Agriculture Notes - Part 3/ Form 3 Agriculture Notes
Click Here - Free KCSE Past Papers » KNEC Past Exams » Free Downloads » KCSE Papers & Marking Schemes
Agriculture
Form 3
Notes
Livestock Production III
(Selection and Breeding)
Introduction
The performance of an animal is influenced by two major factors;
◦ Feeding,
◦ Health,
◦ Care
◦ The ecological conditions.
Reproduction and Reproductive Systems
Reproduction in Cattle
Reproductive system of a bull
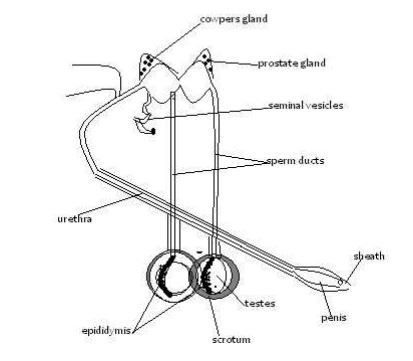
> There are two testes hanging loosely between hind legs.
> Enclosed by loose skin (scrotum)scrotum regulate temperature of testis for optimum production of sperms.
> Produce spermatozoa(sperms)which are stored in coiled tube called epididymis
> Conveys sperm from the testis and urine through the penis.
> sphincter muscles contract to allow each to pass separetly.
> Surrounded by a sheath which is an extension of skin.
> It introduces sperms into the vagina of a cow through the vulva during mating
> It is a copulatory organ, also used for urination.
Reproductive system of a cow
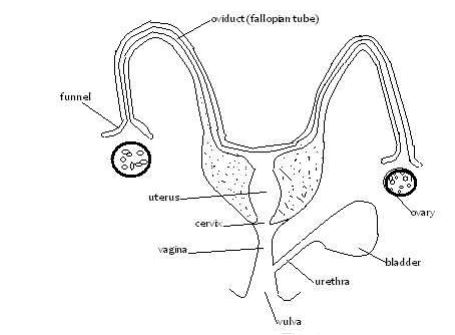
Ovaries and fallopian tubes(oviduct)
Fallopian tubes:
The uterus:
The cervix: Closes the uterus.
The vagina and Vulva:
Pregnancy
Parturition(giving birth)
When an animal is about to give birth, it shows sign;
> Distended udder which produces thick milky fluid called colostrums.
> Swollen vulva producing thick mucus.
> Loose and slackened pelvic girdle.
> Visible pin bones.
> General restlessness.
Reproduction in Poultry
The Reproductive System of a Hen
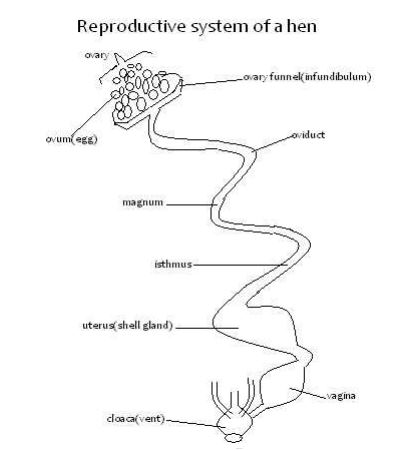
Ovary
Funnel(infundibulum)
Magnum
Isthmus
Uterus(shell gland)
Vagina
Cloaca
NB;
Selection of a Breeding Stock
The degree to which selection affects a character depends on the following factors;
Factors To Consider When Selecting A Breeding Stock.
> Young animals,
> Those that have not parturated for more than 3-times, should be selected.
> They have a longer productive life.
> Old animals are poor breeders and low producers.
> Production and breeding efficiency decline with age.
> Animals with highest production level selected.
> Performance best indicated by records.
Good performance of animal indicated by;
> High milk, wool and egg production
> Good mothering ability
> High prepotency which is the ability of a parent to pass good qualities to their offsprings.
> The animals with poor performance should be culled.
> Good records kept and used by the farmer for this purpose.
Animals selected should be free from any physical defect
e.g.
> mono-eyed,
> limping,
> irregular number of teats,
> scrotal hernia,
> defective and weak backline
> Sick animals do not breed well and are expensive to keep.
> Animals that are resistant to diseases pass these characteristics to their offsprings
> Animals for breeding to be selected according to proper body conformation.
> A dairy cow should be wedge-shaped with a large udder, thin legs, long neck.
> Animals with bad behaviors should be culled.eg
> Cannibalism, egg eating, aggressiveness, kicking
> Select animals that give products of high quality.
