Biology Notes Form 2
Biology Notes Form 2
Click Here - Free KCSE Past Papers » KNEC Past Exams » Free Downloads » KCSE Papers & Marking Schemes
By the end of form two work, the learner should be able to:
Introduction
Transport in plants
Internal structure of roots and root hairs
The main functions of roots are ;
Internal structure of a root hair cell
The Stem
Collenchyma
Parenchyma
Absorption of Water and Mineral Salts Absorption of Water
Uptake of Mineral Salts
Transpiration
Cuticular transpiration:
Lenticular transpiration
Structure and function of Xylem
Xylem Vessels
The bordered pits are areas without lignin on xylem vessels and allow passage of water in and out of the lumen to neighbouring cells.
Tracheids
Xylem fibres ;
Xylem parenchyma:
Forces involved in Transportation of Water and Mineral Salts
Transpiration pull
Cohesion and Adhesion:
Capillarity:
Root Pressure:
Importance of Transpiration
Some beneficial effects are:
Factors Affecting Transpiration The factors that affect transpiration are grouped into two.
Environmental factors
Temperature
Humidity
Wind
Light Intensity
Atmospheric Pressure
Availability of Water
Structural Factors Cuticle
Stomata
Leaf size and shape
Translocation of organic compounds
Phloem
phloem is made up of;
Companion Cells
Transport in Animals
The Circulatory System
The types of circulatory system exist in animals: open and closed.
A closed circulatory system;
Transport in Insects
Mammalian Circulatory System
Structure and Function of the Heart
Pumping Mechanism of the heart
Diastole
Structure and Function of Arteries,Capillaries and Veins
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Diseases and Defects of Circulatory System
Thrombosis
Arteriosclerosis
Varicose Veins
Structure and Function of Blood
Composition of Blood
Plasma
The functions of plasma include:
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
Leucocytes (White Blood Cells)
- Granulocytes (also phagocytes or polymorphs) - Agranulocytes .
Antibodies include:
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
ABO Blood Groups
Blood groups
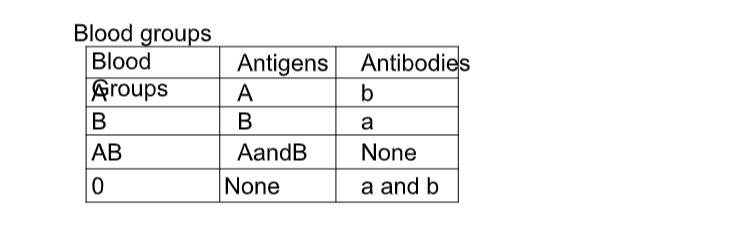
Blood transfusion is the transfer of blood from a donor to the circulatory system of the recipient.
A recipient will receive blood from a donor if the recipient has no corresponding antibodies to the donor's antigens.
If the donor's blood and the recipient's blood are not compatible, agglutination occurs whereby red blood cells clump together.
Blood typing
Rhesus Factor
Lymphatic System
Lymph is excess tissue fluid.
Immune Responses
Types of Immunity
Artificial Acquired Immunity:
Artificial Passive Acquired Immunity:
Importance of Vaccination
Allergic Reactions
Respiration
Meaning and Significance of Respiration
Mitochondrion Structure and Function
Structure
Adaptations of Mitochondrion to its Function
Aerobic Respiration
Glycolysis.
Anaerobic Respiration
Products of Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic Respiration in Plants
C6HI206 _ 2C2H50H + 2C02 + Energy
(Glucose) (Ethanol) (Carbon (IV) oxide)
Fermentation
Lactate Fermentation
Anaerobic Respiration in Animals
C6H1P6 _ 2CH3CHOH.COOH + energy (Glucose) (Lactic acid) + energy
Practical Activities
To Show the Gas Produced When the Food is burned
Experiment to Show the Gas Produced During Fermentation
Experiment to Show Germinating Seeds Produce Heat
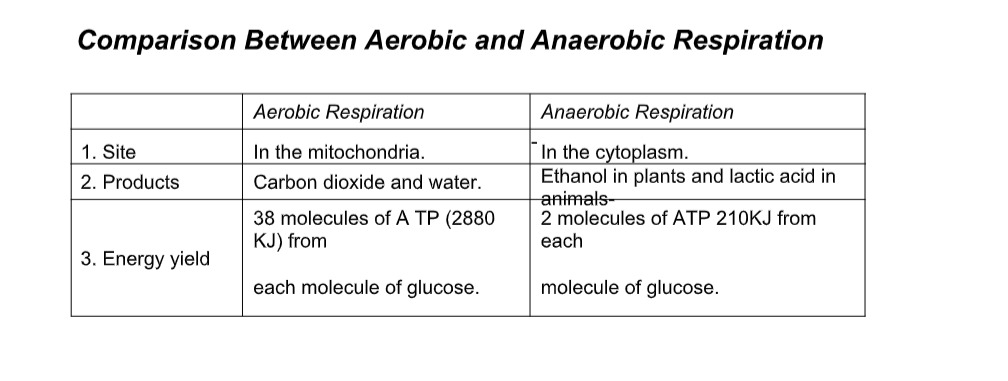
Comparison Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration

Substrates for Respiration
R.Q. = Amount of carbon (IV) oxide produced/ Amount of oxygen used
Application of Anaerobic Respiration in Industry and at Home Industry
Home
End of Topic
Gaseous Exchange in Plants and Animals
Necessity for Gaseous Exchange in Living Organisms
Gaseous Exchange in Plants
Structure of Guard Cells
Mechanism of Opening and Closing of Stomata
Proposed causes of turgor changes in guard cells.
Accumulation of sugar.
pH changes in guard cells occur due to photosynthesis.
This favours conversion of sugar to starch.
low sugar concentration lead to loss of turgidity in guard cells and stoma closes.
Explanation is based on accumulation of potassium ions
Process of Gaseous Exchange in Root Stem and Leaves of Aquatic and Terrestrial Plants
Gaseous Exchange in leaves of Terrestrial Plants
Gaseous exchange in the leaves of aquatic(floating)plants
Observation of internal structure of leaves of aquatic plants
The following are some of the features that can be observed in the leave of an aquatic plant;
Gaseous Exchange Through Stems Terrestrial Plants
Aquatic Plant Stems
Gaseous Exchange in Roots
Terrestrial Plants
Aquatic Plants
Gaseous Exchange in Animals
Types and Characteristics of Respiratory surfaces
Different animals have different respiratory surfaces.
Characteristics of Respiratory Surfaces
Gaseous Exchange in Amoeba
Gaseous Exchange in Insects
Mechanism of Gaseous Exchange in Insects
Adaptation of Insect Tracheoles for Gaseous Exchange
Ventilation in Insects
Gaseous Exchange in Bony Fish (e.g, Tilapia)
Adaptation of Gills for Gaseous Exchange
Ventilation
Counter Current Flow
Observation of Gills of a Bony Fish (Tilapia)
Gaseous Exchange in an Amphibian - Frog
Skin
Adaptations of a Frog's Skin for Gaseous Exchange
Buccal (Mouth) Cavity
Lungs
Adaptation of Lungs
Ventilation
Inspiration
Expiration
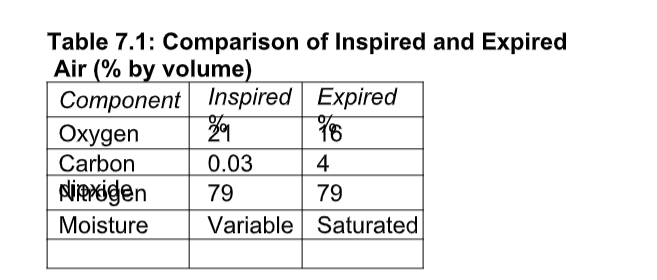
Gaseous Exchange in a Mammal -Human
Adaptations of Alveolus to Gaseous Exchange
Gaseous Exchange Between the Alveoli and the Capillaries
Inspiration
Expiration
Control of Rate Of Breathing
Factors Affecting Rate of Breathing in Humans
Factors that cause a decrease or increase in energy demand directly affect rate of breathing.
Effects of Exercise on Rate of Breathing
Dissection of a Small Mammal (Rabbit) to Show Respiratory Organs
Diseases of the Respiratory System
Asthma
Causes:
Allergy
Emotional or mental stress
Symptoms
Treatment and Control
Bronchitis
Causes
Symptoms
Treatment
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Causes
Symptoms
Prevention
Treatment
Pneumonia
Symptoms
Prevention
Treatment
Whooping Cough
Causes
Symptoms:
Prevention
Treatment
Practical Activities Observation of permanent slides of terrestrial and aquatic leaves and stems Leaves
Excretion and Homeostasis
Introduction
Excretion in Plants
Plant Excretory Products their source and uses
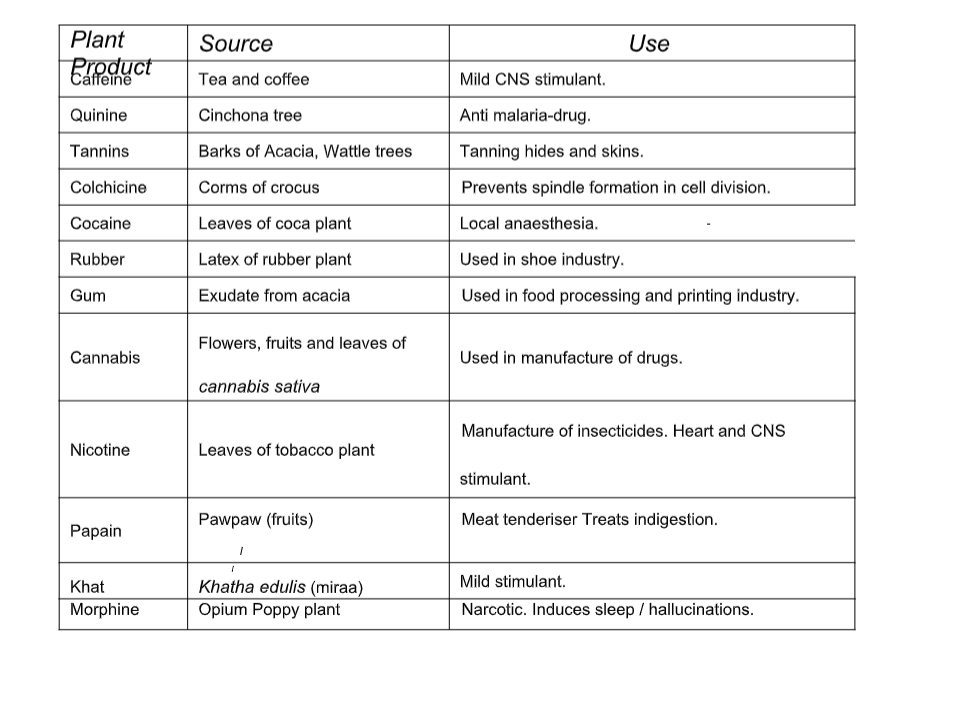
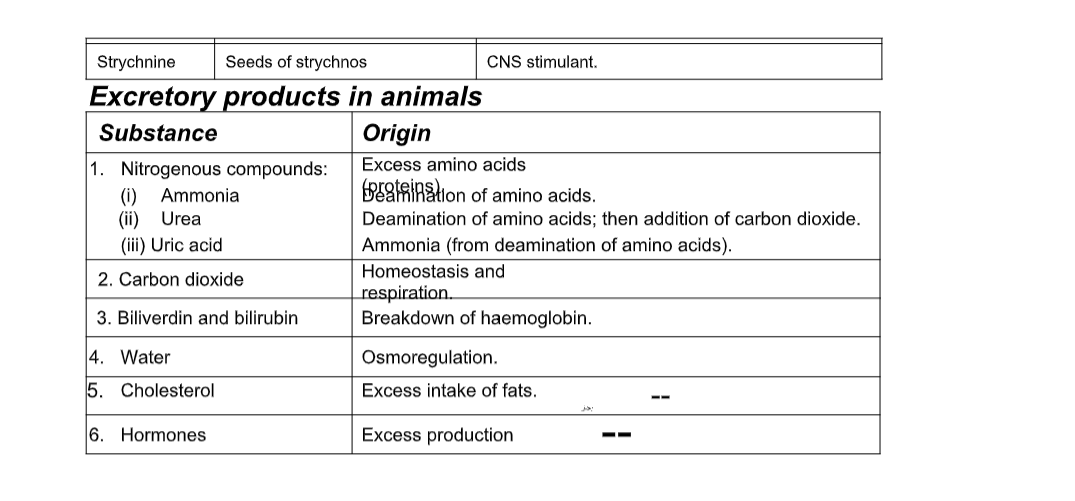
Excretion in Human Beings
Structure and function of the human skin
Nerve Endings:
Subcutaneous Fat:
The Lungs
Structure and Functions of the Kidneys
The Nephron
Mechanism of Excretion
Selective Reabsorption
Removal
Common Kidney Diseases
Uraemia
Symptoms
Kidney Stones
Causes: the stones are formed due to crystallisation of salts around pus, blood or dead tissue.
