology Revision Notes Pdf
A Level Biology Textbook Pdf
A Level Biology Year 1 / as Aqa Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Edexcel Notes a* Biology
aa Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers
Advance KCSE Past Papers
Advance-africa.com KCSE Rev Quiz
Advantages and Disadvantages.
Aerobic Respiration in Plants
All Biology Essays
All Biology Notes for Senior Two
All KCSE Past Papers Biology With Making Schemes
All Marking Schemes Questions and Answers
All Past K.c.s.e Questions With Answers
Alliance Mocks 2017
Anaerobic Respiration Equation
Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers
Animal Cell Questions and Answers
Animal Cell Quiz
Animal Cell Quiz Labeling
Ap Bio Quizzes
Ap Biology 1 Textbook Pdf
Ap Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Are Sourced From KNEC.
As Level Biology Notes
Atika Biology Notes
Atika School Biology Notes
B/s Book 2 Notes
Basic Biology Books Pdf
basic Biology Interview Questions and Answers Pdf
Basic Biology Interview Questions and Answers Pdf
Basic Biology Pdf
Basic Biology Questions and Answers
Basic Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Bbc Bitesize Biology Ks3
Bihar Board Biology Objective Answer 2017
Bihar Board Biology Objective Answer 2018
Bio Answers
Bio Quesions
Biology 0478
Biology 101
Biology 12th
Biology 12th Class Notes Pdf
Biology 2019 Syllabus
Biology All KCSE Short Notes
Biology Answers
Biology Answers Online Free
Biology Answers Quizlet
Biology Bk 2 Notes
Biology Book 1
Biology Book 1 Notes
Biology Book 2
Biology Book 2 Notes
Biology Book 3
Biology Book 3 KLB
Biology Book 3 Notes
Biology Book 4
Biology Book 4 Notes
Biology Book 4 Pdf
Biology Book for Class 11
Biology Book Four
Biology Book Four Notes
Biology Book One
Biology Book One Notes
Biology Book Pdf Free Download
Biology Book Three
Biology Book Three Notes
Biology Book Three Pdf
Biology Book Two
Biology Book Two Notes
Biology Books Form Three
Biology Bowl Biology Study Guide
Biology Bowl Questions Biology
Biology Bowl Questions Earth Biology
Biology Bowl Questions Math
Biology Bowl Questions Middle School
Biology Brekthrough Form Two Notes
Biology Cell Structure Test
Biology Class 12 Ncert Solutions
Biology Class 12 Pdf
Biology Communication Syllabus
Biology Diagram of Female Reproductive System
Biology Diagram Software
Biology Diagrams for Class 11
Biology Diagrams for Class 12
Biology Diagrams for Class 9
Biology Diagrams for Class-10
Biology Diagrams in Form 1
Biology Diagrams in Form 2
Biology Diagrams in Form 3
Biology Diagrams in Form 4
Biology Diagrams Pdf
Biology Diagrams to Label
Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Biology Essay Questions and Answers 2018
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Essay Revision Q
Biology Essays and Answers
Biology Essays Form One to Form Four
Biology Essays Form One to Form Three
Biology Essays KCSE
Biology Essays Pdf
Biology Exam 1 Multiple Choice
Biology Exam 2 Advance
Biology Exam 2 Test
Biology Exam 2016
Biology Exam Form Four
Biology Exam Form One
Biology Exam Form Three
Biology Exam Form Two
Biology Exam Practice Test
Biology Exam Questions
Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Exam Study Guide
Biology Exams
Biology Excretion Notes
Biology Exercise Form 4 With Answers
Biology Final Exam Answer Key
Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2016
Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2017
Biology Final Exam Answers 2018
Biology Final Exam Answers 2019
Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers
Biology Fom 1 Notes
Biology Fom 2 Notes
Biology Fom 3 Notes
Biology Fom 4 Notes
Biology Form 1
Biology Form 1 & 2 and Answers
Biology Form 1 and 2 Essays
Biology Form 1 and 2 Essays Questions and Answers
Biology Form 1 Chapter 1
Biology Form 1 Diagrams
Biology Form 1 Exams
Biology Form 1 Mid Year Exam
Biology Form 1 Notes
Biology Form 1 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 1 Notes Download
Biology Form 1 Notes Free Download
Biology Form 1 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 1 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 1 Past Papers
Biology Form 1 Pdf
Biology Form 1 Pressure
Biology Form 1 Question Papers
Biology Form 1 Questions
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 1 Quiz
Biology Form 1 Revision Questions
Biology Form 1 Summary Notes
Biology Form 1 Syllabus
Biology Form 1 Work
Biology Form 1-4 Notes
Biology Form 2
Biology Form 2 Chapter 1
Biology Form 2 Chapter 2
Biology Form 2 Diagrams
Biology Form 2 Exam Paper 2014
Biology Form 2 Exams
Biology Form 2 Notes
Biology Form 2 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 2 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 2 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 2 Past Papers
Biology Form 2 Pdf
Biology Form 2 Question Papers
Biology Form 2 Questions
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 2 Quiz
Biology Form 2 Revision Notes
Biology Form 2 Salts
Biology Form 2 Structure and Bonding
Biology Form 2 Summary Notes
Biology Form 2 Syllabus
Biology Form 2 Work
Biology Form 3
Biology Form 3 and 4 Essays
Biology Form 3 and 4 Essays Questions and Answers
Biology Form 3 Chapter 3
Biology Form 3 Classification
Biology Form 3 Diagrams
Biology Form 3 Ecology
Biology Form 3 Exams
Biology Form 3 Notes
Biology Form 3 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 3 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 3 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 3 Notes Topic 1
Biology Form 3 Past Papers
Biology Form 3 Pdf
Biology Form 3 Question Papers
Biology Form 3 Questions
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Term 3
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers+pdf
Biology Form 3 Quiz
Biology Form 3 Revision Notes
Biology Form 3 Revision Questions
Biology Form 3 Summary Notes
Biology Form 3 Syllabus
Biology Form 3 Syllabus Pdf
Biology Form 3 Topics
Biology Form 3 Work
Biology Form 4
Biology Form 4 All Chapter
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Conversion of Units
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Mind Map
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Experiment
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Formula
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Mind Map
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Momentum
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Paper 2
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Slideshare
Biology Form 4 Chapter 3
Biology Form 4 Chapter 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 4
Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Light Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Diagrams
Biology Form 4 Exam Paper 1
Biology Form 4 Exams
Biology Form 4 Exercise
Biology Form 4 Exercise Pdf
Biology Form 4 Module With Answer
Biology Form 4 Note
Biology Form 4 Notes
Biology Form 4 Notes (Pdf)
Biology Form 4 Notes All Chapter Pdf
Biology Form 4 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 1
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 2
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3
Biology Form 4 Notes Download
Biology Form 4 Notes Free Download
Biology Form 4 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 4 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 4 Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Past Papers
Biology Form 4 Question Papers
Biology Form 4 Questions
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 4 Quiz
Biology Form 4 Revision Notes
Biology Form 4 Schemes of Work
Biology Form 4 Summary Notes
Biology Form 4 Syllabus
Biology Form 4 Textbook Pdf
Biology Form 4 Work
Biology Form 5 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers
Biology Form 5 Chapter 1 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 5 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 5 Chapter 2 Slideshare
Biology Form 5 Chapter 3 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 5 Notes Pdf
Biology Form Four Book
Biology Form Four Notes
Biology Form Four Notes and Questions
Biology Form Four Notes GCSE
Biology Form Four Notes Pdf
Biology Form Four Past Papers
Biology Form Four Questions
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Four Quiz
Biology Form Four Study Notes
Biology Form Four Syllabus
Biology Form Four Topic 2
Biology Form Four Topic 4
Biology Form Four Topics
Biology Form Four Work
Biology Form One
Biology Form One Book
Biology Form One Book Pdf
Biology Form One Download Topic 1 Upto 3
Biology Form One Exam
Biology Form One Notes
Biology Form One Notes and Questions
Biology Form One Notes GCSE
Biology Form One Notes Pdf
Biology Form One Pdf
Biology Form One Questions
Biology Form One Questions and Answers
Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form One Questions and Their Answers
Biology Form One Quiz
Biology Form One Revision Question
Biology Form One Schemes of Work
Biology Form One Study Notes
Biology Form One Syllabus
Biology Form One Term Three Test
Biology Form One to Three Notes
Biology Form One Work
Biology Form Three
Biology Form Three Book
Biology Form Three Notes
Biology Form Three Notes and Questions
Biology Form Three Notes GCSE
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Three Quiz
Biology Form Three Reproduction
Biology Form Three Reproduction.