> Animals selected should have a good mothering ability,
> That is animals with good natural instinct towards their young ones.
> This will enable them to rear the young ones up to weaning.
> Animals selected should be well adapted to the prevailing climatic condition in the area.
> Animals selected should be highly prolific.
> That is, animals with the ability to give birth to many offsprings at a time(larger litter).
> This is a quality that should be considered when selecting pigs and rabbits.
Selection in cattle, and sheep,
Selection in cattle
Consider the following;
> Milk Yield Buter Content.
> Length Of Lactation Period.
> Calving Intervals.
Selection in sheep
Consider the following;
> Mothering ability
> Growth rate
> Wool quality
> Carcass quality
> Twining rate
Selection in Goats
Consider the following:
Selection in Camels
Method of Selection
These include:
Breeding
Reasons:
Terms Used in Breeding inheritance
Dominant and Recessive Characteristics
Hybrid and Hybrid Vigour
Epistasis
Breeding Systems
Inbreeding
Limitations
Systems of Inbreeding
Reasons:
Limitations
Systems of Outbreeding
Mating of animals from two different pure breeds.
Mating of unrelated animals from the same breed.
Mating where the female of a cow grade stock (locals) is mated with a pure breed sire. The resultant animal is referred to as a high grade.
Mating in Livestock
Mating in Cattle
Heat Signs
Mating in Pigs
Signs of Heat
Mating in Rabbits
Methods of Service in Livestock
Natural Mating
Advantages:
Advantages
Disadvantages
Embryo Transplant
Advantages
Disadvantages
Parturition in Cattle
Signs of Parturition
Parturition in Pigs
Signs of Parturition
Signs of Parturition
Livestock Production IV
(Livestock Rearing Practice)
Introduction
Feeding Practice
These include:
Flushing
Importance of Flushing
Steaming Up
Importance Steaming Up
Creep Feeding
Piglets
Lambs
Kids
Vaccination
Administration of Vaccination done through:
Deworming
Hoof Trimming
importance
Docking /tailing
importance
Methods of Docking /tailing
Dipping and Spraying
Dusting
Breeding Practices
> Crutching - cutting of wool around the external reproductive organs of female sheep.
> Ringing - trimming wool around the sheath of the penis of the rams to facilitate mating.
Tupping and Serving
> Tupping refers to mating in sheep and goats.
> Sen/ing refers to mating in cattle and pigs.
> This is the practice of fitting the rams with breeding chutes which are painted in different colours during mating
> to identify mated ewes and to indicate the active rams hence help in culling of the weak rams.
Identification
Importance purpose of Identification
> record keeping
> Setting disputes in case animals get mixed up in the pasture.
Debeaking
Importance
Tooth Clipping
Dehorning
Importance
Shearing
Castration
Importance
Methods Used:
> involves use of burdizzo or rubber ring and elastrator.
> Animals do not bleed but may not be 100% effective.
>A surgical method used for castrating cocks, piglets and rabbits whose testes are internal.
> Also used for lambs, kids and calves.
> Animals bleed a lot.
> However, it is 100% effective.
> It is not recommended for mature adults.
It is the practice of making male birds lose their male characteristics by use of hormones.
> Hormones used include stilboestrol which is injected into the birds when they are one day old and female hormones implanted beneath the skin at the neck.
> Birds which have lost their male characteristics in this way are referred to as capons.
Management During Parturition
Parturition in Cattle
Parturition in Sheep
Parturition in Goats
Parturition in Pigs
Signs of Farrowing
After the signs are seen;
Parturition in Rabbits
Signs of Parturition
Bee Keeping (Apiculture)
Bees are insects which live in very well organised colonies.
Each colony consists of:
Duties of Workers
Importance of Bees
Routine Management
Siting/locating of an Apiary
Factors to consider;
Feeding
Parasites
Control of Parasites
Diseases and Control
Harvesting Honey
Factors to consider;
Procedure
Honey Processing
Precautions When Handling Bees
Fish Keeping (Aquaculture)
introduction
A good fish-pond should have the following features:
Construction should provide for:
Feeding Fish
Management Practices to Ensure Maximum Harvest of Fish
Harvesting Fish
Two main methods:
Hook-and-line method:
> This is slow, injures small fish and is inefficient.
> It is only suitable for small-scale fishing.
Use of fishing nets:
> This is the most efficient method as long as a net with the correct mesh sizes is used.
> Harvesting may be done 6-8 months after the introduction of fingerlings into the fish pond.