Symptoms: include blood in urine, frequent urination, pain, chills and fever. Severe pain when urinating.
Treatment
Nephritis
Causes: Bacterial infection, sore throat or tonsillitis, blockage of glomeruli by antibody-antigen complex.
Signs and Symptoms: include headaches, fever, vomiting, oedema.
Role of Liver in Excretion
Breakdown and Elimination of Haemoglobin
Elimination of Sex Hormones
Common Liver Diseases
Cirrhosis
Symptoms
Control and Treatment
Jaundice
Cause: Presence of excess bile pigments.
Symptoms: Yellow pigmentation of skin and eyes, nausea, vomiting and lack of appetite. Itching of skin.
Treatment
Homeostasis
Neuro-Endocrine System and Homeostasis
The Skin and Temperature Regulation
When the body temperature is above optimum the following takes place:
Sweat:
Vasodilation of Arterioles:
Relaxation of hair erector muscle:
When body temperature is below optimum the following takes place:
Vasoconstriction of Arterioles:
Homeostatic Control of Body Temperature in Humans
Body size and Heat Loss
Skin and Osmoregulation
The Kidney and Osmoregulation
Diabetes insipidus is a disease that results from the failure of the pituitary gland to produce ADH and the body gets dehydrated.
Manufacture of Plasma Proteins.
Detoxification.
Toxic substances ingested e.g. drugs or produced from metabolic reactions in the body are converted to harmless substances in a process called detoxification.
KCSE Revision Notes Form 1 - Form 4 All Subjects
Biology Notes FAQ Form
Please insert your question in the form below. Check and ensure that your question has not been asked and answered in the enquiries appearing beneath the form.
Kenya Scholarships for Undergraduate Students » Kenya Scholarships for Postgraduate Students » Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyan Students » Kenya Undergraduate Scholarships » Full Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyans » Kenya Postgraduate Scholarships » Scholarships & Grants » Undergraduate Scholarships » Universities in Kenya » Kenya Universities and Colleges Central Placement Service (KUCCPS) » Colleges in Kenya » KASNEB Registration & Results » Secondary Schools Scholarships in Kenya » Undergraduate & Graduate Scholarships for Kenyans
Scholarships for African Students » Undergraduate Scholarships » African Women Scholarships & Grants » Developing Countries Scholarships » Erasmus Mundus Scholarships for Developing Countries » Fellowship Programs » Funding Grants for NGOs » Government Scholarships » LLM Scholarships » MBA Scholarships » PhD and Masters by Research Scholarships » Public Health Scholarships - MPH Scholarships » Refugees Scholarships » Research Grants » Scholarships and Grants
Scholarships in Australia » Scholarships in Belgium » Scholarships in Canada » Scholarships in Germany » Scholarships in Italy » Scholarships in Japan » Scholarships in Korea » Scholarships in Netherlands » Scholarships in UK » Scholarships in USA
aa Biology Questions and Answers 10th Grade Biology Questions and Answers 10th Grade Biology Test 11th Ncert Biology 12th Class Biology Book Free Download 2017 Biology Hsc Answers 9th Grade Biology Study Guide A Level Biology Biological Molecules Questions A Level Biology Exam Questions by Topic A Level Biology Notes Edexcel A Level Biology Notes Xtremepapers A Level Biology Questions and Answers A Level Biology Questions and Answers (Pdf) A Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf A Level Biology Questions by Topic - Kidney Questions With Markschemes A Level Biology Revision A Level Biology Revision Edexcel A Level Biology Revision Guide A Level Biology Revision Notes A Level Biology Revision Notes Pdf A Level Biology Textbook Pdf A Level Biology Year 1 / as Aqa Exam Questions by Topic A Level Edexcel Notes - a* Biology Aerobic Respiration in Plants All Biology Essays All Biology Essays Form 1 All Biology Essays Form 2 All Biology Essays Form 3 All Biology Essays Form 4 Anaerobic Respiration Equation Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers Animal Cell Questions and Answers Animal Cell Quiz Animal Cell Quiz Labeling Ap Bio Quizzes Ap Biology Essay Questions and Answers As Level Biology Notes Bbc Bitesize Biology Ks3 Biology 101 Biology 12th Biology 12th Class Notes Pdf Biology 2019 Syllabus Biology Book 3 Klb Biology Book 3 Notes Biology Book for Class 11 Biology Book Pdf Free Download Biology Cell Structure Test Biology Class 12 Ncert Solutions Biology Class 12 Pdf Biology Communication Syllabus Biology Diagrams for Class 12 - Biology Diagram Software - Biology Diagrams for Class-10 - Biology Diagrams for Class 11 - Biology Diagrams for Class 9 - Biology Diagrams to Label - Biology Diagram of Female Reproductive System - Biology Diagrams Pdf - Biology Diagrams in Form 1 - Biology Diagrams in Form 2 - Biology Diagrams in Form 3 - Biology Diagrams in Form 4 - Kcse Biology Diagrams -biology Revision Tips Biology Essay Questions and Answers Biology Essay Questions and Answers 2018 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 2 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 1 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 4 Biology Essays and Answers Biology Essays and Answers Form 1 Biology Essays and Answers Form 2 Biology Essays and Answers Form 3 Biology Essays and Answers Form 4 Biology Essays Kcse Biology Essays Kcse Form 1 Biology Essays Kcse Form 2 Biology Essays Kcse Form 3 Biology Essays Kcse Form 4 Biology Essays Pdf Biology Exam 2 Test Biology Exam Form Four Biology Exam Form One Biology Exam Form Three Biology Exam Form Two Biology Exam Practice Test Biology Exam Questions and Answers Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Exam Study Guide Biology Excretion Notes Biology Exercise Form 4 With Answers Biology Final Exam Answer Key Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2016 Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2017 Biology Final Exam Answers 2018 Biology Final Exam Answers 2019 Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers Biology Form 1 & 2 and Answers Biology Form 1 Chapter 1 Biology Form 1 Diagrams Biology Form 1 Notes Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf Biology Form 1 Past Papers Biology Form 1 Questions Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 1 Biology Form 1 Revision Questions Biology Form 1 Syllabus Biology Form 2 Chapter 1 Biology Form 2 Chapter 2 Biology Form 2 Diagrams Biology Form 2 Notes Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf Biology Form 2 Past Papers Biology Form 2 Pdf Biology Form 2 Questions Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2 Biology Form 2 Revision Notes Biology Form 2 Syllabus Biology Form 3 Chapter 3 Biology Form 3 Classification Biology Form 3 Diagrams Biology Form 3 Ecology Biology Form 3 Notes Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Biology Form 3 Past Papers Biology Form 3 Questions Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3 Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Term 3 Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers+pdf Biology Form 3 Revision Notes Biology Form 3 Syllabus Biology Form 3 Topics Biology Form 4 All Chapter Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Biology Form 4 Diagrams Biology Form 4 Notes Biology Form 4 Notes All Chapter Pdf Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 1 Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf Biology Form 4 Past Papers Biology Form 4 Questions Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 4 Biology Form 4 Syllabus Biology Form 4 Textbook Pdf Biology Form Four Notes Pdf Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One Biology Form One Exam Biology Form One Notes Pdf Biology Form One Questions Biology Form One Questions and Answers Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One Term Three Test Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Three Reproduction Biology Form Three Reproduction. Biology Form Three-questions and Answers Biology Form Two Diagrams Biology Form Two Notes Pdf Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form2 Biology Form2 Textbook Biology Grade 10 Exam Papers Biology Hsc Pdf Biology Human Reproduction Video Biology Kcse 2017 Biology Kcse 2017 Paper 1 Biology Kcse Questions Biology Made Familiar Biology Mcq for Class 11 Biology Mcq for Class 12 Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams Pdf Biology Mcq for Neet Pdf Biology Mcq With Answers Pdf Biology Mcqs for Class 12 Pdf Biology Mid Familia Form One Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cxc Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf Biology Notes Biology Notes for High School Students Biology Notes for Igcse 2014 Biology Notes Form 1 Biology Notes Form 1 Pdf Biology Notes Form 2 Biology Notes Form 2 Pdf Biology Notes Form 3 Biology Notes Form 3 Pdf Biology Notes Form 4 Biology Notes Form 4 Chapter 2 Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf Biology Notes Form One Pdf Biology Notes Form Three Biology Notes Form Two Biology Objective Answer Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Pdf Biology Paper 1 Biology Paper 1 Notes Biology Paper 1 Questions Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Paper 1 Topics Biology Paper 2 2017 Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Form 2 Biology Paper 2 Revision Biology Paper 2018 Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Paper 4 Questions and Answers Form 4 Biology Paper One Questions and Answers Biology Past Papers 2017 Biology Past Papers Form 3 Biology Practical Book Class 12 Pdf Biology Practical Exam Biology Practicals Questions and Answers Biology Practice Test 9th Grade Biology Practice Test Answers Biology Practice Test Questions and Answers Biology Question and Answers Note Biology Questions Biology Questions and Answers Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Biology Questions and Answers on Cells Biology Questions and Answers Online Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Questions for High School Biology Questions for High School Students With Answers Biology Questions Multiple Choice Biology Questions Quizlet Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher Biology Quiz for Class 9 Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 12 Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for High School Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Quiz Questions for Class 12 Biology Quiz Questions for College Students Biology Quiz With Answers Biology Quiz With Answers Pdf Biology Revision Biology Revision a Level Biology Revision Notes Form 1 Biology Revision Notes Form 2 Biology Revision Notes Form 3 Biology Revision Notes Form 4 Biology Revision Notes Igcse Biology Revision Questions Biology Study Guide Biology Study Guide - Biology Questions and Answers Biology Study Guide Answer Key Biology Study Guide Answers Biology Study Guide Ib Biology Study Guide Pdf Biology Study Notes Biology Syllabus in Kenya Biology Test Questions and Answers Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Topics Form One Biology Unit 1 Quiz Biology | Revision Science Cell Biology Exam Questions and Answers Cell Biology Exam Questions Pdf Cell Biology Mcq With Answers Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions Pdf Cell Biology Previous Question Papers Cell Biology Question Bank Cell Biology Question Bank Pdf Cell Biology Question Paper Pdf Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Pdf Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf in Hindi Cell Biology Short Answer Questions Cell Biology Test Bank Questions Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf Cell Mcq Pdf Cell Organelles Labeling Quiz Cell Organelles Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cell Questions and Answers Cell Questions and Answers Pdf Cell Questions Quizlet Cell Structure and Function Pdf Cell Structure and Function Pdf Class 11 Cell Structure and Function Quiz Answers Cell Structure and Function Test Answer Key Cell Structure and Function Test Pdf Cells Cells Questions Cellular Organization Pdf Chemical Equation for Aerobic Respiration Chemistry Form 1 Questions and Answers Chemistry Form 2 Exams Chemistry Form 2 Questions and Answers Chemistry Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Chemistry Form 3 Questions and Answers Chemistry Form 3 Revision Questions Chemistry Form 4 Questions and Answers Chemistry Form One Questions and Answers Pdf Chemistry Kcse Questions and Answer Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers Chemistry Paper 3 Question and Answer Cie a Level Biology Notes 2016 Cie a Level Biology Notes Pdf Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 Mcqs College Biology Practice Test College Biology Quiz College Biology Quiz Chapter 1 College Biology Quizlet College Biology Study Guide College Biology Study Guide Pdf College Biology Test Questions and Answers Complete Biology for Cambridge Igcse Revision Guide Pdf Cytology Mcqs With Answers Pdf Difficult Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Animals Download Form Three Biology Notes Download Klb Biology Book 2 Easy Biology Questions Easy Cell Questions Edexcel a Level Biology B Edexcel a Level Biology Notes Pdf Edexcel a Level Biology Salters Nuffield Edexcel A2 Biology Notes Edexcel as Biology Revision Guide Pdf Edexcel Biology A2 Revision Notes Pdf Edexcel Biology Unit 2 Revision Notes Edexcel Gcse Science Revision Guide Pdf Energy Questions Science Bowl Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Answers Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Download Free Exam Notes for Biology 101 Excretion Question and Answer Form 4 Work Excretion Questions and Answers Excretory System Questions and Answers Pdf Excretory System Structure F3 Biology Test Paper Form 1 Biology Exam Form 1 Biology Notes Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Syllabus Form 1 Mathematics