Biology Form Three Study Notes
Biology Form Three Work
Biology Form Three-questions and Answers
Biology Form Two
Biology Form Two Book
Biology Form Two Diagrams
Biology Form Two Notes
Biology Form Two Notes and Questions
Biology Form Two Notes GCSE
Biology Form Two Notes Pdf
Biology Form Two Notes-pdf
Biology Form Two Pdf
Biology Form Two Questions
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Two Quiz
Biology Form Two Study Notes
Biology Form Two Topics
Biology Form Two Work
Biology Form Two,schemes of Work
Biology Form2
Biology Form2 Textbook
Biology Game Form Four Question End Answers
Biology Grade 10 Exam Papers
Biology Hsc Pdf
Biology Human Reproduction Video
Biology IGCSE Past Papers Xtremepapers
Biology K.c.s.e 2017
Biology KCSE
Biology KCSE 2016
Biology KCSE 2017
Biology KCSE 2017 Paper 1
Biology KCSE Past Papers
Biology KCSE Questions
Biology KCSE Questions and Answer
Biology KCSE Quizzes & Answers
Biology KCSE Revision
Biology KCSE Revision Notes
Biology KCSE Setting Questions Form One and Two
Biology Ksce 2015
Biology Last Year K.c.s.e Questions
Biology Lesson Plan Form Two
Biology Made Familiar
Biology Mcq for Class 11
Biology Mcq for Class 12
Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams
Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams Pdf
Biology Mcq for Neet Pdf
Biology Mcq for Ssc
Biology Mcq Questions With Answers
Biology Mcq With Answers Pdf
Biology Mcqs for Class 12 Pdf
Biology Mcqs With Answers Pdf
Biology Mid Familia Form One
Biology Mock Papers
Biology Module Form 5
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cxc
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf
Biology Note
Biology Note Form Two All Chapters
Biology Notes
Biology Notes and Guestion and Answear
Biology Notes and Syllabus
Biology Notes Class 10
Biology Notes for Class 11 Pdf
Biology Notes for Class 12 Pdf
Biology Notes for High School Students
Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014
Biology Notes Form 1
Biology Notes Form 1 4
Biology Notes Form 1 Free Download
Biology Notes Form 1 KLB
Biology Notes Form 1 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 1-4
Biology Notes Form 1-4(1) Biology
Biology Notes Form 14
Biology Notes Form 2
Biology Notes Form 2 KLB
Biology Notes Form 2 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 2; Biology Notes
Biology Notes Form 3
Biology Notes Form 3 KLB
Biology Notes Form 3 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 4
Biology Notes Form 4 Chapter 2
Biology Notes Form 4 KLB
Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 4-pdf
Biology Notes Form Four
Biology Notes Form Four KLB
Biology Notes Form Four Pdf
Biology Notes Form One
Biology Notes Form One KLB
Biology Notes Form One Pdf
Biology Notes Form One to Form Four
Biology Notes Form Three
Biology Notes Form Three KLB
Biology Notes Form Three Pdf
Biology Notes Form Two
Biology Notes Form Two KLB
Biology Notes Form Two Pdf
Biology Notes Form2
Biology Notes IGCSE
Biology Notes Kenya
Biology Notes on Agroforestry
Biology Notes Pdf
Biology Notes:
Biology Objective Answer
Biology Objective Answer 2018
Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams
Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Pdf
Biology Oral Exam Questions
Biology Paper 1
Biology Paper 1 2018 Marking Rules
Biology Paper 1 Notes
Biology Paper 1 Questions
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 1 Topics
Biology Paper 1 With Answers
Biology Paper 2
Biology Paper 2 2017
Biology Paper 2 2018 Marking Rules
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Paper 2 Revision
Biology Paper 2 Topics
Biology Paper 2018
Biology Paper 3 2018 Marking Rules
Biology Paper 3 Question and Answer
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2014 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2015 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2016 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2017 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2018 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper One Questions and Answers
Biology Paper One Topics
Biology Paper Two Qestions With Answers
Biology Paper1
Biology Paper2
Biology Paper3
Biology Paper4
Biology Past Papers
Biology Past Papers 2017
Biology Past Papers a Level
Biology Past Papers Form 1
Biology Past Papers Form 2
Biology Past Papers Form 3
Biology Past Papers O Level
Biology Pdf Download
Biology Pp1 KCSE 2016
Biology Practical Book Class 12 Pdf
Biology Practical Exam
Biology Practicals Form One
Biology Practicals Questions and Answers
Biology Practice Test 9th Grade
Biology Practice Test Answers
Biology Practice Test Questions and Answers
Biology Practice Test Quizlet
Biology Predicted Questions This Year KCSE
Biology Preparation Notes
Biology Pretest High School Pdf
Biology Question and Answer With Explanation
Biology Question and Answers 2019
Biology Question and Answers 2020
Biology Question and Answers 2021
Biology Question and Answers 2022
Biology Question and Answers 2025
Biology Question and Answers 2026
Biology Question and Answers Note
Biology Questions
Biology Questions and Answers
Biology Questions and Answers for High School
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers for Secondary Schools
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Biology Questions and Answers Notes
Biology Questions and Answers O
Biology Questions and Answers on Cells
Biology Questions and Answers Online
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf for Class 12
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf for Competitive Exams
Biology Questions and Answers-form 2
Biology Questions for High School
Biology Questions for High School Students With Answers
Biology Questions for Senior 1
Biology Questions for Senior 2
Biology Questions for Senior 3
Biology Questions for Senior 4
Biology Questions for Senior 5
Biology Questions for Senior 6
Biology Questions for Senior Five
Biology Questions for Senior Four
Biology Questions for Senior One
Biology Questions for Senior Six
Biology Questions for Senior Three
Biology Questions for Senior Two
Biology Questions Form One
Biology Questions Multiple Choice
Biology Questions Quizlet
Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher
Biology Quetion and Answer Form Four
Biology Quetion and Answer Form One
Biology Quetion and Answer Form Three
Biology Quetion and Answer Form Two
Biology Quiz for Class 9
Biology Quiz for Class 9 Biology
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 12
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for High School
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions for Class 12
Biology Quiz Questions for College Students
Biology Quiz With Answers
Biology Quiz With Answers Pdf
Biology Quizlet
Biology Revision
Biology Revision a Level
Biology Revision Biology Notes Biology
Biology Revision Exam
Biology Revision Examination
Biology Revision Form One
Biology Revision Notes
Biology Revision Notes Biology
Biology Revision Notes Form 1
Biology Revision Notes Form 2
Biology Revision Notes Form 3
Biology Revision Notes Form 4
Biology Revision Notes IGCSE
Biology Revision Paper One
Biology Revision Questions
Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Four
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form One
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Three
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Two
Biology Revision Questions Form 1
Biology Revision Questions Form 2
Biology Revision Questions Form 3
Biology Revision Questions Form 4
Biology Revision Questions Form Four
Biology Revision Questions Form One
Biology Revision Questions Form Three
Biology Revision Questions Form Two
Biology Revision Quiz
Biology Revision Test
Biology Secondary School Revision
Biology Simple Notes
Biology Spm Notes Download
Biology Spm Notes Pdf
Biology Spm Questions
Biology Study Form 2
Biology Study Guide
Biology Study Guide Answer Key
Biology Study Guide Answers
Biology Study Guide Biology Questions and Answers
Biology Study Guide Ib
Biology Study Guide Pdf
Biology Study Guides
Biology Study Notes
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 1 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 2 3 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 2 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 3 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 4 Pdf
Biology Syllabus in Kenya
Biology Syllabus Pdf
Biology Test 1 Quizlet
Biology Test Questions
Biology Test Questions and Answers
Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Topic One Form Four
Biology Topics Form One
Biology Unit 1 Quiz
Biology Vol 3
Biology | Revision Biology
Biology,form 4
Biology.form Four.topic Three
BiologyExam Form Three
BiologyModule Form 5
BiologyNotes
BiologyNotes for Class 11 Pdf
BiologyNotes for Class 12 Pdf
BiologyNotes Form 1
BiologyNotes Form 1 Free Download
BiologyNotes Form 2
BiologyNotes Form 3
BiologyNotes Form 3 Pdf
BiologyNotes IGCSE
BiologyNotes Pdf
BiologyPast Papers
BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
BiologySimple Notes
BiologySpm Notes Download
BiologySpm Notes Pdf
BiologySpm Questions
BiologyStudy Guide Answers
BiologyStudy Guide Pdf
BiologyStudy Guides
Blologytextpapers
Bridge Biology
Business Past KCSE Past Papers
Business Studies Form 3 Notes Pdf
Business Studies Form 4 Notes Pdf
C R E Form One KLB
C R E Form One Oli Topic
C.r.e Form 1 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 2 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 3 Notes
C.r.e Form 3 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 3 Pdf
C.r.e Form 4 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form One Notes Pdf
C.r.e Notes Form 1
C.r.e Revision Notes
C.r.e Short Notes
Cambridge IGCSE Biology
Cambridge IGCSE Biology 3rd Edition
Cambridge IGCSE Biology 3rd Edition Plus Cd South Asia Edition
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Answers
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Coursebook Pdf Download
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Practical Workbook