Maintenance of the Fish Pond
Fish Preservation
Practices before preservation:
Methods of Preservation
Appropriate Handling of Livestock During Management
Farm Structures
Introduction
Construction of Farm Structures
Involves:
Planning for farm structures ;
Consider;
Siting farm structures;
Consider:
Materials for Construction
Structural Materials and Use
Factors which determine the type of materials to use are;
Advantages
Disadvantages
These include;
Advantages
Disadvantages
Advantages
Disadvantages
Concrete
Uses
Advantages
These materials are;
Disadvantages
These materials are;
Animal handling structures
Spraying livestock to control ticks,
milking,
examining sick animals,
> artificial insemination,
> treating animals, eg drenching, vaccination,
> dong routine jobs such as dehorning, identification marks,
Farm Buildings
Factors to be considered in site selection;
Types of farm buildings
Parts of a building
Parts of a Roof
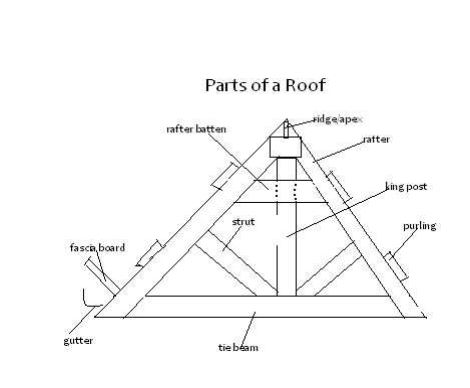
Include;
parts of a wall
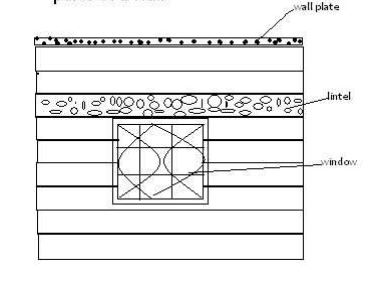
Pants of the foundation
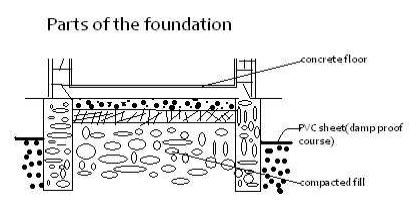
Include;
Fences
Types
Fencing Practice
>wires,
>staples,
>nails,
>posts,
>droppers
>concrete materials.
> General purpose 2.5m by 25cm in diameter
> Strainer units and corner posts 3m by 30cm in diameter:
3m between posts, 10m if droppers are to be used.
> zoom between strainer units.
Gate Posts, Gates and Strainer Units
Steps in Fencing
Agricultural Economics ll (Land Tenure and Land Reforms)
Introduction
Land Tenure
Land Tenure System
Collective Tenure Systems
This includes:
Communal Tenure Systems
Advantages of Communal Tenure
Disadvantages of Communal Tenure
> controlled breeding,
proper feeding,
> disease and parasite control.
Co-operative Tenure System
Advantages of Co-operative Tenure
Disadvantages of co-operative tenure.
State ownership
Examples in Kenya;
Advantages of state ownership
Disadvantages
individual Tenure system
The various forms of individual land tenure are;
Owner operator
Advantages
Disadvantages
Plantation and concession
Advantages
Disadvantages
Landlordism and tenancy
Advantages
Disadvantages
Land Reforms
Definition
Forms of Land Reform
Land Consolidation
The objective of land consolidation are :
Land Fragmentation and Sub-division
> To sell part of the land.
> The parent may wish to subdivide and distribute his land among the sons, daughters and other dependants.
> The government may decide to subdivide large farms in order to settle landless citizens.
Land Adjudication and Registration
> Establishing the legitimate ownership,
> Measurements (to make permanent boundaries)
> Recording of land details.
Importance of land title deed
Land Settlement and Resettlement
Definition
Objectives
Soil and Water Conservation
Introduction
Soil Erosion
Factors Influencing Soil Erosion
> The steeper the land the higher the velocity of surface runoff.
> The higher the velocity of surface runoff the greater is its erosive power/effect.
> The deeper the soil, the longer it takes to be saturated with water.
> Overstocking leads to bareness of the land and looseness of the soil.
> Deforestation - indiscriminate removal of trees leads to exposure of soil to > heavy rainfall and high temperatures.
> indiscriminate burning of vegetation exposes the soil to erosive agents.
> Clean weeding leaves the soil bare.
> Ploughing along the slope.
> Monoculture or continuous cultivation.
> Trees act as windbreakers.
> Roots of vegetation cover hold the soil particles together.
> Leaf fall act as mulch which reduces erosion.