Questions and Answers Form 1 Mathematics Test Paper Pdf Form 1 Revision Papers Form 2 Biology Exam Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers > Form 2 Biology Syllabus Form 2 Mathematics Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Book Form 3 Biology Exam Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 Chemistry Exam Paper Form 3 Chemistry Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3 English Exam Paper Form 3 History Exam Paper Form 3 Maths Exam Paper Form 4 Biology Exam Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers Form Four Biology Book Form Four Biology Revision Questions Form Four Biology Syllabus Form Four Biology Topics Form One Biology Book Form One Biology Questions Form One Biology Revision Questions Form One Biology Syllabus Form One Biology Topics Form One Geography Questions and Answers Form One Notes of Biology Form One Past Papers Form Three Biology Book Form Three Biology Notes Form Three Biology Revision Questions Form Three Biology Syllabus Form Three Biology Topics Form Three Cre Notes Pdf Form Two Biology Book Form Two Biology Examination Form Two Biology Notes Form Two Biology Revision Questions Form Two Biology Syllabus Form Two Biology Topics Form Two Chemistry Cat Form Two Chemistry Past Papers Form Two Chemistry Questions and Answers Form Two Chemistry Questions and Answers Pdf Form Two Notes Free a-level Biology Revision App | Pass Your Biology Exams Free Biology Form 1 Notes Free Biology Form 2 Notes Free Biology Form 3 Notes Free Biology Form 4 Notes Free College Biology Practice Test Free Kcse Revision Notes Fun Biology Questions Funny Biology Questions and Answers Funny Biology Quotes Funny Science Questions Funny Science Questions to Ask Gas Exchange Exam Questions Gas Exchange Practice Test Gas Exchange Quiz Gcse Biology Exam Questions and Answers Gcse Biology Past Papers Gcse Biology Revision Gcse Biology Revision Notes Gcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf Gcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf 9-1 Gcse Biology Revision Questions and Answers Gcse Biology Textbook Pdf Gcse Biology Topics - Pass My Exams: Easy Exam Revision Notes General Biology Practice Test With Answers General Biology Quiz General Biology Test Questions and Answers General Knowledge in Biology Human Body General Science Mcq for Ssc General Science Mcqs With Answers Pdf General Science Notes Pdf Geography Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Geography Form 1 Revision Questions Geography Form 3 Questions Good Biology Questions to Ask Gre Biology Practice Test Gre Biology Subject Test Pdf Hard Biology Quiz Questions Hard Science Questions and Answers Hard Science Questions to Ask Your Teacher High School Biology Final Exam Doc High School Biology Final Exam Pdf High School Biology Final Exam Questions High School Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers High School Biology Practice Test High School Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf How Does the Excretory System Work How Many Chromosomes Do Gametes Have How Many Copies of Each Gene Do Gametes Have How Much Genetic Information Is Found in a Gamete How to Study Biology: 5 Study Techniques to Master Biology Hsc Biology 2018 Hsc Biology 2019 Ial Biology Notes Ib Biology Question Bank by Topic Igcse Biology Alternative to Practical Revision Igcse Biology Notes 2017 Pdf Igcse Biology Notes Edexcel Igcse Biology Paper 6 Notes Igcse Biology Revision Guide Igcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf Igcse Biology Revision Worksheets Igcse Biology Znotes Igcse Notes Chemistry Igcse Physics Revision Notes Pdf Interesting Biology Questions Interesting Questions to Ask About Biology Interesting Science Questions and Answers Intro to Biology Quiz K.c.s.e Mathematics Paper 1 2017 Kcse 2015 Biology Paper 3 Kcse 2016 Biology Paper 1 Kcse 2016 Biology Paper 2 Kcse 2017 Biology Paper 2 Kcse 2017 Papers Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Kcse Biology Essays Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 1 Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 2 Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 3 Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 4 Kcse Biology Notes Kcse Biology Notes Pdf Kcse Biology Paper 1 Kcse Biology Paper 1 2017 Kcse Biology Paper 1 2017 Pdf Kcse Biology Paper 2 Kcse Biology Paper 2 2013 Kcse Biology Paper 2 2015 Kcse Biology Paper 2 2017 Kcse Biology Paper 3 2016 Kcse Biology Paper 3 Past Papers Kcse Biology Past Papers and Answers Kcse Biology Practical Past Papers Kcse Biology Practicals Kcse Biology Questions and Answers Kcse Chemistry Notes Kcse Chemistry Paper 1 2013 Kcse Chemistry Paper 1 2016 Kcse Chemistry Paper 2 2014 Kcse Chemistry Paper 2 2016 Kcse Chemistry Past Papers Kcse Chemistry Past Papers and Answers Kcse Chemistry Practical Kcse Cre Past Papers and Answers Kcse English Paper 3 2016 Kcse Essays Kcse Made Familiar Chemistry Kcse Made Familiar Geography Kcse Made Familiar Kiswahili Kcse Made Familiar Mathematics Pdf Kcse Mathematics Paper 1 2016 Kcse Mathematics Past Papers Pdf Kcse Mock Papers Pdf Kcse Past Papers Kcse Past Papers 2012 Kcse Past Papers 2013 Kcse Past Papers 2014 Pdf Kcse Past Papers 2017 Kcse Past Papers Biology Kcse Past Papers Chemistry Kcse Revision Question Kcse Revision Question for Biology Kcse Syllabus Pdf Kenya Secondary School Chemistry Syllabus Kenya Secondary School Syllabus Pdf Klb Biology Book 2 Klb Biology Book 2 Notes Klb Biology Book 2 Pdf Klb Biology Book 3 Pdf Klb Biology Form 1 Klb Biology Form 1 Notes Klb Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf Klb Biology Form 1 Pdf Klb Biology Form 2 Book Klb Biology Form 2 Notes Klb Biology Form 2 Pdf Klb Biology Form 3 Notes Klb Biology Form 3 Pdf Klb Biology Form 4 Notes Klb Biology Form 4 Pdf Klb Biology Form One Klb Geography Form 3 Knec Biology Syllabus Kusoma Biology Notes Kusoma Biology Notes Pdf Kusoma.com Past Papers Made Familiar Biology Pdf Made Familiar Mathematics Mathematics Form 3 Questions and Answers Mathematics Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Mcq on Cell Biology Class 9 Mcqs About Gaseous Exchange Middle School Science Bowl Biology Questions More Than 1800 Biology Questions and Answers to Help You Study Most Tested Questions in Form 1 Biology and Their Answers Most Tested Questions in Form 2 Biology and Their Answers Most Tested Questions in Form 3 Biology and Their Answers Most Tested Questions in Form 4 Biology and Their Answers Most Tested Questions in Form Four Biology and Their Answers Most Tested Questions in Form One Biology and Their Answers Most Tested Questions in Form Three Biology and Their Answers Most Tested Questions in Form Two Biology and Their Answers Multiple Choice Questions on Biology Multiple Choice Questions on Cell Structure and Function O Level Biology Practical Experiments Orm Three Biology Notes Page Navigation Past Paper Questions by Topic Biology Pdf Biology Form 3 Physics Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Physics Form One Questions and Answers Physics Questions and Answers Pdf for Competitive Exams Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers Plant and Animal Cell Quiz for 5th Grade Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Grade 8 Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Pdf Plant Cell Plant Cell Pdf Download Plant Cell Questions and Answers Plant Cell Test Questions Practical Biology Experiments Pdf Practical Biology Question and Answer Pdf Preliminary Biology Questions About Cells Biology Questions and Answers on Gaseous Exchange Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Two Questions Based to Introduction to Biology Questions on Cell Structure and Function Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Humans Questions to Ask in Biology Class Questions to Confuse Your Science Teacher Respiration and Gas Exchange Worksheet Respiration Notes My Elim Form Two Revision Papers Revision Quiz for Biology for Form Three Science Bowl Biology Study Guide Science Bowl Questions Biology Science Bowl Questions Chemistry Science Bowl Questions Earth Science Science Bowl Questions Math Science Bowl Questions Middle School Science Bowl Questions Physics Science Quiz for Class 9 Biology Science Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Science Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Pdf Science Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Pdf Simple Scientific Questions Smart Questions to Ask a Physics Teacher Smart Questions to Ask a Science Teacher Snab Biology Revision Notes The Animal Cell Quiz Answers The Excretory System Answer Key The Excretory System Worksheet Answers The Plant Cell Quiz Answer Key Tricky Biology Questions and Answers Tricky Science Questions for Adults Tricky Science Quiz Questions Two Biology Revision Questions Types of Respiration What Are Gametes What Are Gametes in Biology What Are Gametes in Plants What Are Gametes in Punnett Squares What Are Gametes Quizlet What Are the Types of Gametes Working of Excretory System Year 11 Biology Znotes as Biology
"Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form 2 "Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form 3 "Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form 4 "Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form Four "Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form One "Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form Three "Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form Two 1 a a KCSE Past Papers 10th Grade Biology Questions and Answers 10th Grade Biology Test 11th Ncert Biology 12th Class Biology Book Free Download 2014 KCSE Marking Schemes 2014 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2015 2015 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 2016 KCSE Papers 2016 KCSE Prediction Questions 2017 Biology Hsc Answers 2017 KCSE Prediction Questions 2018 Biology KCSE Leakage 2018 Biology KCSE Questions 2018 KCSE Busineness Studies 2018 KCSE Exam 2018 KCSE Leakage 2018 KCSE Prediction Questions 2018 KCSE Questions 2019 Biology KCSE Leakage 2019 Biology KCSE Questions 2019 KCSE Leakage 2019 KCSE Questions 9th Grade Biology Study Guide A a a Biology Notes a a a Biology Notes! a a a BiologyNotes! A a KCSE Past Papers A Biblical View of Social Justice A Level Biology Biological Molecules Questions A Level Biology Exam Questions by Topic A Level Biology Notes Edexcel A Level Biology Notes Xtremepapers A Level Biology Past Papers A Level Biology Questions and Answers a Level Biology Questions and Answers A Level Biology Questions and Answers (Pdf) A Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf A Level Biology Questions by Topic Kidney Questions With Markschemes A Level Biology Revision A Level Biology Revision Edexcel A Level Biology Revision Guide A Level Biology Revision Notes A Level Biology Revision Notes Pdf A Level Biology Textbook Pdf A Level Biology Year 1 / as Aqa Exam Questions by Topic A Level Edexcel Notes a* Biology aa Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Advance KCSE Past Papers Advance-africa.com KCSE Rev Quiz Advantages and Disadvantages. Aerobic Respiration in Plants All Biology Essays All Biology Notes for Senior Two All KCSE Past Papers Biology With Making Schemes All Marking Schemes Questions and Answers All Past K.c.s.e Questions With Answers Alliance Mocks 2017 Anaerobic Respiration Equation Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers Animal Cell Questions and Answers Animal Cell Quiz Animal Cell Quiz Labeling Ap Bio Quizzes Ap Biology 1 Textbook Pdf Ap Biology Essay Questions and Answers Are Sourced From KNEC. As Level Biology Notes Atika Biology Notes Atika School Biology Notes B/s Book 2 Notes Basic Biology Books Pdf basic Biology Interview Questions and Answers Pdf Basic Biology Interview Questions and Answers Pdf Basic Biology Pdf Basic Biology Questions and Answers Basic Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Bbc Bitesize Biology Ks3 Bihar Board Biology Objective Answer 2017 Bihar Board Biology Objective Answer 2018 Bio Answers Bio Quesions Biology 0478 Biology 101 Biology 12th Biology 12th Class Notes Pdf Biology 2019 Syllabus Biology All KCSE Short Notes Biology Answers Biology Answers Online Free Biology Answers Quizlet Biology Bk 2 Notes Biology Book 1 Biology Book 1 Notes Biology Book 2 Biology Book 2 Notes Biology Book 3 Biology Book 3 KLB Biology Book 3 Notes Biology Book 4 Biology Book 4 Notes Biology Book 4 Pdf Biology Book for Class 11 Biology Book Four Biology Book Four Notes Biology Book One Biology Book One Notes Biology Book Pdf Free Download Biology Book Three Biology Book Three Notes Biology Book Three Pdf Biology Book Two Biology Book Two Notes Biology Books Form Three Biology Bowl Biology Study Guide Biology Bowl Questions Biology Biology Bowl Questions Earth Biology Biology Bowl Questions Math Biology Bowl Questions Middle School Biology Brekthrough Form Two Notes Biology Cell Structure Test Biology Class 12 Ncert Solutions Biology Class 12 Pdf Biology Communication Syllabus Biology Diagram of Female Reproductive System Biology Diagram Software Biology Diagrams for Class 11 Biology Diagrams for Class 12 Biology Diagrams for Class 9 Biology Diagrams for Class-10 Biology Diagrams in Form 1 Biology Diagrams in Form 2 Biology Diagrams in Form 3 Biology Diagrams in Form 4 Biology Diagrams Pdf Biology Diagrams to Label Biology Essay Questions and Answers Biology Essay Questions and Answers 2018 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 2 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Essay Revision Q Biology Essays and Answers Biology Essays Form One to Form Four Biology Essays Form One to Form Three Biology Essays KCSE Biology Essays Pdf Biology Exam 1 Multiple Choice Biology Exam 2 Advance Biology Exam 2 Test Biology Exam 2016 Biology