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Study and Revision Guide 2nd Edition Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Study and Revision Guide Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Workbook Free Download
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Workbook Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE® Biology Coursebook
Caucasian Chalk Circle Essay Questions
Cell Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Cell Biology Exam Questions Pdf
Cell Biology Mcq With Answers
Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions Pdf
Cell Biology Previous Question Papers
Cell Biology Question Bank
Cell Biology Question Bank Pdf
Cell Biology Question Paper Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf in Hindi
Cell Biology Short Answer Questions
Cell Biology Test Bank Questions
Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers
Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Mcq Pdf
Cell Organelles Labeling Quiz
Cell Organelles Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Cell Questions and Answers
Cell Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Questions Quizlet
Cell Structure and Function Pdf
Cell Structure and Function Pdf Class 11
Cell Structure and Function Quiz Answers
Cell Structure and Function Test Answer Key
Cell Structure and Function Test Pdf
Cells
Cells Questions
Cellular Organization Pdf
Chapter 1 Introduction to Biology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Biology Studies
Chemical Equation for Aerobic Respiration
Cie a Level Biology Notes 2016
Cie a Level Biology Notes Pdf
Cie Past Papers
Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 Mcqs
Class 8 Biology Notes KCSE-kcse
College Biology Notes
College Biology Practice Test
College Biology Quiz
College Biology Quiz Chapter 1
College Biology Quizlet
College Biology Study Guide
College Biology Study Guide Pdf
College Biology Test Questions and Answers
College Biology Volume 3 Pdf
College BiologyNotes
Complete Biology for Cambridge IGCSE
Complete Biology for Cambridge IGCSE Revision Guide Pdf
County Mocks 2017
Cse Past Papers Biology 2017
Cytology Mcqs With Answers Pdf
Difficult Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Animals
Dl Biology Form 3 Pdf Kusoma
Download Biology Form 1
Download Biology Form 2
Download Biology Form 2 Notes
Download Biology Form 3
Download Biology Form 3 Notes
Download Biology Form 4
Download Biology Form Four
Download Biology Form One
Download Biology Form Three
Download Biology Form Two
Download Biology Notes Form 3
Download Biology Notes Form One
Download BiologyNotes Form 3
Download Form Three Biology Notes
Download Free KCSE Past Papers Biology
Download Free KCSE Past Papers From KNEC.
Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Download KCSE Revision Notes
Download KLB Biology Book 2
Download KLB Biology Book 3
Download KLB Biology Book 4
Download Notes of Biology
Downloads | Biology | Form Four Exams | Exams
Downloads | Biology | Form One Exams | Exams
Downloads | Biology | Form Three Exams | Exams
Downloads | Biology | Form Two Exams | Exams
Downloads | KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes |
Dvance KCSE Past Papers
Easy Biology Questions
Easy Cell Questions
Edexcel a Level Biology B
Edexcel a Level Biology Notes Pdf
Edexcel a Level Biology Salters Nuffield
Edexcel A2 Biology Notes
Edexcel as Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel Biology A2 Revision Notes Pdf
Edexcel Biology Unit 2 Revision Notes
Edexcel GCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Past Papers
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Free Pdf Download
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Download
Electronics Form Four Notes
Energy Questions Biology Bowl
Essay Questions and Answers KCSE Biology Notes
Essay Questions and Answers on Betrayal in the City
Essay Questions Based on Betrayal in the City
Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Answers
Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Download Free
Evolving World Biology Book 1 Pdf
Evolving World Biology Book 4 Notes
Evolving World Biology Book Form 1
Evolving World-history Book 3
Exam Notes for Biology 101
Exams KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Excretion Question and Answer Form 4 Work
Excretion Questions and Answers
Excretory System Questions and Answers Pdf
Excretory System Structure
F3 Biology Test Paper
Find Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Find KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Form 1 Biology Exam
Form 1 Biology Notes
Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 1 Biology Revision Notes
Form 1 Biology Summurized Revision Pdf
Form 1 Biology Syllabus
Form 1 Biology Test Paper Pdf
Form 1 Biology Topics
Form 1 BiologyNotes
Form 1 BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form 1 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 1 BiologySyllabus
Form 1 BiologyTest Paper Pdf
Form 1 Past Papers
Form 1 Past Papers With Answers
Form 1 Revision Papers
Form 1 Subjects in Kenya
Form 2 Biology Exam
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper 2016
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper Free Download
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper With Answer
Form 2 Biology Final Year Exam Paper 2
Form 2 Biology Notes
Form 2 Biology Notes and Revision Questions
Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 2 Biology Past Papers
Form 2 Biology Questions
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers >
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 2 Biology Revision Notes
Form 2 Biology Short Notes
Form 2 Biology Syllabus
Form 2 BiologyExam Paper
Form 2 BiologyExam Paper Free Download
Form 2 BiologyExam Paper With Answer
Form 2 BiologyFinal Year Exam Paper 2
Form 2 BiologyPast Papers
Form 2 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 2 BiologyShort Notes
Form 2 BiologySyllabus
Form 2 Revision Papers
Form 2 Subjects in Kenya
Form 3 Biology Book
Form 3 Biology Exam
Form 3 Biology Exam Paper
Form 3 Biology Notes
Form 3 Biology Past Papers
Form 3 Biology Questions
Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 3 Biology Revision Notes
Form 3 Biology Syllabus
Form 3 BiologyExam Paper
Form 3 BiologyNotes
Form 3 BiologyPast Papers
Form 3 BiologyQuestions
Form 3 BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form 3 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 3 BiologySyllabus
Form 3 C.r.e
Form 3 Notes of Biology Topic on Fish
Form 3 Past Papers
Form 3 Revision Papers
Form 3 Subjects in Kenya
Form 4 Biology Exam
Form 4 Biology Notes
Form 4 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 4 Biology Revision Notes
Form 4 Biology Syllabus
Form 4 Biology Topics
Form 4 BiologyNotes
Form 4 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 4 BiologySyllabus
Form 4 BiologyTopics
Form 4 Exam Papers
Form 4 Revision Papers
Form 4 Subjects in Kenya
Form 5 Biology Topics
Form 5 BiologyTopics
Form Five Biology Notes
Form Five BiologyNotes
Form Four Biology Book
Form Four Biology Notes
Form Four Biology Notes Pdf
Form Four Biology Questions and Answers
Form Four Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Four Biology Revision Questions
Form Four Biology Syllabus
Form Four Biology Topics
Form Four BiologyNotes
Form Four BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form Four BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Four BiologyTopics
Form Four Notes
Form Four Revision Papers
Form Four Subjects in Kenya
Form One Biology Book
Form One Biology Examination
Form One Biology First Topic
Form One Biology Lesson Plan
Form One Biology Notes Pdf
Form One Biology Past Papers Pdf
Form One Biology Questions
Form One Biology Questions and Answers
Form One Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form One Biology Revision Questions
Form One Biology Short Notes
Form One Biology Syllabus
Form One Biology Topics
Form One BiologyExamination
Form One BiologyPast Papers Pdf
Form One BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form One BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form One BiologyTopics
Form One Exams
Form One Notes of Biology
Form One Past Papers
Form One Subjects in Kenya
Form One Term One Biology Exam
Form One Term One BiologyExam
Form Three Biology Book
Form Three Biology Book Pdf
Form Three Biology Notes
Form Three Biology Notes Pdf
Form Three Biology Questions and Answers
Form Three Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Three Biology Revision Questions
Form Three Biology Syllabus
Form Three Biology Topics
Form Three BiologyNotes
Form Three BiologyNotes Pdf
Form Three BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form Three BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Three BiologyTopics
Form Three Subjects in Kenya
Form Two Biology Book
Form Two Biology Cat
Form Two Biology Examination
Form Two Biology Notes
Form Two Biology Notes Pdf
Form Two Biology Past Papers
Form Two Biology Questions and Answers
Form Two Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Two Biology Revision Questions
Form Two Biology Syllabus
Form Two Biology Topics
Form Two BiologyNotes
Form Two BiologyNotes Pdf
Form Two BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form Two BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Two BiologySyllabus
Form Two BiologyTopics
Form Two Notes
Form Two Subjects in Kenya
Free a-level Biology Revision App | Pass Your Biology Exams
Free Biology Form 1 Notes
Free Biology Notes Form 1
Free Biology Notes Pdf
Free BiologyNotes Pdf
Free College Biology Practice Test
Free Form1,form2,form3 Past Papers Free KCSE Past Papers
Free KCSE Mocks 2015
Free KCSE Past Papers 2014
Free KCSE Past Papers KCSE Past
Free KCSE Past Papers Kenya,
Free KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Free KCSE Questions and Answers on Biology
Free KCSE Revision Notes
Free Marking Schemes
Free Mocks Online KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers
Free Revision Papers
From Three Notes Topic One KLB
Fun Biology Questions