> Leaves of vegetation cover intercepts raindrops reducing their erosive power.
Agents of Erosion
Types of Erosion
> Slip movement of earth or rock masses for a short distance.
> Debris slide - materials move at a greater speed.
> Debris fall - movement of materials/debris along vertical cliff.
> Rock fall - movement of rock down a very steep slope.
> Rock slides - mass of rock materials that slide along a bedding plate, a joint or a fault face.
Soil Erosion Control Measures
Soil conservation measures can be classified into:
Biological or Cultural Control Measures
These measures are applicable where land slope is between 2-12%.
> These are narrow uncultivated strips along the contour left between cultivated strips.
> The establishment of a crop that spreads out over the surface of the soil to provide it with a cover.
> Carrying out all land operations along the contour.
> Covering of the soil with either organic or synthetic materials.
Proper cropping systems such as:
> Crop rotation
> Correct spacing
> Inter-cropping
> Ridging/furrowing
> Strip cropping
> Proper stocking rate, rotational grazing.
> Growing crops which give little ground cover in alternate strips with crops such as beans which have a good ground cover.
> Afforestation ~ growing of trees where non-existed.
> Re-afforestation - growing of trees where they have been cut down.
> Agroforestry - land use that involves the growing of trees in combination with crops and pastures on the same piece of land.
Physical or Structural Control Measures
They include:
> It involves the growing of an open crop in the upper side of the slope followed by a dense crop to reduce speed of water.
This increases infiltration.
> Are structures constructed across a slope to reduce the length of a slope thus reducing run-off.
> Are constructed where the slope is 35-55%.
> Tree crops are suitable for such areas.
Importance of a Bench Terrace:
> Reduces slope of the land.
> Conserves soil moisture.
> Better retention of soil fertility.
> Have a drainage channel to lead off excess water to a vegetated place.
> They should be about 100m in length.
> Have no outlet channels,
> The aim is to have water infiltrating,
> Hence no water can flow from the ends of the terrace.
> A ridge made by digging a channel and throwing the soil uphill.
> An open trench with an embankment on the lower side into which water from the farm drains.
Water from the trench should be discharged into;
> Natural waterways,
> Artificial waterways,
> Rocky ground
> Grassland
> Galvanized wire mesh boxes filled with stones which are built across slopes and gullies.
> Dams - barriers built across ariver/waterway to hold and store water. It reduces speed of runoff.
> Reservoirs - these are large storage tanks.
They retain the water for some time.
Water Harvesting Methods
This should be done using the following methods:
>Dam - a barrier constructed across a river or a dry valley so that it can hold water. >Weirs - barriers constructed across a river or a stream to raise the water level and still allow water to flow over it.
Micro-Catchments
Types of Microcatchments;
> V-shaped bunds measuring 25cm
> Are built with soil from the excavated planting holes to direct runoff water towards the basin area around the base of each plant
> Formed around the growing plant to hold water around the plant.
> Trapezoidal shaped bunds, which enclose a large area where the crops are grown.
> These are furrows made along the contours between the rows of crops where agroforestry trees are intercropped with annual crops.
> These are extra large planting holes made and filled with dry plant materials before filling in with soil.
Use of Micro-Catchments
Weeds and Weed Control
Introduction
Definition:
Harmful Effects of Weeds
> Mexican marigold gives undesirable flavour to milk if dairy cows feed on it.
> Devils horsewhip, black jack, bristly fox-tail and others get attached to sheep
> Thorn apple (Datura stramonium)
> Sodom apple (Solanum incanum)
> Wild oat (avena fatua) is an alternate host for rusts.
> Mallow (malva verticillata) is an alternate host for cotton stainers.
> Tickberry (Lantana camara)
> Nut grass (Cyperus rotundus),
> Manyatta grass (Eleusine jaegeri)
> Double thorn (Oxygonum sinuatum),
> Stinging nettle (Urtica massaica) ,
> Devil's horse whip (Achyranthes aspera).
Factors Contributing to the Competitive Ability of Weeds
Weed Classification
it is based on:
Life cycles for example:
> Annuals - complete their life cycle in only one season.
> Biennuals - complete their life cycles in two seasons only.
> Perennials - complete their life cycle in more than two seasons.
Morphology - leaf formation such as size, shape and venation.
> Broad leaved weeds for example black jack, lantana, pig weed, oxalis and others.
> Narrow leaved weeds for example couch grass, setaria, nut-grass, manyatta grass and others.
Habitat - some weeds are terrestrial (grow on land) while others are aquatic (grow on aquatic/marine conditions).