Exam Form Four Biology Exam Form One Biology Exam Form Three Biology Exam Form Two Biology Exam Practice Test Biology Exam Questions Biology Exam Questions and Answers Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Exam Study Guide Biology Exams Biology Excretion Notes Biology Exercise Form 4 With Answers Biology Final Exam Answer Key Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2016 Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2017 Biology Final Exam Answers 2018 Biology Final Exam Answers 2019 Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers Biology Fom 1 Notes Biology Fom 2 Notes Biology Fom 3 Notes Biology Fom 4 Notes Biology Form 1 Biology Form 1 & 2 and Answers Biology Form 1 and 2 Essays Biology Form 1 and 2 Essays Questions and Answers Biology Form 1 Chapter 1 Biology Form 1 Diagrams Biology Form 1 Exams Biology Form 1 Mid Year Exam Biology Form 1 Notes Biology Form 1 Notes and Questions Biology Form 1 Notes Download Biology Form 1 Notes Free Download Biology Form 1 Notes GCSE Biology Form 1 Notes KCSE-kcse Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf Download Biology Form 1 Past Papers Biology Form 1 Pdf Biology Form 1 Pressure Biology Form 1 Question Papers Biology Form 1 Questions Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 1 Quiz Biology Form 1 Revision Questions Biology Form 1 Summary Notes Biology Form 1 Syllabus Biology Form 1 Work Biology Form 1-4 Notes Biology Form 2 Biology Form 2 Chapter 1 Biology Form 2 Chapter 2 Biology Form 2 Diagrams Biology Form 2 Exam Paper 2014 Biology Form 2 Exams Biology Form 2 Notes Biology Form 2 Notes and Questions Biology Form 2 Notes GCSE Biology Form 2 Notes KCSE-kcse Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf Download Biology Form 2 Past Papers Biology Form 2 Pdf Biology Form 2 Question Papers Biology Form 2 Questions Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 2 Quiz Biology Form 2 Revision Notes Biology Form 2 Salts Biology Form 2 Structure and Bonding Biology Form 2 Summary Notes Biology Form 2 Syllabus Biology Form 2 Work Biology Form 3 Biology Form 3 and 4 Essays Biology Form 3 and 4 Essays Questions and Answers Biology Form 3 Chapter 3 Biology Form 3 Classification Biology Form 3 Diagrams Biology Form 3 Ecology Biology Form 3 Exams Biology Form 3 Notes Biology Form 3 Notes and Questions Biology Form 3 Notes GCSE Biology Form 3 Notes KCSE-kcse Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Download Biology Form 3 Notes Topic 1 Biology Form 3 Past Papers Biology Form 3 Pdf Biology Form 3 Question Papers Biology Form 3 Questions Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Term 3 Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers+pdf Biology Form 3 Quiz Biology Form 3 Revision Notes Biology Form 3 Revision Questions Biology Form 3 Summary Notes Biology Form 3 Syllabus Biology Form 3 Syllabus Pdf Biology Form 3 Topics Biology Form 3 Work Biology Form 4 Biology Form 4 All Chapter Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Conversion of Units Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise Pdf Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Mind Map Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise and Answers Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise Pdf Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Experiment Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Formula Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Mind Map Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Momentum Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective Questions and Answers Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Paper 2 Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Slideshare Biology Form 4 Chapter 3 Biology Form 4 Chapter 3 Questions and Answers Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Notes Pdf Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Light Questions and Answers Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Notes Pdf Biology Form 4 Diagrams Biology Form 4 Exam Paper 1 Biology Form 4 Exams Biology Form 4 Exercise Biology Form 4 Exercise Pdf Biology Form 4 Module With Answer Biology Form 4 Note Biology Form 4 Notes Biology Form 4 Notes (Pdf) Biology Form 4 Notes All Chapter Pdf Biology Form 4 Notes and Questions Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 1 Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 2 Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3 Biology Form 4 Notes Download Biology Form 4 Notes Free Download Biology Form 4 Notes GCSE Biology Form 4 Notes KCSE-kcse Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf Download Biology Form 4 Paper 2 Questions and Answers Biology Form 4 Past Papers Biology Form 4 Question Papers Biology Form 4 Questions Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 4 Quiz Biology Form 4 Revision Notes Biology Form 4 Schemes of Work Biology Form 4 Summary Notes Biology Form 4 Syllabus Biology Form 4 Textbook Pdf Biology Form 4 Work Biology Form 5 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers Biology Form 5 Chapter 1 Notes Pdf Biology Form 5 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf Biology Form 5 Chapter 2 Slideshare Biology Form 5 Chapter 3 Notes Pdf Biology Form 5 Notes Pdf Biology Form Four Book Biology Form Four Notes Biology Form Four Notes and Questions Biology Form Four Notes GCSE Biology Form Four Notes Pdf Biology Form Four Past Papers Biology Form Four Questions Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Four Quiz Biology Form Four Study Notes Biology Form Four Syllabus Biology Form Four Topic 2 Biology Form Four Topic 4 Biology Form Four Topics Biology Form Four Work Biology Form One Biology Form One Book Biology Form One Book Pdf Biology Form One Download Topic 1 Upto 3 Biology Form One Exam Biology Form One Notes Biology Form One Notes and Questions Biology Form One Notes GCSE Biology Form One Notes Pdf Biology Form One Pdf Biology Form One Questions Biology Form One Questions and Answers Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One Questions and Their Answers Biology Form One Quiz Biology Form One Revision Question Biology Form One Schemes of Work Biology Form One Study Notes Biology Form One Syllabus Biology Form One Term Three Test Biology Form One to Three Notes Biology Form One Work Biology Form Three Biology Form Three Book Biology Form Three Notes Biology Form Three Notes and Questions Biology Form Three Notes GCSE Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Three Quiz Biology Form Three Reproduction Biology Form Three Reproduction. Biology Form Three Study Notes Biology Form Three Work Biology Form Three-questions and Answers Biology Form Two Biology Form Two Book Biology Form Two Diagrams Biology Form Two Notes Biology Form Two Notes and Questions Biology Form Two Notes GCSE Biology Form Two Notes Pdf Biology Form Two Notes-pdf Biology Form Two Pdf Biology Form Two Questions Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Two Quiz Biology Form Two Study Notes Biology Form Two Topics Biology Form Two Work Biology Form Two,schemes of Work Biology Form2 Biology Form2 Textbook Biology Game Form Four Question End Answers Biology Grade 10 Exam Papers Biology Hsc Pdf Biology Human Reproduction Video Biology IGCSE Past Papers Xtremepapers Biology K.c.s.e 2017 Biology KCSE Biology KCSE 2016 Biology KCSE 2017 Biology KCSE 2017 Paper 1 Biology KCSE Past Papers Biology KCSE Questions Biology KCSE Questions and Answer Biology KCSE Quizzes & Answers Biology KCSE Revision Biology KCSE Revision Notes Biology KCSE Setting Questions Form One and Two Biology Ksce 2015 Biology Last Year K.c.s.e Questions Biology Lesson Plan Form Two Biology Made Familiar Biology Mcq for Class 11 Biology Mcq for Class 12 Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams Pdf Biology Mcq for Neet Pdf Biology Mcq for Ssc Biology Mcq Questions With Answers Biology Mcq With Answers Pdf Biology Mcqs for Class 12 Pdf Biology Mcqs With Answers Pdf Biology Mid Familia Form One Biology Mock Papers Biology Module Form 5 Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cxc Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf Biology Note Biology Note Form Two All Chapters Biology Notes Biology Notes and Guestion and Answear Biology Notes and Syllabus Biology Notes Class 10 Biology Notes for Class 11 Pdf Biology Notes for Class 12 Pdf Biology Notes for High School Students Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014 Biology Notes Form 1 Biology Notes Form 1 4 Biology Notes Form 1 Free Download Biology Notes Form 1 KLB Biology Notes Form 1 Pdf Biology Notes Form 1-4 Biology Notes Form 1-4(1) Biology Biology Notes Form 14 Biology Notes Form 2 Biology Notes Form 2 KLB Biology Notes Form 2 Pdf Biology Notes Form 2; Biology Notes Biology Notes Form 3 Biology Notes Form 3 KLB Biology Notes Form 3 Pdf Biology Notes Form 4 Biology Notes Form 4 Chapter 2 Biology Notes Form 4 KLB Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf Biology Notes Form 4-pdf Biology Notes Form Four Biology Notes Form Four KLB Biology Notes Form Four Pdf Biology Notes Form One Biology Notes Form One KLB Biology Notes Form One Pdf Biology Notes Form One to Form Four Biology Notes Form Three Biology Notes Form Three KLB Biology Notes Form Three Pdf Biology Notes Form Two Biology Notes Form Two KLB Biology Notes Form Two Pdf Biology Notes Form2 Biology Notes IGCSE Biology Notes Kenya Biology Notes on Agroforestry Biology Notes Pdf Biology Notes: Biology Objective Answer Biology Objective Answer 2018 Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Pdf Biology Oral Exam Questions Biology Paper 1 Biology Paper 1 2018 Marking Rules Biology Paper 1 Notes Biology Paper 1 Questions Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Biology Paper 1 Topics Biology Paper 1 With Answers Biology Paper 2 Biology Paper 2 2017 Biology Paper 2 2018 Marking Rules Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Paper 2 Revision Biology Paper 2 Topics Biology Paper 2018 Biology Paper 3 2018 Marking Rules Biology Paper 3 Question and Answer Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2014 KCSE Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2015 KCSE Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2016 KCSE Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2017 KCSE Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2018 KCSE Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers Biology Paper One Questions and Answers Biology Paper One Topics Biology Paper Two Qestions With Answers Biology Paper1 Biology Paper2 Biology Paper3 Biology Paper4 Biology Past Papers Biology Past Papers 2017 Biology Past Papers a Level Biology Past Papers Form 1 Biology Past Papers Form 2 Biology Past Papers Form 3 Biology Past Papers O Level Biology Pdf Download Biology Pp1 KCSE 2016 Biology Practical Book Class 12 Pdf Biology Practical Exam Biology Practicals Form One Biology Practicals Questions and Answers Biology Practice Test 9th Grade Biology Practice Test Answers Biology Practice Test Questions and Answers Biology Practice Test Quizlet Biology Predicted Questions This Year KCSE Biology Preparation Notes Biology Pretest High School Pdf Biology Question and Answer With Explanation Biology Question and Answers 2019 Biology Question and Answers 2020 Biology Question and Answers 2021 Biology Question and Answers 2022 Biology Question and Answers 2025 Biology Question and Answers 2026 Biology Question and Answers Note Biology Questions Biology Questions and Answers Biology Questions and Answers for High School Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Biology Questions and Answers for Secondary Schools Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Biology Questions and Answers Notes Biology Questions and Answers O Biology Questions and Answers on Cells Biology Questions and Answers Online Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Questions and Answers Pdf for Class 12 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf for Competitive Exams Biology Questions and Answers-form 2 Biology Questions for High School Biology Questions for High School Students With Answers Biology Questions for Senior 1 Biology Questions for Senior 2 Biology Questions for Senior 3 Biology Questions for Senior 4 Biology Questions for Senior 5 Biology Questions for Senior 6 Biology Questions for Senior Five Biology Questions for Senior Four Biology Questions for Senior One Biology Questions for Senior Six Biology Questions for Senior Three Biology Questions for Senior Two Biology Questions Form One Biology Questions Multiple Choice Biology Questions Quizlet Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher Biology Quetion and Answer Form Four Biology Quetion and Answer Form One Biology Quetion and Answer Form Three Biology Quetion and Answer Form Two Biology Quiz for Class 9 Biology Quiz for Class 9 Biology Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Pdf Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 12 Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Pdf Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for High School Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Quiz Questions for Class 12 Biology Quiz Questions for College Students Biology Quiz With Answers Biology Quiz With Answers Pdf Biology Quizlet Biology Revision Biology Revision a Level Biology Revision Biology Notes Biology Biology Revision Exam Biology Revision Examination Biology Revision Form One Biology Revision Notes Biology Revision Notes Biology Biology Revision Notes Form 1 Biology Revision Notes Form 2 Biology Revision Notes Form 3 Biology Revision Notes Form 4 Biology Revision Notes IGCSE Biology Revision Paper One Biology Revision Questions Biology Revision Questions and Answers Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 2 Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 