Funny Biology Questions
Funny Biology Questions and Answers
Funny Biology Questions to Ask
Funny Biology Quotes
Gas Exchange Exam Questions
Gas Exchange Practice Test
Gas Exchange Quiz
GCSE Biology Exam Questions and Answers
GCSE Biology Past Papers
GCSE Biology Revision
GCSE Biology Revision Notes
GCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf
GCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf 9-1
GCSE Biology Revision Questions and Answers
GCSE Biology Textbook Pdf
GCSE Biology Topics Pass My Exams: Easy Exam Revision Notes
General Biology Notes Pdf
General Biology Practice Test With Answers
General Biology Quiz
General Biology Quiz Pdf
General Biology Test Questions and Answers
General Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
General Knowledge in Biology Human Body
Good Biology Questions to Ask
GRE Biology Practice Test
GRE Biology Subject Test Pdf
Handbook of Biology Pdf Free Download
Hard Biology Questions
Hard Biology Questions and Answers
Hard Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher
Hard Biology Quiz Questions
Hard Form 3 Biology Question
High School Biology Final Exam Doc
High School Biology Final Exam Pdf
High School Biology Final Exam Questions
High School Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers
High School Biology Notes
High School Biology Practice Test
High School Biology Pretest With Answers
High School Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
High School Biology Study Guide
High School Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
High School BiologyNotes
High School BiologyStudy Guide
How Does the Excretory System Work
How Many Chromosomes Do Gametes Have
How Many Copies of Each Gene Do Gametes Have
How Much Genetic Information Is Found in a Gamete
How to Answer KCSE Biology Question
How to Motivate a Form 4 Student
How to Motivate a KCSE Candidate
How to Motivate a KCSE Student
How to Pass Biology Questions & Answers Form 1&2 | Text Book
How to Revise Biology
How to Revise Effectively for KCSE
How to Study Biology: 5 Study Techniques to Master Biology
Hsc Biology 2018
Hsc Biology 2019
Https://www.knec.ac.ke/ Www.knec-portal.ac.ke/ KNEC Portal:
Ial Biology Notes
Ib Biology Cold War Notes
Ib Biology Notes
Ib Biology Notes Pdf
Ib Biology of the Americas Notes
Ib Biology of the Americas Study Guide
Ib Biology Paper 2 Study Guide
Ib Biology Question Bank by Topic
Ib Biology Study Guide Pdf
Ict Notes Form 1
IGCSE Biology Alternative to Practical Revision
IGCSE Biology Alternative to Practical Revision Notes
IGCSE Biology Book
IGCSE Biology Book Pdf Download
IGCSE Biology Notes
IGCSE Biology Notes 2017 Pdf
IGCSE Biology Notes Edexcel
IGCSE Biology Paper 2 Notes
IGCSE Biology Paper 6 Notes
IGCSE Biology Past Papers
IGCSE Biology Past Papers 2014
IGCSE Biology Past Papers 2017
IGCSE Biology Pdf
IGCSE Biology Pre Release Material 2018
IGCSE Biology Resources
IGCSE Biology Revision Guide
IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Free Download
IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Download
IGCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf
IGCSE Biology Revision Worksheets
IGCSE Biology Workbook Pdf
IGCSE Biology Znotes
IGCSE BiologyPast Papers
IGCSE Notes Biology
Importance of Agroforestry
Inorganic Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf
Inorganic Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Interesting Biology Questions
Interesting Biology Questions and Answers
Interesting Questions to Ask About Biology
Intro to Biology Quiz
Introduction of Biology Form One
Introduction to Biology
Introduction to Biology Notes
Introduction to Biology Pdf
Introduction to BiologyNotes
Is Agroforestry Sustainable?
K.c.s.e Answers Biology Paper One 2018
K.c.s.e Biology 2017
K.c.s.e Biology 2018
K.c.s.e Biology Paper 1 2017
K.c.s.e Mocks 2018
K.c.s.e Papers 2015
K.c.s.e Papers 2016
K.c.s.e Past Papers 2014
K.c.s.e.Biology Paper 2 Year 2018
K.c.s.e.results 2018 for Busia County
K.l.b Biology Form 3
K.l.b Biology Notes
K.l.b BiologyNotes
Kasneb Past Papers for Colleges Biology Past Papers
KCSE 2010 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2010 Past Papers
KCSE 2011 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2011 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2012 Biology Paper 2 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2012 Marking Schemes
KCSE 2013 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme Pdf
KCSE 2014
KCSE 2015 Biology Paper 2
KCSE 2015 Biology Paper 3
KCSE 2015 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2015 Past Papers
KCSE 2016 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2016 Biology Paper 2
KCSE 2017 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2017 Biology Paper 2
KCSE 2017 Hostory Papers With Answers.com
KCSE 2017 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2017 Papers
KCSE 2017 Papers and Marking Scheme
KCSE 2017 Papers Pdf
KCSE 2017 Past Papers
KCSE 2017 Prediction Pdf
KCSE 2018 Biology and Answers
KCSE 2018 Biology Prediction
KCSE 2018 Leakage
KCSE 2018 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2018 Papers
KCSE 2018 Prediction Pdf
KCSE 2018 Predictions
KCSE 2018 Questions
KCSE 2018 Questions and Answers
KCSE 2019 Leakage Biology
KCSE 2019 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2019 Questions
KCSE 2019 Questions and Answers
KCSE 2020 Questions
KCSE 2020 Questions and Answers
KCSE Answers
KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers Downloads |
KCSE Biology 2011
KCSE Biology 2016
KCSE Biology Diagramsbiology Revision Tips
KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
KCSE Biology Essays
KCSE Biology Essays Pdf
KCSE Biology Marking Schemes
KCSE Biology Notes
KCSE Biology Notes Pdf
KCSE Biology Notes, Syllabus, Questions, Answers
KCSE Biology Paper 1
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2011
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2012
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2013
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2015
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2016
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2017 Pdf
KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Paper 2
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2012
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2012 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2015
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2013
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2014
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2015
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2016
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 3
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2012
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2016
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 3 Past Papers
KCSE Biology Past Papers
KCSE Biology Past Papers and Answers
KCSE Biology Past Papers Pdf
KCSE Biology Practical
KCSE Biology Practical 2015
KCSE Biology Practical 2016
KCSE Biology Practical Past Papers
KCSE Biology Practicals
KCSE Biology Practicals KCSE Biology Paper 1
KCSE Biology Question and Answer
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers Ap Biology
KCSE Biology Revision
KCSE Biology Revision Notes
KCSE Biology Revision Papers
KCSE Biology Revision Questions
KCSE Biology Revision Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Syllabus
KCSE BiologyNotes
KCSE BiologyPaper 1
KCSE BiologyPaper 2
KCSE BiologyPaper 2 Pdf
KCSE BiologySyllabus
KCSE Business Paper 1 2016
KCSE Business Past Papers
KCSE Business Studies Past Papers
KCSE Essay Questions in Betrayal in the City
KCSE Essays
KCSE Exam Papers 2018
KCSE Exam Papers Answers
KCSE Form 1 Biology Revision
KCSE Form 2 Biology Revision
KCSE Form 3 Biology Revision
KCSE Form 4 Biology Revision
KCSE Form Four Biology Revision
KCSE Form One Biology Revision
KCSE Form Three Biology Revision
KCSE Form Two Biology Revision
KCSE KCSE Past Papers KNEC
KCSE Leakage
KCSE Leakage Biology
KCSE Made Familiar Biology
KCSE Made Familiar Biology Pdf
KCSE Marking Scheme 2016
KCSE Marking Schemes
KCSE Marking Schemes 2017
KCSE Marking Schemes Pdf
KCSE Mock Exams
KCSE Mock Papers 2015
KCSE Mock Papers 2017
KCSE Mock Papers 2018
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf 2018
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf KCSE Past Papers
KCSE Mocks 2017
KCSE Mocks 2018
KCSE Notes
KCSE Online Notes
KCSE Online Past Papers
KCSE Online Registration
KCSE Papers 2015
KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes | Exams
KCSE Past Papers
KCSE Past Papers 2007
KCSE Past Papers 2009
KCSE Past Papers 2010
KCSE Past Papers 2011
KCSE Past Papers 2011 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2012
KCSE Past Papers 2013
KCSE Past Papers 2013knec
KCSE Past Papers 2014
KCSE Past Papers 2014 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2015
KCSE Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes
KCSE Past Papers 2015 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2016
KCSE Past Papers 2016 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2017
KCSE Past Papers 2017 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2018
KCSE Past Papers Biology
KCSE Past Papers Biology and Answers
KCSE Past Papers Biology Pdf
KCSE Past Papers Biology With Answers
KCSE Past Papers Biologyand Answers
KCSE Past Papers Business Studies and Answers
KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers
KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers Free Mocks Online
KCSE Past Papers Marking Scheme
KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download
KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download KCSE 2013
KCSE Past Papers With Answers
KCSE Past Papers Woodwork and Answers
KCSE Prediction 2017
KCSE Prediction 2018
KCSE Prediction 2018 Pdf
KCSE Prediction Papers 2018
KCSE Prediction Questions
KCSE Prediction Questions 2018
KCSE Prediction Questions and Answers
KCSE Questions
KCSE Questions and Answers
KCSE Questions and Answers.
KCSE Questions on Biology
KCSE Results, Online Registration, KCSE Result Slip.
KCSE Revision
KCSE Revision Notes
KCSE Revision Notes Biology
KCSE Revision Notes Pdf
KCSE Revision Papers
KCSE Revision Papers 2014
KCSE Revision Papers With Answers
KCSE Revision Question for Biology
KCSE Revision Questions
KCSE Revision Questions and Answers
KCSE Revision | Secondary School | Text Books | Text Book Centre
KCSE Syllabus Pdf
KCSE Trial 2017
KCSE Trial Exams 2017
Kenya Secondary School Biology Syllabus
Kenya Secondary School Biology Syllabus Pdf
Kenya Secondary School BiologySyllabus Pdf
Kenya Secondary School Syllabus Pdf
Kenya-kcse-christian Religious Education Syllabus
Kenyaplex KCSE Past Papers
Kenyaplex Past Papers for Secondary
KLB Biology Book 1 Download
KLB Biology Book 1 Notes
KLB Biology Book 1 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 2
KLB Biology Book 2 Notes
KLB Biology Book 2 Notes Pdf
KLB Biology Book 2 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 3 Notes
KLB Biology Book 3 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 3 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Book 4 Notes
KLB Biology Book 4 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 4 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Book 4 Topics
KLB Biology Book One
KLB Biology Form 1
KLB Biology Form 1 Notes
KLB Biology Form 1 Pdf
KLB Biology Form 2
KLB Biology Form 2 Book
KLB Biology Form 2 Notes
KLB Biology Form 2 Pdf
KLB Biology Form 2 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Form 2 Schemes of Work
KLB Biology Form 3
KLB Biology Form 3 Notes
KLB Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
KLB Biology Form 3 Pdf
KLB Biology Form 3 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Form 4
KLB Biology Form 4 Notes
KLB Biology Form 4 Pdf
KLB Biology Form Four
KLB Biology Form Four Notes
KLB Biology Form One
KLB Biology Form One Notes
KLB Biology Form Three
KLB Biology Form Three Notes
KLB Biology Form Two
KLB Biology Form Two Notes
KLB Biology Notes
KLB Biology Notes Form 4
KLB Biology Pdf
KLB BiologyNotes
KLB BiologyNotes Form 4
KLB BiologyPdf
KNEC Biology Syllabus
KNEC Examiners Portal KNEC Website
KNEC Ict Past Papers
KNEC Past Papers for Colleges
KNEC Past Papers Free Download
KNEC Past Papers Free Downloads
KNEC Past Papers Pdf
KNEC Portal Confirmation
KNEC Portal KCSE Results
KNEC Portal KNEC Past Papers for Colleges Kasneb Past Papers
KNEC Revision Papers
KNEC Technical Exams Past Papers
Kusoma Biology Notes
Kusoma Biology Notes Pdf
Kusoma Notes Biology
Kusoma.co.ke
Kusoma.com Past Papers
Learner Guide for Cambridge IGCSE Biology
Longhorn Biology Book 3 Pdf
Made Familiar Biology
Made Familiar Biology Pdf
Made Familiar Biology Questions
Maktaba Tetea Notes
Marking Scheme KCSE Biology Past Papers
Math Form2 Note
Mcq on Cell Biology Class 9
Mcqs About Gaseous Exchange
Middle School Biology Bowl Biology Questions
Mock Past Papers 2017
Mock Past Papers With Answers
Mokasa Mock 2017
More Than 1800 Biology Questions and Answers to Help You Study
Multiple Choice Questions on Biology
Multiple Choice Questions on Cell Structure and Function
Necta Biology Past Papers
Necta Biology Practicals
Necta BiologyPast Papers
Necta BiologyPracticals
Necta Form Four Past Papers
Necta Past Papers Form 4
Necta Past Papers Form 4 2016
Necta Past Papers Form Six
Necta Past Papers Form Two
Necta Questions and Answers
Necta Review Questions
Notes Biology Form 1
Notes Biology Form 2
Notes Biology Form 3
Notes Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
Notes Biology Form 3 Syllabus
Notes Biology Form 4 Syllabus
Notes on Biology Studies
Notes Za Biology 4m 2
Notes Za Biology Form One
Notes Za Biology Form Three
O Level Biology Practical Experiments
O Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Orm Three Biology Notes
Page Navigation
Papacambridge Biology IGCSE
Papers KNEC KCSE Online Past
Papers KNEC KCSE Results Past Papers
Past KCSE Papers
Past Paper Questions by Topic Biology
Past Papers 2014
Past Papers in Kenya
Pdf Biology Form 3
Pdf Biology Notes
Pdf Biology Notes Form 1
Pdf Biology Notes Form 2
Pdf Biology Notes Form 3
Pdf Biology Notes Form 4
Pdf Biology Notes Form Four
Pdf Biology Notes Form One
Pdf Biology Notes Form Three
Pdf Biology Notes Form Two
Pdf Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Four Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form One Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Three Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Two Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Free KCSE Past Papers and Marking Schemes
Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form 1
Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz
Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz for 5th Grade
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Grade 8
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Pdf
Plant Cell
Plant Cell Pdf Download
Plant Cell Questions and Answers
Plant Cell Test Questions
Practical Biology Experiments Pdf
Practical Biology Question and Answer Pdf
Pre Mocks 2018
Preliminary Biology
Primary and Secondary Tillage Implements Ppt
Pte KNEC Past Papers
Questions About Cells Biology
Questions and Answers on Gaseous Exchange
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 1
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 2
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 4
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Four
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Three
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Two
Questions Based to Introduction to Biology
Questions on Cell Structure and Function
Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Humans
Questions on Introduction to Biology
Questions to Ask in Biology Class
Questions to Confuse Your Biology Teacher
Quizlet Biology Cells
Quizlet Biology Test
Quizlet Test Questions
Qustions in Biology and Answers
Radioactivity Form Four
Respiration and Gas Exchange Worksheet
Respiration Notes My Elim Form Two
Revision
Revision Biology Notes and Questions?