4 Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Four Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form One Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Three Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Two Biology Revision Questions Form 1 Biology Revision Questions Form 2 Biology Revision Questions Form 3 Biology Revision Questions Form 4 Biology Revision Questions Form Four Biology Revision Questions Form One Biology Revision Questions Form Three Biology Revision Questions Form Two Biology Revision Quiz Biology Revision Test Biology Secondary School Revision Biology Simple Notes Biology Spm Notes Download Biology Spm Notes Pdf Biology Spm Questions Biology Study Form 2 Biology Study Guide Biology Study Guide Answer Key Biology Study Guide Answers Biology Study Guide Biology Questions and Answers Biology Study Guide Ib Biology Study Guide Pdf Biology Study Guides Biology Study Notes Biology Study Notes Materials Form 1 Pdf Biology Study Notes Materials Form 2 3 Pdf Biology Study Notes Materials Form 2 Pdf Biology Study Notes Materials Form 3 Pdf Biology Study Notes Materials Form 4 Pdf Biology Syllabus in Kenya Biology Syllabus Pdf Biology Test 1 Quizlet Biology Test Questions Biology Test Questions and Answers Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Topic One Form Four Biology Topics Form One Biology Unit 1 Quiz Biology Vol 3 Biology | Revision Biology Biology,form 4 Biology.form Four.topic Three BiologyExam Form Three BiologyModule Form 5 BiologyNotes BiologyNotes for Class 11 Pdf BiologyNotes for Class 12 Pdf BiologyNotes Form 1 BiologyNotes Form 1 Free Download BiologyNotes Form 2 BiologyNotes Form 3 BiologyNotes Form 3 Pdf BiologyNotes IGCSE BiologyNotes Pdf BiologyPast Papers BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf BiologySimple Notes BiologySpm Notes Download BiologySpm Notes Pdf BiologySpm Questions BiologyStudy Guide Answers BiologyStudy Guide Pdf BiologyStudy Guides Blologytextpapers Bridge Biology Business Past KCSE Past Papers Business Studies Form 3 Notes Pdf Business Studies Form 4 Notes Pdf C R E Form One KLB C R E Form One Oli Topic C.r.e Form 1 Notes Kenya C.r.e Form 2 Notes Kenya C.r.e Form 3 Notes C.r.e Form 3 Notes Kenya C.r.e Form 3 Pdf C.r.e Form 4 Notes Kenya C.r.e Form One Notes Pdf C.r.e Notes Form 1 C.r.e Revision Notes C.r.e Short Notes Cambridge IGCSE Biology Cambridge IGCSE Biology 3rd Edition Cambridge IGCSE Biology 3rd Edition Plus Cd South Asia Edition Cambridge IGCSE Biology Answers Cambridge IGCSE Biology Coursebook Pdf Download Cambridge IGCSE Biology Practical Workbook Cambridge IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Cambridge IGCSE Biology Study and Revision Guide 2nd Edition Pdf Cambridge IGCSE Biology Study and Revision Guide Pdf Cambridge IGCSE Biology Workbook Free Download Cambridge IGCSE Biology Workbook Pdf Cambridge IGCSE® Biology Coursebook Caucasian Chalk Circle Essay Questions Cell Biology Exam Questions and Answers Cell Biology Exam Questions Pdf Cell Biology Mcq With Answers Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions Pdf Cell Biology Previous Question Papers Cell Biology Question Bank Cell Biology Question Bank Pdf Cell Biology Question Paper Pdf Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Pdf Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf in Hindi Cell Biology Short Answer Questions Cell Biology Test Bank Questions Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf Cell Mcq Pdf Cell Organelles Labeling Quiz Cell Organelles Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cell Questions and Answers Cell Questions and Answers Pdf Cell Questions Quizlet Cell Structure and Function Pdf Cell Structure and Function Pdf Class 11 Cell Structure and Function Quiz Answers Cell Structure and Function Test Answer Key Cell Structure and Function Test Pdf Cells Cells Questions Cellular Organization Pdf Chapter 1 Introduction to Biology Chapter 1 Introduction to Biology Studies Chemical Equation for Aerobic Respiration Cie a Level Biology Notes 2016 Cie a Level Biology Notes Pdf Cie Past Papers Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 Mcqs Class 8 Biology Notes KCSE-kcse College Biology Notes College Biology Practice Test College Biology Quiz College Biology Quiz Chapter 1 College Biology Quizlet College Biology Study Guide College Biology Study Guide Pdf College Biology Test Questions and Answers College Biology Volume 3 Pdf College BiologyNotes Complete Biology for Cambridge IGCSE Complete Biology for Cambridge IGCSE Revision Guide Pdf County Mocks 2017 Cse Past Papers Biology 2017 Cytology Mcqs With Answers Pdf Difficult Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Animals Dl Biology Form 3 Pdf Kusoma Download Biology Form 1 Download Biology Form 2 Download Biology Form 2 Notes Download Biology Form 3 Download Biology Form 3 Notes Download Biology Form 4 Download Biology Form Four Download Biology Form One Download Biology Form Three Download Biology Form Two Download Biology Notes Form 3 Download Biology Notes Form One Download BiologyNotes Form 3 Download Form Three Biology Notes Download Free KCSE Past Papers Biology Download Free KCSE Past Papers From KNEC. Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers Download KCSE Revision Notes Download KLB Biology Book 2 Download KLB Biology Book 3 Download KLB Biology Book 4 Download Notes of Biology Downloads | Biology | Form Four Exams | Exams Downloads | Biology | Form One Exams | Exams Downloads | Biology | Form Three Exams | Exams Downloads | Biology | Form Two Exams | Exams Downloads | KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes | Dvance KCSE Past Papers Easy Biology Questions Easy Cell Questions Edexcel a Level Biology B Edexcel a Level Biology Notes Pdf Edexcel a Level Biology Salters Nuffield Edexcel A2 Biology Notes Edexcel as Biology Revision Guide Pdf Edexcel Biology A2 Revision Notes Pdf Edexcel Biology Unit 2 Revision Notes Edexcel GCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Edexcel IGCSE Biology Past Papers Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Free Pdf Download Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Download Electronics Form Four Notes Energy Questions Biology Bowl Essay Questions and Answers KCSE Biology Notes Essay Questions and Answers on Betrayal in the City Essay Questions Based on Betrayal in the City Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Answers Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Download Free Evolving World Biology Book 1 Pdf Evolving World Biology Book 4 Notes Evolving World Biology Book Form 1 Evolving World-history Book 3 Exam Notes for Biology 101 Exams KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Excretion Question and Answer Form 4 Work Excretion Questions and Answers Excretory System Questions and Answers Pdf Excretory System Structure F3 Biology Test Paper Find Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers Find KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Exam Form 1 Biology Notes Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form 1 Biology Revision Notes Form 1 Biology Summurized Revision Pdf Form 1 Biology Syllabus Form 1 Biology Test Paper Pdf Form 1 Biology Topics Form 1 BiologyNotes Form 1 BiologyQuestions and Answers Form 1 BiologyRevision Notes Form 1 BiologySyllabus Form 1 BiologyTest Paper Pdf Form 1 Past Papers Form 1 Past Papers With Answers Form 1 Revision Papers Form 1 Subjects in Kenya Form 2 Biology Exam Form 2 Biology Exam Paper Form 2 Biology Exam Paper 2016 Form 2 Biology Exam Paper Free Download Form 2 Biology Exam Paper With Answer Form 2 Biology Final Year Exam Paper 2 Form 2 Biology Notes Form 2 Biology Notes and Revision Questions Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf Form 2 Biology Past Papers Form 2 Biology Questions Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers > Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2 Biology Revision Notes Form 2 Biology Short Notes Form 2 Biology Syllabus Form 2 BiologyExam Paper Form 2 BiologyExam Paper Free Download Form 2 BiologyExam Paper With Answer Form 2 BiologyFinal Year Exam Paper 2 Form 2 BiologyPast Papers Form 2 BiologyRevision Notes Form 2 BiologyShort Notes Form 2 BiologySyllabus Form 2 Revision Papers Form 2 Subjects in Kenya Form 3 Biology Book Form 3 Biology Exam Form 3 Biology Exam Paper Form 3 Biology Notes Form 3 Biology Past Papers Form 3 Biology Questions Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3 Biology Revision Notes Form 3 Biology Syllabus Form 3 BiologyExam Paper Form 3 BiologyNotes Form 3 BiologyPast Papers Form 3 BiologyQuestions Form 3 BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf Form 3 BiologyRevision Notes Form 3 BiologySyllabus Form 3 C.r.e Form 3 Notes of Biology Topic on Fish Form 3 Past Papers Form 3 Revision Papers Form 3 Subjects in Kenya Form 4 Biology Exam Form 4 Biology Notes Form 4 Biology Notes Pdf Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form 4 Biology Revision Notes Form 4 Biology Syllabus Form 4 Biology Topics Form 4 BiologyNotes Form 4 BiologyRevision Notes Form 4 BiologySyllabus Form 4 BiologyTopics Form 4 Exam Papers Form 4 Revision Papers Form 4 Subjects in Kenya Form 5 Biology Topics Form 5 BiologyTopics Form Five Biology Notes Form Five BiologyNotes Form Four Biology Book Form Four Biology Notes Form Four Biology Notes Pdf Form Four Biology Questions and Answers Form Four Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form Four Biology Revision Questions Form Four Biology Syllabus Form Four Biology Topics Form Four BiologyNotes Form Four BiologyQuestions and Answers Form Four BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf Form Four BiologyTopics Form Four Notes Form Four Revision Papers Form Four Subjects in Kenya Form One Biology Book Form One Biology Examination Form One Biology First Topic Form One Biology Lesson Plan Form One Biology Notes Pdf Form One Biology Past Papers Pdf Form One Biology Questions Form One Biology Questions and Answers Form One Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form One Biology Revision Questions Form One Biology Short Notes Form One Biology Syllabus Form One Biology Topics Form One BiologyExamination Form One BiologyPast Papers Pdf Form One BiologyQuestions and Answers Form One BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf Form One BiologyTopics Form One Exams Form One Notes of Biology Form One Past Papers Form One Subjects in Kenya Form One Term One Biology Exam Form One Term One BiologyExam Form Three Biology Book Form Three Biology Book Pdf Form Three Biology Notes Form Three Biology Notes Pdf Form Three Biology Questions and Answers Form Three Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form Three Biology Revision Questions Form Three Biology Syllabus Form Three Biology Topics Form Three BiologyNotes Form Three BiologyNotes Pdf Form Three BiologyQuestions and Answers Form Three BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf Form Three BiologyTopics Form Three Subjects in Kenya Form Two Biology Book Form Two Biology Cat Form Two Biology Examination Form Two Biology Notes Form Two Biology Notes Pdf Form Two Biology Past Papers Form Two Biology Questions and Answers Form Two Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form Two Biology Revision Questions Form Two Biology Syllabus Form Two Biology Topics Form Two BiologyNotes Form Two BiologyNotes Pdf Form Two BiologyQuestions and Answers Form Two BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf Form Two BiologySyllabus Form Two BiologyTopics Form Two Notes Form Two Subjects in Kenya Free a-level Biology Revision App | Pass Your Biology Exams Free Biology Form 1 Notes Free Biology Notes Form 1 Free Biology Notes Pdf Free BiologyNotes Pdf Free College Biology Practice Test Free Form1,form2,form3 Past Papers Free KCSE Past Papers Free KCSE Mocks 2015 Free KCSE Past Papers 2014 Free KCSE Past Papers KCSE Past Free KCSE Past Papers Kenya, Free KCSE Past Papers With Answers Free KCSE Questions and Answers on Biology Free KCSE Revision Notes Free Marking Schemes Free Mocks Online KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers Free Revision Papers From Three Notes Topic One KLB Fun Biology Questions Funny Biology Questions Funny Biology Questions and Answers Funny Biology Questions to Ask Funny Biology Quotes Gas Exchange Exam Questions Gas Exchange Practice Test Gas Exchange Quiz GCSE Biology Exam Questions and Answers GCSE Biology Past Papers GCSE Biology Revision GCSE Biology Revision Notes GCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf GCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf 9-1 GCSE Biology Revision Questions and Answers GCSE Biology Textbook Pdf GCSE Biology Topics Pass My Exams: Easy Exam Revision Notes General Biology Notes Pdf General Biology Practice Test With Answers General Biology Quiz General Biology Quiz Pdf General Biology Test Questions and Answers General Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf General Knowledge in Biology Human Body Good Biology Questions to Ask GRE Biology Practice Test GRE Biology Subject Test Pdf Handbook of Biology Pdf Free Download Hard Biology Questions Hard Biology Questions and Answers Hard Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher Hard Biology Quiz Questions Hard Form 3 Biology Question High School Biology Final Exam Doc High School Biology Final Exam Pdf High School Biology Final Exam Questions High School Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers High School Biology Notes High School Biology Practice Test High School Biology Pretest With Answers High School Biology Questions and Answers Pdf High School Biology Study Guide High School Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf High School BiologyNotes High School BiologyStudy Guide How Does the Excretory System