Revision Quiz for Biology for Form Three
S.1 Biology Questions
S.2 Biology Questions
S.3 Biology Questions
S.4 Biology Questions
Sample Essays on Betrayal in the City
School Biology Notes
Secondary Biology Notes
Secondary Biology Notes Pdf
Secondary BiologyNotes Pdf
Senior 1 Biology Notes
Senior 2 Biology Notes
Senior 3 Biology Notes
Senior 4 Biology Notes
Senior 5 Biology Notes
Senior 6 Biology Notes
Senior Five Biology Notes
Senior Four Biology Notes
Senior One Biology Notes
Senior Six Biology Notes
Senior Three Biology Notes
Senior Two Biology Notes
Simple Scientific Questions
Smart Questions to Ask a Biology Teacher
Snab Biology Revision Notes
Southwest Mock Paper 2 2016 Biology Only
Spm Biology Revision Notes
Spm Notes
Success Biology Spm Pdf
Success BiologySpm Pdf
Summary of Biology Form 3
Tahossa Past Papers
The Animal Cell Quiz Answers
The Excretory System Answer Key
The Excretory System Worksheet Answers
The Plant Cell Quiz Answer Key
To Motivate a Form 4 KCSE Student
To Motivate a Form 4 Student
Topical Revision Material
Tricky Biology Questions and Answers
Tricky Biology Questions for Adults
Tricky Biology Questions With Answers
Tricky Biology Quiz Questions
Two Biology Revision Questions
Types of Respiration
University Biology Volume 3 Openstax
University Biology Volume 3 Pdf
University Biology Volume 4 Pdf
Ur Revision Guide IGCSE Biology
What Are Gametes
What Are Gametes in Biology
What Are Gametes in Plants
What Are Gametes in Punnett Squares
What Are Gametes Quizlet
What Are the Types of Gametes
Working of Excretory System
Www.Biology Form One Notes.com
Www.Biology From One KLB.com
Www.form 1 Biology.com
Www.form 2 Biology.com
Www.form 3 Biology.com
Www.form 4 Biology.com
Www.form Four Biology.com
Www.form One Biology.com
Www.form Three Biology.com
Www.form Two Biology.com
Www.kusoma Notes
Www.kusoma Revision Materials
Www.kusoma.co.ke Biology Notes
Xtremepapers IGCSE Biology
Year 11 Biology
Z Notes Biology IGCSE
Znotes as Biology
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 1
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 2
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 3
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 4
15 Common Biology Questions From Form Four
15 Common Biology Questions From Form One
15 Common Biology Questions From Form Three
15 Common Biology Questions From Form Two
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 1
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 2
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 3
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 4
150 Common Biology Questions From Form Four
150 Common Biology Questions From Form One
150 Common Biology Questions From Form Three
150 Common Biology Questions From Form Two
2019 KCSE Exams Biology Papers
2019 KCSE Exams Papers
2020 KCSE Exams Biology Papers
2021 KCSE Exams Biology Papers
Best Biology Books for KCSE Knec
Biology
Biology 2 Topic Form Two
Biology Diagrams
Biology Form 1 and 2 Notes
Biology Form 1 Download
Biology Form 1 Notes Online
Biology Form 1 Notes Revision
Biology Form 1 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 1 Revision Notes
Biology Form 1 Text Book
Biology Form 1 Text Book Notes
Biology Form 2 Download
Biology Form 2 Notes
Biology Form 2 Notes Online
Biology Form 2 Notes Revision
Biology Form 2 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 2 Pdf
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 2 Revision Notes
Biology Form 2 Text Book
Biology Form 2 Text Book Notes
Biology Form 3 Download
Biology Form 3 Notes Online
Biology Form 3 Notes Revision
Biology Form 3 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 3 Revision Notes
Biology Form 3 Text Book
Biology Form 3 Text Book Notes
Biology Form 4 Download
Biology Form 4 Notes Online
Biology Form 4 Notes Revision
Biology Form 4 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 4 Revision Notes
Biology Form 4 Text Book
Biology Form 4 Text Book Notes
Biology Form Four Download
Biology Form Four Notes Online
Biology Form Four Notes Revision
Biology Form Four Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Four Revision Notes
Biology Form Four Text Book
Biology Form Four Text Book Notes
Biology Form One Download
Biology Form One Notes Online
Biology Form One Notes Revision
Biology Form One Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form One Questions and Answers
Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form One Revision Notes
Biology Form One Text Book
Biology Form One Text Book Notes
Biology Form Three Download
Biology Form Three Notes Online
Biology Form Three Notes Revision
Biology Form Three Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Three Revision Notes
Biology Form Three Text Book
Biology Form Three Text Book Notes
Biology Form Two Download
Biology Form Two Notes Online
Biology Form Two Notes Revision
Biology Form Two Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Two Revision Notes
Biology Form Two Text Book
Biology Form Two Text Book Notes
Biology Full Exam Papers
Biology K.C.S.E Revision Papers
Biology KCSE Revision
Biology Notes Book Four
Biology Notes Book One
Biology Notes Book Three
Biology Notes Book Two
Biology Notes Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 1
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 2
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 3
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 4
Biology Short Note for Revising Form Four
Biology Short Note for Revising Form One
Biology Short Note for Revising Form Three
Biology Short Note for Revising Form Two
Biology Short Notes Form 1
Biology Short Notes Form 2
Biology Short Notes Form 3
Biology Short Notes Form 4
Biology Short Notes Form Four
Biology Short Notes Form One
Biology Short Notes Form Three
Biology Short Notes Form Two
Biologyy Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Brief Notes Biology Form 1
Brief Notes Biology Form 2
Brief Notes Biology Form 3
Brief Notes Biology Form 4
Brief Notes Biology Form Four
Brief Notes Biology Form One
Brief Notes Biology Form Three
Brief Notes Biology Form Two
Brief Notes Biology Form3 Chapter1
Download Book 1 Biology Notes
Download Book 2 Biology Notes
Download Book 3 Biology Notes
Download Book 4 Biology Notes
Download Book Four Biology Notes
Download Book One Biology Notes
Download Book Three Biology Notes
Download Book Two Biology Notes
Download Book1 Biology Notes
Download Book2 Biology Notes
Download Book3 Biology Notes
Download Book4 Biology Notes
Download KCSE Biology Study Notes
Download Secondary Subjects
Download Secondary Subjects in Kenya
Download Secondary Subjects KCSE
Exams Revision Kenya
Exams Revision Kenya KCSE
Expected Questions and Answers in Biology Form One
Form 2 Biology Notes
Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 2 Biology Topics
Form 3 Biology Book Pdf
Form Iii Topics of Biology Revisios
How to Answer Biology Paper 1 Questions?
How to Answer Biology Paper 2 Questions?
How to Answer Biology Paper 3 Questions?
How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions?
How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 2 Questions?
How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 3 Questions?
How to Answer Paper 1 Biology Questions?
How to Answer Paper 2 Biology Questions?
How to Answer Paper 3 Biology Questions?
K.C.S.E Revision Papers
K.C.S.E Revision Papers Biology
KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
KCSE Biology Revisions
KCSE Biology Study Notes
KCSE Free Biology Qussions
KCSE Free Qussions
KCSE Revision Kenya
KCSE Revisions
Biology Form Two Questions
Revision Kenya
Revision Kenya Kcsse
Sammary Note for Biology Form 1
Sammary Note for Biology Form 2
Sammary Note for Biology Form 3
Sammary Note for Biology Form 4
Sammary Note for Biology Form Four
Sammary Note for Biology Form One
Sammary Note for Biology Form Three
Sammary Note for Biology Form Two
Www.last Year KCSE Exams.com
Biology Past Papers and Marking Scheme
Igcse Biology Past Papers
Igcse Biology Past Papers 2015
Igcse Biology Past Papers by Topic
Edexcel Igcse Biology Past Papers
Biology Questions Book Two
Biology Form One
Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 3 Notes
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf - Fill Online, Printable ...
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf - Fill Online, Printable, Fillable, Blank | Pdffiller
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form Three Full Notes Download Your Document
Biology Notes Form 3 Classification
Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 - High School Biology Tests
Form 3 Biology Book Pdf
Form 3 Biology Notes
Form 3 History Notes Pdf Download
Form 3 Notes Pdf - Fill Online, Printable
Form 3 Notes Pdf - Fill Online, Printable, Fillable, Blank | Pdffiller
Kenya Form 3 Biology Notes
Klb Biology Book 3 Pdf Download
Klb Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
A Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
All Biology Questions and Answers Pdf,ppt
Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Notes Form 1-4 Pdf
Free High School Notes Kenya
Free Kcse Revision Notes
General Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
High School Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Kcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf
Kcse Revision Books Pdf
Kcse Revision Notes Pdf
Kenya Secondary School Notes Pdf
Notes of Form 123 and 4 All Subject
Biology Notes Form 1 Free Download
Advice to KCSE Candidates
Best Revision Books for KCSE
How to Pass an Exam Successfully
How to Pass KCSE 2018
How to Pass KCSE 2019
How to Pass KCSE Biology Paper
How to Pass KCSE Biology
How to Pass KCSE Biology
How to Pass KCSE 2019
K.c.s.e Biology Paper 1 2017
KCSE 2019 Prediction
KCSE Prediction 2019
KCSE Revision Tips
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2018
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2018
KCSE Biology Past Papers Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2012
KCSE Past Papers 2017 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2018
KCSE Past Papers of Biology Pp2
KCSE Biology Past Papers Pdf
Answers for K.c.s.e Past Papers for Biology
Biology Paper 1 With Answers
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper One Questions and Answers
Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Kcse Biology Paper 1 2017
Kcse Biology Paper 1 2018
Kcse Biology Paper 3 Past Papers
Kcse Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes
Biology KCSE Papers With Their Marking Schemes
Biology Paper 1 and Answers
KCSE 2017 Papers and Marking Scheme
KCSE 2019 Papers and Marking Scheme
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2018
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2019
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2019 Past Papers
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2018
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2019
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2019 Past Papers
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2019 Past Papers
KCSE Biology Past Papers and Answers
KCSE Marking Schemes Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes
KCSE Past Papers 2019 Marking Schemes
KCSE Past Papers Biology Paper 1 2019
KCSE Past Papers Biology Paper 2 2019
KCSE Past Papers Biology Paper 3 2019
Past Papers KCSE Biology Paper 1 2019
Past Papers KCSE Biology Paper 2 2019
Past Papers KCSE Biology Paper 3 2019
9th Grade Biology Notes
All Biology Essays Pdf
Ap Bio Chapter 1 Notes
Ap Biology Chapter 3 Summary
Bio Chapter 4
Bio F4 C2
Biology 9
Biology Chapter 2
Biology Chapter 2 Notes
Biology Chapter 3
Biology Chapter 4 Notes
Biology Chapter 5
Biology Class 9 Chapter 2 Notes
Biology Class 9 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf
Biology Essays and Answers Pdf
Biology Essays Kcse
Biology Essays Notes
Biology Essays Pdf Download
Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 4 Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Topics
Biology Movement of Substances
Biology Notes for Class 9 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 1-4
Biology Notes Form 1-4 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 2
Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Answers
Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Campbell Biology
Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Focus Questions
Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Multiple Choice
Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Powerpoint
Chapter 4 Cells and Tissues Answer Key
Class 9th Biology Notes
Download Biology Notes
Form Four Notes
Free Biology Notes
Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf
Kcse Biology Notes Pdf
Klb Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf
Mastering Biology Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life
Notes of Biology
Section 2.1 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key
State the Level of Cell Organisation of Amoeba Sp
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Kcse Revision Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper One Questions and Answers
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers
Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Kcse Biology Past Papers and Answers
All Biology Questions and Answers Pdf,ppt
Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Question Paper 2015 With Answer
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Gs 2015 Biology Answer Key
Tifr 2017 Biology Answer Key
Tifr Gs 2011 Biology Answer Key
Tifr Gs 2012 Biology Answer Key
Tifr Previous Year Question Papers of Biology With Answers
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 1 2018
Biology Paper 2 2018
Biology Paper 1 2019
Biology Paper 2 2019
Biology Paper 1 Notes
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2018
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2018
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2019
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2019
Most Tested KCSE Biology Questions
Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 2 Pdf
Biology Form 2 Syllabus KLB Notes
Biology Form Two Topics
Biology Notes Form 3
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers
KLB Biology Form 2 Book Pdf
KLB Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf
4m1 Notes Viusasa
4m2 Notes Viusasa
4m3 Notes Viusasa
4m4 Notes Viusasa
Download on Viusasa - Download Now for Free
Elimu - Viusasa
Elimu Library | Notes, Exams, Lesson Plans, Schemes
Elimu Online
High School Notes - Revision Materials for Kenyan Schools
Https //www.viusasa.com/elimu Kenya
Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 1
Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 2
Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 3
Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 4
Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Four
Notes Viusasa Elimu Form One
Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Three
Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Two
Viusasa
Viusasa Education
Viusasa Elimu
Viusasa Elimu Class 6
Viusasa Elimu Form 1
Viusasa Elimu Form 1 Notes
Viusasa Elimu Form 2
Viusasa Elimu Form 2 Notes
Viusasa Elimu Form 3
Viusasa Elimu Form 3 Notes
Viusasa Elimu Form 4
Viusasa Elimu Form 4 Notes
Viusasa Elimu Form Four
Viusasa Elimu Form Four Notes
Viusasa Elimu Form One
Viusasa Elimu Form One Notes
Viusasa Elimu Form Three
Viusasa Elimu Form Three Notes
Viusasa Elimu Form Two
Viusasa Elimu Form Two Notes
Viusasa High School Notes - Revision Materials for Kenyan Schools
Viusasa Notes
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 - Biology Form Two Notes
Biology Questions and Answers Form 4 - Biology Form Four Notes
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 - Biology Form Three Notes
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 - Biology Form One Notes
Biology Mock Papers
Biology Paper 1 2019
Biology Paper 1 Notes
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Paper 2 Form 3
Biology Paper 2 Notes
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Past Papers
Biology Past Papers Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Revision Questions Pdf
Common Exam Questions in Biology Paper 1
Common Exam Questions in Biology Paper 2
Common Test Questions in Biology Paper 1
Common Tested Questions in Biology Paper 1
Commonly Tested Questions in Biology Paper 1
K.c.s.e.Biology Questions and Answers
KCSE 2019 Biology Paper 1 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2019 Biology Paper 2
KCSE 2019 Biology Paper 2 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2020 Prediction Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2019
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2016
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2018
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2019
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers
Most Tested Questions in Biology Paper 1
Most Tested Questions in Biology Paper 2
Mostly Tested Questions in Biology Paper 1
Mostly Tested Questions in Biology Paper 2
Biology Form 4
Biology Revision Questions Form 1
Combined Science Notes Form 1
Form 4 Notes
High Flyer Series Biology Form 1-4
Kcse Past Papers Biology With Answers
Biology Notes Download
Secondary Biology Notes Pdf
Water and Hydrogen Form 1 Notes
High Flyer Series KCSE Revision in Biology
High Flyer Series KCSE Revision Biology Form 1-4 Revised
A Level Biology Notes Uganda Pdf Download
Buddo Junior School Holiday Work
Biology Notes for a Level Pdf
Biology Notes Form 1
Biology Notes Form 3 the Mole
Biology Notes Form 4
Biology Notes O Level
Biology Notes O Level Uganda
Biology Notes O Level Uganda Pdf
Biology Notes Pdf
Download Biology Notes
Form 3 Biology Notes
Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers
Form Three Biology Syllabus Pdf
Gayaza High School Biology Notes
Gayaza High School Biology Notes Pdf
Gayaza High School Biology Past Papers
Gayaza High School Biology Past Papers Answers
Gayaza High School Biology Past Papers Questions and Answers
Gayaza High School E Learning
Gayaza High School Elearning Platform
Gayaza High School Examinations
Gayaza High School Holiday Work
Gayaza High School Notes
Gayaza High School Notes 2021
Gayaza High School Notes 2022
Gayaza High School Notes 2025
Gayaza High School Notes 2026
Gayaza High School Notes Pdf
Gayaza Junior School E Learning Platform
Gayaza Junior School Holiday Work
Gayaza O Level Biology Notes
Home › Gayaza High School | Elearning Platform
Kabojja Junior School Holiday Work Pdf
Klb Biology Book 3
Klb Biology Form 3 Teachers Guide
Klb Biology Notes
List of Ugandan E-learning Platforms for Students
Mirembe Junior School Holiday Work
Ntare School Past Papers
O Level Biology Notes Free Download
O Level Biology Notes in Uganda
O Level Biology Notes Pdf
O Level Biology Notes Uganda Pdf
O Level Biology Notes Uganda Pdf Download
O Level General - Home › Gayaza High School | Elearning
S.1 Biology Notes | Standard High School Zzana
S.3 Biology Notes
S.4 Biology 2 Notes | Standard High School Zzana
Seeta High School Elearning
Seeta High School Holiday Work
Seeta High School Notes
Seeta High School Notes Pdf
Seeta High School Past Papers
Seeta High School Past Papers Pdf
Senior 1 Biology Notes
Senior 1 Biology Notes in Uganda
Senior 1 Biology Notes Uganda
Senior 1 Biology Questions
Senior 1 Exams
Senior 1 Work
Senior 1 Work 2020
Senior 1 Work 2020 Uganda
Senior 2 Biology Notes
Senior 2 Biology Notes in Uganda
Senior 2 Biology Notes Uganda
Senior 2 Biology Questions
Senior 2 Exams
Senior 2 Work
Senior 2 Work 2020
Senior 2 Work 2020 Uganda
Senior 3 Biology Notes
Senior 3 Biology Notes in Uganda
Senior 3 Biology Notes Uganda
Senior 3 Biology Questions
Senior 3 Exams
Senior 3 Work
Senior 3 Work 2020
Senior 3 Work 2020 Uganda
Senior 4 Biology Notes
Senior 4 Biology Notes in Uganda
Senior 4 Biology Notes Uganda
Senior 4 Biology Questions
Senior 4 Exams
Senior 4 Work
Senior 4 Work 2020
Senior 4 Work 2020 Uganda
Senior Four Biology Notes
Senior Four Biology Notes in Uganda
Senior Four Biology Notes Uganda
Senior Four Biology Questions
Senior Four Exams
Senior Four Work
Senior Four Work 2020
Senior Four Work 2020 Uganda
Senior One Biology Notes
Senior One Biology Notes in Uganda
Senior One Biology Notes Uganda
Senior One Biology Questions
Senior One Exams
Senior One Work
Senior One Work 2020
Senior One Work 2020 Uganda
Senior Three Biology Notes
Senior Three Biology Notes in Uganda
Senior Three Biology Notes Uganda
Senior Three Biology Questions
Senior Three Exams
Senior Three Work
Senior Three Work 2020
Senior Three Work 2020 Uganda
Senior Two Biology Notes
Senior Two Biology Notes in Uganda
Senior Two Biology Notes Pdf
Senior Two Biology Notes Uganda
Senior Two Biology Questions
Senior Two Exams
Senior Two Work
Senior Two Work 2020
Senior Two Work 2020 Uganda
St Mary's Kitende E Learning
Standard High School Notes
Standard High School Zana a Level Notes
Standard High School Zana Com Notes
Standard High School Zana E Learning
Standard High School Zana E Learning Platform
Standard High School Zana E-learning Platform
Standard High School Zana Notes for Senior Two
Standard High School Zana Notes Pdf
Standard High School Zana Website
Standard High Zana Notes
Uace Biology Notes
Uace Biology Notes Pdf
Uce Biology Notes Pdf
Uce Biology Notes Pdf Download
Uce Past Papers
Uganda Secondary Schools E-learning Platform
Uneb Marking Guides Pdf
Uneb Past Papers and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 3 Notes on Ecology
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Notes Form 3 Classification
Biology Notes Form 3 Growth and Development
Biology Notes Form 3 Pdf Free Download
Ecology Notes
Ecology Revision Questions and Notes
Form 3 Biology Notes on Reproduction
Klb Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Download
Before You Start Writing the Exam | Kcpe-kcse
Kcse 2019 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Kcse 2020 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Kcse 2020 Leakage Biology Questions
Kcse 2020 Prediction Questions and Answers
Kcse 2021 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Kcse 2021 Leakage Biology Questions
Kcse 2021 Prediction Questions and Answers
Kcse 2022 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Kcse 2025 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Kcse 2025 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Kcse 2025 Leakage Biology Questions
Kcse 2026 Leakage Biology Questions
Kcse 2025 Prediction Questions and Answers
Kcse 2026 Prediction Questions and Answers
Kcse 2025 Prediction Questions and Answers
Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Kcse Biology Past Papers and Answers
Kcse Past Papers and Answers Biology
Kcse Past Papers
Kcse Prediction Questions
Tips to Passing Kcse Examinations » Kcse Revision
What to Watch Out for When Answering Questions in Kcse
Which Questions Always Must Appear on Kcse Paper?