Work How Many Chromosomes Do Gametes Have How Many Copies of Each Gene Do Gametes Have How Much Genetic Information Is Found in a Gamete How to Answer KCSE Biology Question How to Motivate a Form 4 Student How to Motivate a KCSE Candidate How to Motivate a KCSE Student How to Pass Biology Questions & Answers Form 1&2 | Text Book How to Revise Biology How to Revise Effectively for KCSE How to Study Biology: 5 Study Techniques to Master Biology Hsc Biology 2018 Hsc Biology 2019 Https://www.knec.ac.ke/ Www.knec-portal.ac.ke/ KNEC Portal: Ial Biology Notes Ib Biology Cold War Notes Ib Biology Notes Ib Biology Notes Pdf Ib Biology of the Americas Notes Ib Biology of the Americas Study Guide Ib Biology Paper 2 Study Guide Ib Biology Question Bank by Topic Ib Biology Study Guide Pdf Ict Notes Form 1 IGCSE Biology Alternative to Practical Revision IGCSE Biology Alternative to Practical Revision Notes IGCSE Biology Book IGCSE Biology Book Pdf Download IGCSE Biology Notes IGCSE Biology Notes 2017 Pdf IGCSE Biology Notes Edexcel IGCSE Biology Paper 2 Notes IGCSE Biology Paper 6 Notes IGCSE Biology Past Papers IGCSE Biology Past Papers 2014 IGCSE Biology Past Papers 2017 IGCSE Biology Pdf IGCSE Biology Pre Release Material 2018 IGCSE Biology Resources IGCSE Biology Revision Guide IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Free Download IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Download IGCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf IGCSE Biology Revision Worksheets IGCSE Biology Workbook Pdf IGCSE Biology Znotes IGCSE BiologyPast Papers IGCSE Notes Biology Importance of Agroforestry Inorganic Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf Inorganic Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Interesting Biology Questions Interesting Biology Questions and Answers Interesting Questions to Ask About Biology Intro to Biology Quiz Introduction of Biology Form One Introduction to Biology Introduction to Biology Notes Introduction to Biology Pdf Introduction to BiologyNotes Is Agroforestry Sustainable? K.c.s.e Answers Biology Paper One 2018 K.c.s.e Biology 2017 K.c.s.e Biology 2018 K.c.s.e Biology Paper 1 2017 K.c.s.e Mocks 2018 K.c.s.e Papers 2015 K.c.s.e Papers 2016 K.c.s.e Past Papers 2014 K.c.s.e.Biology Paper 2 Year 2018 K.c.s.e.results 2018 for Busia County K.l.b Biology Form 3 K.l.b Biology Notes K.l.b BiologyNotes Kasneb Past Papers for Colleges Biology Past Papers KCSE 2010 Marking Scheme KCSE 2010 Past Papers KCSE 2011 Biology Paper 1 KCSE 2011 Marking Scheme KCSE 2012 Biology Paper 2 Marking Scheme KCSE 2012 Marking Schemes KCSE 2013 Biology Paper 1 KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme Pdf KCSE 2014 KCSE 2015 Biology Paper 2 KCSE 2015 Biology Paper 3 KCSE 2015 Marking Scheme KCSE 2015 Past Papers KCSE 2016 Biology Paper 1 KCSE 2016 Biology Paper 2 KCSE 2017 Biology Paper 1 KCSE 2017 Biology Paper 2 KCSE 2017 Hostory Papers With Answers.com KCSE 2017 Marking Scheme KCSE 2017 Papers KCSE 2017 Papers and Marking Scheme KCSE 2017 Papers Pdf KCSE 2017 Past Papers KCSE 2017 Prediction Pdf KCSE 2018 Biology and Answers KCSE 2018 Biology Prediction KCSE 2018 Leakage KCSE 2018 Marking Scheme KCSE 2018 Papers KCSE 2018 Prediction Pdf KCSE 2018 Predictions KCSE 2018 Questions KCSE 2018 Questions and Answers KCSE 2019 Leakage Biology KCSE 2019 Marking Scheme KCSE 2019 Questions KCSE 2019 Questions and Answers KCSE 2020 Questions KCSE 2020 Questions and Answers KCSE Answers KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers Downloads | KCSE Biology 2011 KCSE Biology 2016 KCSE Biology Diagramsbiology Revision Tips KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf KCSE Biology Essays KCSE Biology Essays Pdf KCSE Biology Marking Schemes KCSE Biology Notes KCSE Biology Notes Pdf KCSE Biology Notes, Syllabus, Questions, Answers KCSE Biology Paper 1 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2011 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2012 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2013 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2015 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2016 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2017 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2017 Pdf KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers KCSE Biology Paper 2 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2012 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2012 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2015 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2013 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2014 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2015 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2016 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2017 KCSE Biology Paper 3 KCSE Biology Paper 3 2012 KCSE Biology Paper 3 2016 KCSE Biology Paper 3 2017 KCSE Biology Paper 3 Past Papers KCSE Biology Past Papers KCSE Biology Past Papers and Answers KCSE Biology Past Papers Pdf KCSE Biology Practical KCSE Biology Practical 2015 KCSE Biology Practical 2016 KCSE Biology Practical Past Papers KCSE Biology Practicals KCSE Biology Practicals KCSE Biology Paper 1 KCSE Biology Question and Answer KCSE Biology Questions and Answers KCSE Biology Questions and Answers Ap Biology KCSE Biology Revision KCSE Biology Revision Notes KCSE Biology Revision Papers KCSE Biology Revision Questions KCSE Biology Revision Questions and Answers KCSE Biology Syllabus KCSE BiologyNotes KCSE BiologyPaper 1 KCSE BiologyPaper 2 KCSE BiologyPaper 2 Pdf KCSE BiologySyllabus KCSE Business Paper 1 2016 KCSE Business Past Papers KCSE Business Studies Past Papers KCSE Essay Questions in Betrayal in the City KCSE Essays KCSE Exam Papers 2018 KCSE Exam Papers Answers KCSE Form 1 Biology Revision KCSE Form 2 Biology Revision KCSE Form 3 Biology Revision KCSE Form 4 Biology Revision KCSE Form Four Biology Revision KCSE Form One Biology Revision KCSE Form Three Biology Revision KCSE Form Two Biology Revision KCSE KCSE Past Papers KNEC KCSE Leakage KCSE Leakage Biology KCSE Made Familiar Biology KCSE Made Familiar Biology Pdf KCSE Marking Scheme 2016 KCSE Marking Schemes KCSE Marking Schemes 2017 KCSE Marking Schemes Pdf KCSE Mock Exams KCSE Mock Papers 2015 KCSE Mock Papers 2017 KCSE Mock Papers 2018 KCSE Mock Papers Pdf KCSE Mock Papers Pdf 2018 KCSE Mock Papers Pdf KCSE Past Papers KCSE Mocks 2017 KCSE Mocks 2018 KCSE Notes KCSE Online Notes KCSE Online Past Papers KCSE Online Registration KCSE Papers 2015 KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes | Exams KCSE Past Papers KCSE Past Papers 2007 KCSE Past Papers 2009 KCSE Past Papers 2010 KCSE Past Papers 2011 KCSE Past Papers 2011 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2012 KCSE Past Papers 2013 KCSE Past Papers 2013knec KCSE Past Papers 2014 KCSE Past Papers 2014 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2015 KCSE Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes KCSE Past Papers 2015 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2016 KCSE Past Papers 2016 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2017 KCSE Past Papers 2017 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2018 KCSE Past Papers Biology KCSE Past Papers Biology and Answers KCSE Past Papers Biology Pdf KCSE Past Papers Biology With Answers KCSE Past Papers Biologyand Answers KCSE Past Papers Business Studies and Answers KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers Free Mocks Online KCSE Past Papers Marking Scheme KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download KCSE 2013 KCSE Past Papers With Answers KCSE Past Papers Woodwork and Answers KCSE Prediction 2017 KCSE Prediction 2018 KCSE Prediction 2018 Pdf KCSE Prediction Papers 2018 KCSE Prediction Questions KCSE Prediction Questions 2018 KCSE Prediction Questions and Answers KCSE Questions KCSE Questions and Answers KCSE Questions and Answers. KCSE Questions on Biology KCSE Results, Online Registration, KCSE Result Slip. KCSE Revision KCSE Revision Notes KCSE Revision Notes Biology KCSE Revision Notes Pdf KCSE Revision Papers KCSE Revision Papers 2014 KCSE Revision Papers With Answers KCSE Revision Question for Biology KCSE Revision Questions KCSE Revision Questions and Answers KCSE Revision | Secondary School | Text Books | Text Book Centre KCSE Syllabus Pdf KCSE Trial 2017 KCSE Trial Exams 2017 Kenya Secondary School Biology Syllabus Kenya Secondary School Biology Syllabus Pdf Kenya Secondary School BiologySyllabus Pdf Kenya Secondary School Syllabus Pdf Kenya-kcse-christian Religious Education Syllabus Kenyaplex KCSE Past Papers Kenyaplex Past Papers for Secondary KLB Biology Book 1 Download KLB Biology Book 1 Notes KLB Biology Book 1 Pdf KLB Biology Book 2 KLB Biology Book 2 Notes KLB Biology Book 2 Notes Pdf KLB Biology Book 2 Pdf KLB Biology Book 3 Notes KLB Biology Book 3 Pdf KLB Biology Book 3 Pdf Download KLB Biology Book 4 Notes KLB Biology Book 4 Pdf KLB Biology Book 4 Pdf Download KLB Biology Book 4 Topics KLB Biology Book One KLB Biology Form 1 KLB Biology Form 1 Notes KLB Biology Form 1 Pdf KLB Biology Form 2 KLB Biology Form 2 Book KLB Biology Form 2 Notes KLB Biology Form 2 Pdf KLB Biology Form 2 Pdf Download KLB Biology Form 2 Schemes of Work KLB Biology Form 3 KLB Biology Form 3 Notes KLB Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf KLB Biology Form 3 Pdf KLB Biology Form 3 Pdf Download KLB Biology Form 4 KLB Biology Form 4 Notes KLB Biology Form 4 Pdf KLB Biology Form Four KLB Biology Form Four Notes KLB Biology Form One KLB Biology Form One Notes KLB Biology Form Three KLB Biology Form Three Notes KLB Biology Form Two KLB Biology Form Two Notes KLB Biology Notes KLB Biology Notes Form 4 KLB Biology Pdf KLB BiologyNotes KLB BiologyNotes Form 4 KLB BiologyPdf KNEC Biology Syllabus KNEC Examiners Portal KNEC Website KNEC Ict Past Papers KNEC Past Papers for Colleges KNEC Past Papers Free Download KNEC Past Papers Free Downloads KNEC Past Papers Pdf KNEC Portal Confirmation KNEC Portal KCSE Results KNEC Portal KNEC Past Papers for Colleges Kasneb Past Papers KNEC Revision Papers KNEC Technical Exams Past Papers Kusoma Biology Notes Kusoma Biology Notes Pdf Kusoma Notes Biology Kusoma.co.ke Kusoma.com Past Papers Learner Guide for Cambridge IGCSE Biology Longhorn Biology Book 3 Pdf Made Familiar Biology Made Familiar Biology Pdf Made Familiar Biology Questions Maktaba Tetea Notes Marking Scheme KCSE Biology Past Papers Math Form2 Note Mcq on Cell Biology Class 9 Mcqs About Gaseous Exchange Middle School Biology Bowl Biology Questions Mock Past Papers 2017 Mock Past Papers With Answers Mokasa Mock 2017 More Than 1800 Biology Questions and Answers to Help You Study Multiple Choice Questions on Biology Multiple Choice Questions on Cell Structure and Function Necta Biology Past Papers Necta Biology Practicals Necta BiologyPast Papers Necta BiologyPracticals Necta Form Four Past Papers Necta Past Papers Form 4 Necta Past Papers Form 4 2016 Necta Past Papers Form Six Necta Past Papers Form Two Necta Questions and Answers Necta Review Questions Notes Biology Form 1 Notes Biology Form 2 Notes Biology Form 3 Notes Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Notes Biology Form 3 Syllabus Notes Biology Form 4 Syllabus Notes on Biology Studies Notes Za Biology 4m 2 Notes Za Biology Form One Notes Za Biology Form Three O Level Biology Practical Experiments O Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Orm Three Biology Notes Page Navigation Papacambridge Biology IGCSE Papers KNEC KCSE Online Past Papers KNEC KCSE Results Past Papers Past KCSE Papers Past Paper Questions by Topic Biology Past Papers 2014 Past Papers in Kenya Pdf Biology Form 3 Pdf Biology Notes Pdf Biology Notes Form 1 Pdf Biology Notes Form 2 Pdf Biology Notes Form 3 Pdf Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf Biology Notes Form Four Pdf Biology Notes Form One Pdf Biology Notes Form Three Pdf Biology Notes Form Two Pdf Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form Four Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form One Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form Three Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Form Two Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Free KCSE Past Papers and Marking Schemes Pdf" Revision Questions Biology Form 1 Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers Plant and Animal Cell Quiz for 5th Grade Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Grade 8 Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Pdf Plant Cell Plant Cell Pdf Download Plant Cell Questions and Answers Plant Cell Test Questions Practical Biology Experiments Pdf Practical Biology Question and Answer Pdf Pre Mocks 2018 Preliminary Biology Primary and Secondary Tillage Implements Ppt Pte KNEC Past Papers Questions About Cells Biology Questions and Answers on Gaseous Exchange Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Two Questions Based to Introduction to Biology Questions on Cell Structure and Function Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Humans Questions on Introduction to Biology Questions to Ask in Biology Class Questions to Confuse Your Biology Teacher Quizlet Biology Cells Quizlet Biology Test Quizlet Test Questions Qustions in Biology and Answers Radioactivity Form Four Respiration and Gas Exchange Worksheet Respiration Notes My Elim Form Two Revision Revision Biology Notes and Questions? Revision Quiz for Biology for Form Three S.1 Biology Questions S.2 Biology Questions S.3 Biology Questions S.4 Biology Questions Sample Essays on Betrayal in the City School Biology Notes Secondary Biology Notes Secondary Biology Notes Pdf Secondary BiologyNotes Pdf Senior 1 Biology Notes Senior 2 Biology Notes Senior 3 Biology Notes Senior 4 Biology Notes Senior 5 Biology Notes Senior 6 Biology