Which Questions Always Must Appear on Kcse Papers?
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Download
Biology Notes Form 1-4
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 1 Biology Topical Questions
Form 1 Biology Exam Paper With Answer Pdf
Form 1 Exams 2020
Form 1 Biology Past Papers
Form 1 Biology Revision Papers With Answers
Sample Biology Test for Form One Exams
Ntare School Past Papers
Seeta High School Notes Pdf
Seeta High School Past Papers
Seeta High School Past Papers Pdf
St Mary's Kitende Past Papers
Uce Biology Notes Pdf
Uce Past Papers
Uneb Marking Guides Pdf
Uneb Past Papers and Answers Pdf
Biology Book 3 Download
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 3 Syllabus
Biology Form 3 Topics
Biology Notes Form 3
Biology Notes Form 3 Coordination
Biology Notes Form 3 Reproduction
Biology Notes Form Three
Biology Notes Pdf Download
Form 3 Biology Exam
Form 3 Biology Notes on Reproduction Pdf
Revision Biology Revision a Level Biology
Revision Notes - Biology
S.1-biology-notes
S.1-biology-notes Uganda
S.2-biology-notes
S.2-biology-notes Uganda
S.3-biology-notes
S.3-biology-notes Uganda
S.4-biology-notes
S.4-biology-notes Uganda
S.5-biology-notes
S.5-biology-notes Uganda
S.6-biology-notes
S.6-biology-notes Uganda
S1 Biology Notes Term 1
S1 Biology Notes Term 2
S1 Biology Notes Term 3
S2 Biology Notes Term 1
S2 Biology Notes Term 2
S2 Biology Notes Term 3
S3 Biology Notes Term 1
S3 Biology Notes Term 2
S3 Biology Notes Term 3
S4 Biology Notes Term 1
S4 Biology Notes Term 2
S4 Biology Notes Term 3
Senior 3 Biology Notes
Senior 3 Biology Notes Uganda
Senior Three Biology Notes
Senior Three Biology Notes Uganda
Biology Form 1 the Cell
Biology Form One Notes Free – Education News
Biology Notes Form 1-4
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 - Biology Form One
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 - Biology Form Two
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 - Biology Form Three
Biology Questions and Answers Form 4 - Biology Form Four
Biology Questions and Answers Senior 1 - Biology Senior One
Biology Questions and Answers Senior 2 - Biology Senior Two
Biology Questions and Answers Senior 3 - Biology Senior Three
Biology Questions and Answers Senior 4 - Biology Senior Four
Biology Topic by Topic Questions and Answers
Combined Science Notes Form 1
Form 1 Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Form 1 Biology Topical Questions
Form 1 Revision Papers With Answers
Form 2 Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Form 3 Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Form Four Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Form One Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Form Three Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Form Two Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Free Biology Form 1 Notes
Free Biology Notes
Introduction to Biology Form One
Kcse Past Papers: Biology Form 1
Kcse Past Papers: Biology Form 1 Topical Questions
Kcse Past Papers: Biology Form 1 Topical Questions and Answers
Most Tested Areas in Biology Kcse
Most Tested Areas in Biology Kcse Exams
Most Tested Areas in Biology Uneb
Most Tested Areas in Form 1 in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Form 2 in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Form 3 in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Form 4 in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Form Four in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Form One in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Form Three in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Form Two in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Kcse Biology
Most Tested Areas in Kcse Biology Exams
Most Tested Areas in Senior 1 in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Senior 2 in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Senior 3 in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Senior 4 in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Senior Four in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Senior One in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Senior Three in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Senior Two in Biology
Most Tested Areas in Uneb Biology
Revision Notes Biology Form 1 - Free Kcse Past Papers
Who Was Biology Champion KCSE 2019
Top 100 Students in Biology KCSE 2019
Best 100 Students in Biology KCSE 2019
Top Student in Biology KCSE
Best Student in Biology KCSE
Who Was Biology Champion KCSE 2020
Top 100 Students in Biology KCSE 2020
Best 100 Students in Biology KCSE 2020
Names of Best Biology Students KCSE
Names of Top Biology Students KCSE
Scheme of work for IGCSC Biology Form 3 to 4 for Botswana
Biology Questions on Human Diseases Form Three
Biology Form 3 Notes
Kcse Made Familiar Biology Pdf Download
Find Kcse Made Familiar Biology Pdf Download
Find Kcse Made Familiar Biology Pdf Download Here!
Summary of Biology Form 1
Popular Questions in Biology Form 2
Kcse Revision Biology Paper Form One
Biology Questions and Answers
A Level Biology Revision Notes Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Two Notes Pdf Download
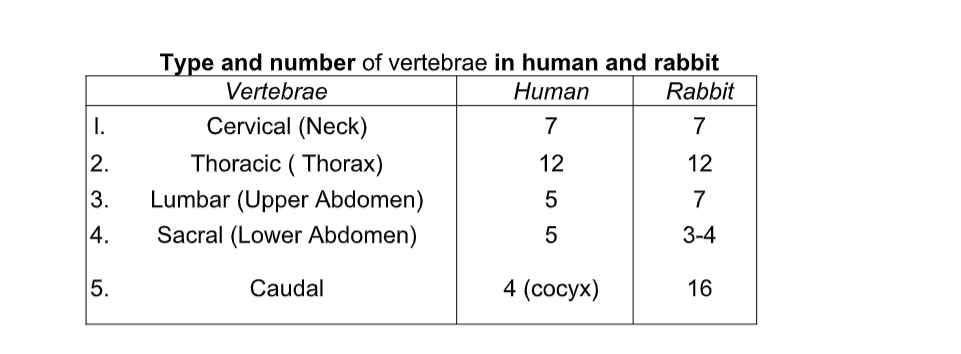
Biology Notes FAQ Form
KCSE Results » KCSE Results Top 100 Schools - Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education – KCSE » KCSE Top 100 Candidates » Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education – KCSE » KNEC - Kenya National Examinations Council » Secondary Schools in Kenya » KNEC - Kenya National Examinations Council » Free KNEC KCSE Past Papers
Scholarship 2026/27
Current Scholarships 2026/2027 - Fully Funded
Full Undergraduate Scholarships 2026 - 2027
Fully Funded Masters Scholarships 2026 - 27
PhD Scholarships for International Students - Fully Funded!
Funding Opportunities for Journalists 2026/2027
Funding for Entrepreneurs 2026/2027
***