Notes Senior Five Biology Notes Senior Four Biology Notes Senior One Biology Notes Senior Six Biology Notes Senior Three Biology Notes Senior Two Biology Notes Simple Scientific Questions Smart Questions to Ask a Biology Teacher Snab Biology Revision Notes Southwest Mock Paper 2 2016 Biology Only Spm Biology Revision Notes Spm Notes Success Biology Spm Pdf Success BiologySpm Pdf Summary of Biology Form 3 Tahossa Past Papers The Animal Cell Quiz Answers The Excretory System Answer Key The Excretory System Worksheet Answers The Plant Cell Quiz Answer Key To Motivate a Form 4 KCSE Student To Motivate a Form 4 Student Topical Revision Material Tricky Biology Questions and Answers Tricky Biology Questions for Adults Tricky Biology Questions With Answers Tricky Biology Quiz Questions Two Biology Revision Questions Types of Respiration University Biology Volume 3 Openstax University Biology Volume 3 Pdf University Biology Volume 4 Pdf Ur Revision Guide IGCSE Biology What Are Gametes What Are Gametes in Biology What Are Gametes in Plants What Are Gametes in Punnett Squares What Are Gametes Quizlet What Are the Types of Gametes Working of Excretory System Www.Biology Form One Notes.com Www.Biology From One KLB.com Www.form 1 Biology.com Www.form 2 Biology.com Www.form 3 Biology.com Www.form 4 Biology.com Www.form Four Biology.com Www.form One Biology.com Www.form Three Biology.com Www.form Two Biology.com Www.kusoma Notes Www.kusoma Revision Materials Www.kusoma.co.ke Biology Notes Xtremepapers IGCSE Biology Year 11 Biology Z Notes Biology IGCSE Znotes as Biology 15 Common Biology Questions From Form 1 15 Common Biology Questions From Form 2 15 Common Biology Questions From Form 3 15 Common Biology Questions From Form 4 15 Common Biology Questions From Form Four 15 Common Biology Questions From Form One 15 Common Biology Questions From Form Three 15 Common Biology Questions From Form Two 150 Common Biology Questions From Form 1 150 Common Biology Questions From Form 2 150 Common Biology Questions From Form 3 150 Common Biology Questions From Form 4 150 Common Biology Questions From Form Four 150 Common Biology Questions From Form One 150 Common Biology Questions From Form Three 150 Common Biology Questions From Form Two 2019 KCSE Exams Biology Papers 2019 KCSE Exams Papers 2020 KCSE Exams Biology Papers 2021 KCSE Exams Biology Papers Best Biology Books for KCSE Knec Biology Biology 2 Topic Form Two Biology Diagrams Biology Form 1 and 2 Notes Biology Form 1 Download Biology Form 1 Notes Online Biology Form 1 Notes Revision Biology Form 1 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 1 Revision Notes Biology Form 1 Text Book Biology Form 1 Text Book Notes Biology Form 2 Download Biology Form 2 Notes Biology Form 2 Notes Online Biology Form 2 Notes Revision Biology Form 2 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Biology Form 2 Pdf Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 2 Revision Notes Biology Form 2 Text Book Biology Form 2 Text Book Notes Biology Form 3 Download Biology Form 3 Notes Online Biology Form 3 Notes Revision Biology Form 3 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3 Revision Notes Biology Form 3 Text Book Biology Form 3 Text Book Notes Biology Form 4 Download Biology Form 4 Notes Online Biology Form 4 Notes Revision Biology Form 4 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 4 Revision Notes Biology Form 4 Text Book Biology Form 4 Text Book Notes Biology Form Four Download Biology Form Four Notes Online Biology Form Four Notes Revision Biology Form Four Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Four Revision Notes Biology Form Four Text Book Biology Form Four Text Book Notes Biology Form One Download Biology Form One Notes Online Biology Form One Notes Revision Biology Form One Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Biology Form One Questions and Answers Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One Revision Notes Biology Form One Text Book Biology Form One Text Book Notes Biology Form Three Download Biology Form Three Notes Online Biology Form Three Notes Revision Biology Form Three Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Three Revision Notes Biology Form Three Text Book Biology Form Three Text Book Notes Biology Form Two Download Biology Form Two Notes Online Biology Form Two Notes Revision Biology Form Two Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Two Revision Notes Biology Form Two Text Book Biology Form Two Text Book Notes Biology Full Exam Papers Biology K.C.S.E Revision Papers Biology KCSE Revision Biology Notes Book Four Biology Notes Book One Biology Notes Book Three Biology Notes Book Two Biology Notes Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Short Note for Revising Form 1 Biology Short Note for Revising Form 2 Biology Short Note for Revising Form 3 Biology Short Note for Revising Form 4 Biology Short Note for Revising Form Four Biology Short Note for Revising Form One Biology Short Note for Revising Form Three Biology Short Note for Revising Form Two Biology Short Notes Form 1 Biology Short Notes Form 2 Biology Short Notes Form 3 Biology Short Notes Form 4 Biology Short Notes Form Four Biology Short Notes Form One Biology Short Notes Form Three Biology Short Notes Form Two Biologyy Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Brief Notes Biology Form 1 Brief Notes Biology Form 2 Brief Notes Biology Form 3 Brief Notes Biology Form 4 Brief Notes Biology Form Four Brief Notes Biology Form One Brief Notes Biology Form Three Brief Notes Biology Form Two Brief Notes Biology Form3 Chapter1 Download Book 1 Biology Notes Download Book 2 Biology Notes Download Book 3 Biology Notes Download Book 4 Biology Notes Download Book Four Biology Notes Download Book One Biology Notes Download Book Three Biology Notes Download Book Two Biology Notes Download Book1 Biology Notes Download Book2 Biology Notes Download Book3 Biology Notes Download Book4 Biology Notes Download KCSE Biology Study Notes Download Secondary Subjects Download Secondary Subjects in Kenya Download Secondary Subjects KCSE Exams Revision Kenya Exams Revision Kenya KCSE Expected Questions and Answers in Biology Form One Form 2 Biology Notes Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf Form 2 Biology Topics Form 3 Biology Book Pdf Form Iii Topics of Biology Revisios How to Answer Biology Paper 1 Questions? How to Answer Biology Paper 2 Questions? How to Answer Biology Paper 3 Questions? How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions? How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 2 Questions? How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 3 Questions? How to Answer Paper 1 Biology Questions? How to Answer Paper 2 Biology Questions? How to Answer Paper 3 Biology Questions? K.C.S.E Revision Papers K.C.S.E Revision Papers Biology KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf KCSE Biology Revisions KCSE Biology Study Notes KCSE Free Biology Qussions KCSE Free Qussions KCSE Revision Kenya KCSE Revisions Biology Form Two Questions Revision Kenya Revision Kenya Kcsse Sammary Note for Biology Form 1 Sammary Note for Biology Form 2 Sammary Note for Biology Form 3 Sammary Note for Biology Form 4 Sammary Note for Biology Form Four Sammary Note for Biology Form One Sammary Note for Biology Form Three Sammary Note for Biology Form Two Www.last Year KCSE Exams.com Biology Past Papers and Marking Scheme Igcse Biology Past Papers Igcse Biology Past Papers 2015 Igcse Biology Past Papers by Topic Edexcel Igcse Biology Past Papers Biology Questions Book Two Biology Form One Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf Biology Form 3 Notes Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf - Fill Online, Printable ... Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf - Fill Online, Printable, Fillable, Blank | Pdffiller Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Download Biology Form Three Full Notes Download Your Document Biology Notes Form 3 Classification Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 - High School Biology Tests Form 3 Biology Book Pdf Form 3 Biology Notes Form 3 History Notes Pdf Download Form 3 Notes Pdf - Fill Online, Printable Form 3 Notes Pdf - Fill Online, Printable, Fillable, Blank | Pdffiller Kenya Form 3 Biology Notes Klb Biology Book 3 Pdf Download Klb Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf A Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf All Biology Questions and Answers Pdf,ppt Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Pdf Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Notes Form 1-4 Pdf Free High School Notes Kenya Free Kcse Revision Notes General Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf High School Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf Kcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf Kcse Revision Books Pdf Kcse Revision Notes Pdf Kenya Secondary School Notes Pdf Notes of Form 123 and 4 All Subject Biology Notes Form 1 Free Download Advice to KCSE Candidates Best Revision Books for KCSE How to Pass an Exam Successfully How to Pass KCSE 2018 How to Pass KCSE 2019 How to Pass KCSE Biology Paper How to Pass KCSE Biology How to Pass KCSE Biology How to Pass KCSE 2019 K.c.s.e Biology Paper 1 2017 KCSE 2019 Prediction KCSE Prediction 2019 KCSE Revision Tips KCSE Biology Paper 1 2018 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2018 KCSE Biology Past Papers Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2012 KCSE Past Papers 2017 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2018 KCSE Past Papers of Biology Pp2 KCSE Biology Past Papers Pdf Answers for K.c.s.e Past Papers for Biology Biology Paper 1 With Answers Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Biology Paper One Questions and Answers Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Kcse Biology Paper 1 2017 Kcse Biology Paper 1 2018 Kcse Biology Paper 3 Past Papers Kcse Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes Biology KCSE Papers With Their Marking Schemes Biology Paper 1 and Answers KCSE 2017 Papers and Marking Scheme KCSE 2019 Papers and Marking Scheme KCSE Biology Paper 1 2018 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2019 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2019 Past Papers KCSE Biology Paper 2 2017 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2018 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2019 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2019 Past Papers KCSE Biology Paper 3 2019 Past Papers KCSE Biology Past Papers and Answers KCSE Marking Schemes Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes KCSE Past Papers 2019 Marking Schemes KCSE Past Papers Biology Paper 1 2019 KCSE Past Papers Biology Paper 2 2019 KCSE Past Papers Biology Paper 3 2019 Past Papers KCSE Biology Paper 1 2019 Past Papers KCSE Biology Paper 2 2019 Past Papers KCSE Biology Paper 3 2019 9th Grade Biology Notes All Biology Essays Pdf Ap Bio Chapter 1 Notes Ap Biology Chapter 3 Summary Bio Chapter 4 Bio F4 C2 Biology 9 Biology Chapter 2 Biology Chapter 2 Notes Biology Chapter 3 Biology Chapter 4 Notes Biology Chapter 5 Biology Class 9 Chapter 2 Notes Biology Class 9 Notes Pdf Download Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf Biology Essays and Answers Pdf Biology Essays Kcse Biology Essays Notes Biology Essays Pdf Download Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf Download Biology Form 4 Paper 2 Questions and Answers Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Biology Form 4 Topics Biology Movement of Substances Biology Notes for Class 9 Pdf Biology Notes Form 1-4 Biology Notes Form 1-4 Pdf Biology Notes Form 2 Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Answers Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Campbell Biology Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Focus Questions Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Multiple Choice Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Powerpoint Chapter 4 Cells and Tissues Answer Key Class 9th Biology Notes Download Biology Notes Form Four Notes Free Biology Notes Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Kcse Biology Notes Pdf Klb Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf Mastering Biology Chapter 2 the Chemical Context of Life Notes of Biology Section 2.1 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key State the Level of Cell Organisation of Amoeba Sp Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Kcse Revision Questions and Answers Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Biology Paper One Questions and Answers Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Kcse Biology Past Papers and Answers All Biology Questions and Answers Pdf,ppt Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Question Paper 2015 With Answer Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Gs 2015 Biology Answer Key Tifr 2017 Biology Answer Key Tifr Gs 2011 Biology Answer Key Tifr Gs 2012 Biology Answer Key Tifr Previous Year Question Papers of Biology With Answers Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Biology Paper 1 2018 Biology Paper 2 2018 Biology Paper 1 2019 Biology Paper 2 2019 Biology Paper 1 Notes Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2018 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2018 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2017 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2017 KCSE Biology Paper 1 2019 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2019 Most Tested KCSE Biology Questions Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf Download Biology Form 2 Pdf Biology Form 2 Syllabus KLB Notes Biology Form Two Topics Biology Notes Form 3 Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers KLB Biology Form 2 Book Pdf KLB Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf 4m1 Notes Viusasa 4m2 Notes Viusasa 4m3 Notes Viusasa 4m4 Notes Viusasa Download on Viusasa - Download Now for Free Elimu - Viusasa Elimu Library | Notes, Exams, Lesson Plans, Schemes Elimu Online High School Notes - Revision Materials for Kenyan Schools Https //www.viusasa.com/elimu Kenya Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 1 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 2 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 3 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 4 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Four Notes Viusasa Elimu Form One Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Three Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Two Viusasa Viusasa Education Viusasa Elimu Viusasa Elimu Class 6 Viusasa Elimu Form 1 Viusasa Elimu Form 1 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 2 Viusasa Elimu Form 2 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 3 Viusasa Elimu Form 3 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 4 Viusasa Elimu Form 4 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Four Viusasa Elimu Form Four Notes Viusasa Elimu Form One Viusasa Elimu Form One Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Three Viusasa Elimu Form Three Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Two Viusasa Elimu Form Two Notes Viusasa High School Notes - Revision Materials for Kenyan Schools Viusasa Notes Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 - Biology Form Two Notes Biology Questions and Answers Form 4 - Biology Form Four Notes Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 - Biology Form Three Notes Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 - Biology Form One Notes Biology Mock Papers Biology Paper 1 2019 Biology Paper 1 Notes Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Paper 2 Form 3 Biology Paper 2 Notes Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Past Papers Biology Past Papers Pdf Biology Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Revision Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Revision Questions Pdf Common Exam Questions in Biology Paper 1 Common Exam Questions in Biology Paper 2 Common Test Questions in Biology Paper 1 Common Tested Questions in Biology Paper 1 Commonly Tested Questions in Biology Paper 1 K.c.s.e.Biology Questions and Answers KCSE 2019 Biology Paper 1 Marking Scheme KCSE 2019 Biology Paper 2 KCSE 2019 Biology Paper 2 Marking Scheme KCSE 2020 Prediction Questions and Answers KCSE Biology Paper 1 2019 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2016 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2017 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2018 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2019 KCSE Biology Questions and Answers Most Tested Questions in Biology Paper 1 Most Tested Questions in Biology Paper 2 Mostly Tested Questions in Biology Paper 1 Mostly Tested Questions in Biology Paper 2 Biology Form 4 Biology Revision Questions Form 1 Combined Science Notes Form 1 Form 4 Notes High Flyer Series Biology Form 1-4 Kcse Past Papers Biology With Answers Biology Notes Download Secondary Biology Notes Pdf Water and Hydrogen Form 1 Notes High Flyer Series KCSE Revision in Biology High Flyer Series KCSE Revision Biology Form 1-4 Revised A Level Biology Notes Uganda Pdf Download Buddo Junior School Holiday Work Biology Notes for a Level Pdf Biology Notes Form 1 Biology Notes Form 3 the Mole Biology Notes Form 4 Biology Notes O Level Biology Notes O Level Uganda Biology Notes O Level Uganda Pdf Biology Notes Pdf Download Biology Notes Form 3 Biology Notes Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers Form Three Biology Syllabus Pdf Gayaza High School Biology Notes Gayaza High School Biology Notes Pdf Gayaza High School Biology Past Papers Gayaza High School Biology Past Papers Answers Gayaza High School Biology Past Papers Questions and Answers Gayaza High School E Learning Gayaza High School Elearning Platform Gayaza High School Examinations Gayaza High School Holiday Work Gayaza High School Notes Gayaza High School Notes 2021 Gayaza High School Notes 2022 Gayaza High School Notes 2025 Gayaza High School Notes 2026 Gayaza High School Notes Pdf Gayaza Junior School E Learning Platform Gayaza Junior School Holiday Work Gayaza O Level Biology Notes Home › Gayaza High School | Elearning Platform Kabojja Junior School Holiday Work Pdf Klb Biology Book 3 Klb Biology Form 3 Teachers Guide Klb Biology Notes List of Ugandan E-learning Platforms for Students Mirembe Junior School Holiday Work Ntare School Past Papers O Level Biology Notes Free Download O Level Biology Notes in Uganda O Level Biology Notes Pdf O Level Biology Notes Uganda Pdf O Level Biology Notes Uganda Pdf Download O Level General - Home › Gayaza High School | Elearning S.1 Biology Notes | Standard High School Zzana S.3 Biology Notes S.4 Biology 2 Notes | Standard High School Zzana Seeta High School Elearning Seeta High School Holiday Work Seeta High School Notes Seeta High School Notes Pdf Seeta High School Past Papers Seeta High School Past Papers Pdf Senior 1 Biology Notes Senior 1 Biology Notes in Uganda Senior 1 Biology Notes Uganda Senior 1 Biology Questions Senior 1 Exams Senior 1 Work Senior 1 Work 2020 Senior 1 Work 2020 Uganda Senior 2 Biology Notes Senior 2 Biology Notes in Uganda Senior 2 Biology Notes Uganda Senior 2 Biology Questions Senior 2 Exams Senior 2 Work Senior 2 Work 2020 Senior 2 Work 2020 Uganda Senior 3 Biology Notes Senior 3 Biology Notes in Uganda Senior 3 Biology Notes Uganda Senior 3 Biology Questions Senior 3 Exams Senior 3 Work Senior 3 Work 2020 Senior 3 Work 2020 Uganda Senior 4 Biology Notes Senior 4 Biology Notes in Uganda Senior 4 Biology Notes Uganda Senior 4 Biology Questions Senior 4 Exams Senior 4 Work Senior 4 Work 2020 Senior 4 Work 2020 Uganda Senior Four Biology Notes Senior Four Biology Notes in Uganda Senior Four Biology Notes Uganda Senior Four Biology Questions Senior Four Exams Senior Four Work Senior Four Work 2020 Senior Four Work 2020 Uganda Senior One Biology Notes Senior One Biology Notes in Uganda Senior One Biology Notes Uganda Senior One Biology Questions Senior One Exams Senior One Work Senior One Work 2020 Senior One Work 2020 Uganda Senior Three Biology Notes Senior Three Biology Notes in Uganda Senior Three Biology Notes Uganda Senior Three Biology Questions Senior Three Exams Senior Three Work Senior Three Work 2020 Senior Three Work 2020 Uganda Senior Two Biology Notes Senior Two Biology Notes in Uganda Senior Two Biology Notes Pdf Senior Two Biology Notes Uganda Senior Two Biology Questions Senior Two Exams Senior Two Work Senior Two Work 2020 Senior Two Work 2020 Uganda St Mary's Kitende E Learning Standard High School Notes Standard High School Zana a Level Notes Standard High School Zana Com Notes Standard High School Zana E Learning Standard High School Zana E Learning Platform Standard High School Zana E-learning Platform Standard High School Zana Notes for Senior Two Standard High School Zana Notes Pdf Standard High School Zana Website Standard High Zana Notes Uace Biology Notes Uace Biology Notes Pdf Uce Biology Notes Pdf Uce Biology Notes Pdf Download Uce Past Papers Uganda Secondary Schools E-learning Platform Uneb Marking Guides Pdf Uneb Past Papers and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3 Notes on Ecology Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Notes Form 3 Classification Biology Notes Form 3 Growth and Development Biology Notes Form 3 Pdf Free Download Ecology Notes Ecology Revision Questions and Notes Form 3 Biology Notes on Reproduction Klb Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Download Before You Start Writing the Exam | Kcpe-kcse Kcse 2019 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Kcse 2020 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Kcse 2020 Leakage Biology Questions Kcse 2020 Prediction Questions and Answers Kcse 2021 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Kcse 2021 Leakage Biology Questions Kcse 2021 Prediction Questions and Answers Kcse 2022 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Kcse 2025 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Kcse 2025 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Kcse 2025 Leakage Biology Questions Kcse 2026 Leakage Biology Questions Kcse 2025 Prediction Questions and Answers Kcse 2026 Prediction Questions and Answers Kcse 2025 Prediction Questions and Answers Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Kcse Biology Past Papers and Answers Kcse Past Papers and Answers Biology Kcse Past Papers Kcse Prediction Questions Tips to Passing Kcse Examinations » Kcse Revision What to Watch Out for When Answering Questions in Kcse Which Questions Always Must Appear on Kcse Paper? Which Questions Always Must Appear on Kcse Papers? Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Download Biology Notes Form 1-4 Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 1 Biology Topical Questions Form 1 Biology Exam Paper With Answer Pdf Form 1 Exams 2020 Form 1 Biology Past Papers Form 1 Biology Revision Papers With Answers Sample Biology Test for Form One Exams Ntare School Past Papers Seeta High School Notes Pdf Seeta High School Past Papers Seeta High School Past Papers Pdf St Mary's Kitende Past Papers Uce Biology Notes Pdf Uce Past Papers Uneb Marking Guides Pdf Uneb Past Papers and Answers Pdf Biology Book 3 Download Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Biology Form 3 Syllabus Biology Form 3 Topics Biology Notes Form 3 Biology Notes Form 3 Coordination Biology Notes Form 3 Reproduction Biology Notes Form Three Biology Notes Pdf Download Form 3 Biology Exam Form 3 Biology Notes on Reproduction Pdf Revision Biology Revision a Level Biology Revision Notes - Biology S.1-biology-notes S.1-biology-notes Uganda S.2-biology-notes S.2-biology-notes Uganda S.3-biology-notes S.3-biology-notes Uganda S.4-biology-notes S.4-biology-notes Uganda S.5-biology-notes S.5-biology-notes Uganda S.6-biology-notes S.6-biology-notes Uganda S1 Biology Notes Term 1 S1 Biology Notes Term 2 S1 Biology Notes Term 3 S2 Biology Notes Term 1 S2 Biology Notes Term 2 S2 Biology Notes Term 3 S3 Biology Notes Term 1 S3 Biology Notes Term 2 S3 Biology Notes Term 3 S4 Biology Notes Term 1 S4 Biology Notes Term 2 S4 Biology Notes Term 3 Senior 3 Biology Notes Senior 3 Biology Notes Uganda Senior Three Biology Notes Senior Three Biology Notes Uganda Biology Form 1 the Cell Biology Form One Notes Free – Education News Biology Notes Form 1-4 Biology Questions and Answers Form 1 - Biology Form One Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 - Biology Form Two Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 - Biology Form Three Biology Questions and Answers Form 4 - Biology Form Four Biology Questions and Answers Senior 1 - Biology Senior One Biology Questions and Answers Senior 2 - Biology Senior Two Biology Questions and Answers Senior 3 - Biology Senior Three Biology Questions and Answers Senior 4 - Biology Senior Four Biology Topic by Topic Questions and Answers Combined Science Notes Form 1 Form 1 Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 1 Biology Topical Questions Form 1 Revision Papers With Answers Form 2 Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Four Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form One Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Three Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Two Biology Revision Questions and Answers Free Biology Form 1 Notes Free Biology Notes Introduction to Biology Form One Kcse Past Papers: Biology Form 1 Kcse Past Papers: Biology Form 1 Topical Questions Kcse Past Papers: Biology Form 1 Topical Questions and Answers Most Tested Areas in Biology Kcse Most Tested Areas in Biology Kcse Exams Most Tested Areas in Biology Uneb Most Tested Areas in Form 1 in Biology Most Tested Areas in Form 2 in Biology Most Tested Areas in Form 3 in Biology Most Tested Areas in Form 4 in Biology Most Tested Areas in Form Four in Biology Most Tested Areas in Form One in Biology Most Tested Areas in Form Three in Biology Most Tested Areas in Form Two in Biology Most Tested Areas in Kcse Biology Most Tested Areas in Kcse Biology Exams Most Tested Areas in Senior 1 in Biology Most Tested Areas in Senior 2 in Biology Most Tested Areas in Senior 3 in Biology Most Tested Areas in Senior 4 in Biology Most Tested Areas in Senior Four in Biology Most Tested Areas in Senior One in Biology Most Tested Areas in Senior Three in Biology Most Tested Areas in Senior Two in Biology Most Tested Areas in Uneb Biology Revision Notes Biology Form 1 - Free Kcse Past Papers Who Was Biology Champion KCSE 2019 Top 100 Students in Biology KCSE 2019 Best 100 Students in Biology KCSE 2019 Top Student in Biology KCSE Best Student in Biology KCSE Who Was Biology Champion KCSE 2020 Top 100 Students in Biology KCSE 2020 Best 100 Students in Biology KCSE 2020 Names of Best Biology Students KCSE Names of Top Biology Students KCSE Scheme of work for IGCSC Biology Form 3 to 4 for Botswana Biology Questions on Human Diseases Form Three Biology Form 3 Notes Kcse Made Familiar Biology Pdf Download Find Kcse Made Familiar Biology Pdf Download Find Kcse Made Familiar Biology Pdf Download Here! Summary of Biology Form 1 Popular Questions in Biology Form 2 Kcse Revision Biology Paper Form One Biology Questions and Answers A Level Biology Revision Notes Pdf Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Two Notes Pdf Download
Scholarship 2026/27
Current Scholarships 2026/2027 - Fully Funded
Full Undergraduate Scholarships 2026 - 2027
Fully Funded Masters Scholarships 2026 - 27
PhD Scholarships for International Students - Fully Funded!
Funding Opportunities for Journalists 2026/2027
Funding for Entrepreneurs 2026/2027
***