Weed Identification
Common Name .....Botanical Name
Weed Control Methods
The methods of weed control determined by:
Methods of weed control include:
Chemical Weed Control-
Classification of Herbicides
Based on:
> Liquids
> Wettable powders
> Emulsion
> Dust
> Pre-emergence - applied before the planted crop germinates.
> Post emergence - applied after the planted crop germinates.
> Selective.
> Non selective.
> Contact - herbicides that kill only the parts of the plant which it comes into contact.
> Translocated systemic herbicides that will kill the whole plant even if it comes into contact with only a small part of it.
Methods of Herbicide Application
Safety Measures in the Use of Chemicals
Advantages of Chemical Weed Control
Disadvantages of Chemical Weed Control
Mechanical Weed Control
Advantages
Disadvantages
Slashing/Mowing
Uprooting
Cultural Weed Control
It involves the following practices:
Biological Weed Control
Examples are:
Legislative Weed Control] Quarantine
Limitations: Only samples are checked while the bulk of the materials may have some weed seeds.
Crop Pests and Diseases
Introduction
> Identify these organisms,
> Know their life cycles, feeding habits
Crop Pests
Definition of a Pest:
Classification of Pests
Pests are classified according to the following:
> Pests with biting and chewing mouth parts - they cause physical damage and reduce the photosynthetic area of the plant.
> Pests with piercing and sucking mouth parts - they suck out the nutritious plant sap and in the process may introduce disease causing organisms.
> Some crop pests attack specific crops for example, stem borers prefer cereal crops.
> There are pests of seedlings attack when the crop is young, for example cutworms.
> Pests of fruits - attack the crops at fruiting stage.
> Pests of grains attack the crops when the grains are formed.
Field and Storage Pests
> Some pests attack the crops while in the field.
> Other pests attack the produce after it has been harvested and stored.
Identification of Common Pests
imagetable44
Harmful Effects of Crop Pests
Control of Pests
Before any control measure is effected ,the following should be considered:
Methods of Controlling the Pests
Cultural Methods:
These include:
Chemical Control
Classification of Pesticides:
Pesticides are classified on the basis of:
Mode of Entry
Mode of Action
Target Pests
Formulation .
Factors That Affect the Efficiency of Pesticides
Advantages of Chemical Pest Control
Disadvantages of Chemical Pest Control
Mechanical Pest Control/Physical
Example:
Biological Pest Control
Advantages
Disadvantages
Integrated Pest Management
Legislative Method/Quarantine
Crop Disease And Their Control
Economic importance of crop diseases
Classification and identification of plant disease
Fungal diseases;
Parasitic fungi divided into;
Examples of fungal disease
Examples of fungal disease
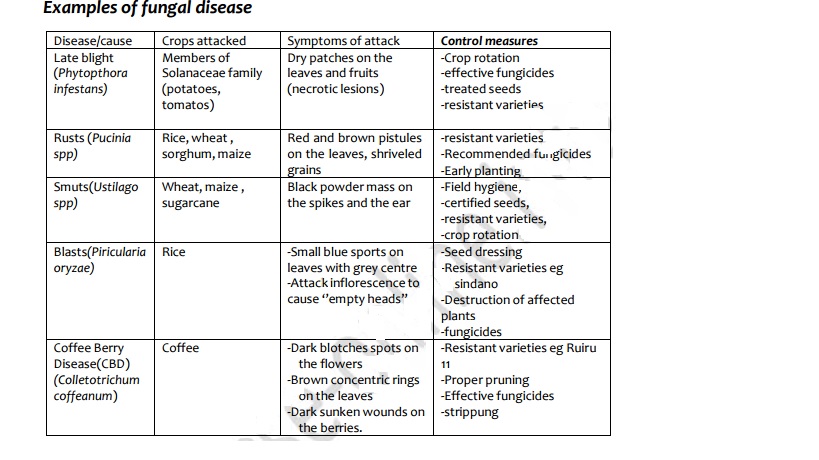
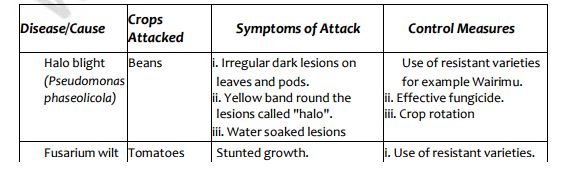
Bacterial Diseases
Symptoms of Bacterial Diseases
Examples of bacterial diseases

Viral Diseases
Symptoms of Viral infection
Transmission
Viral diseases
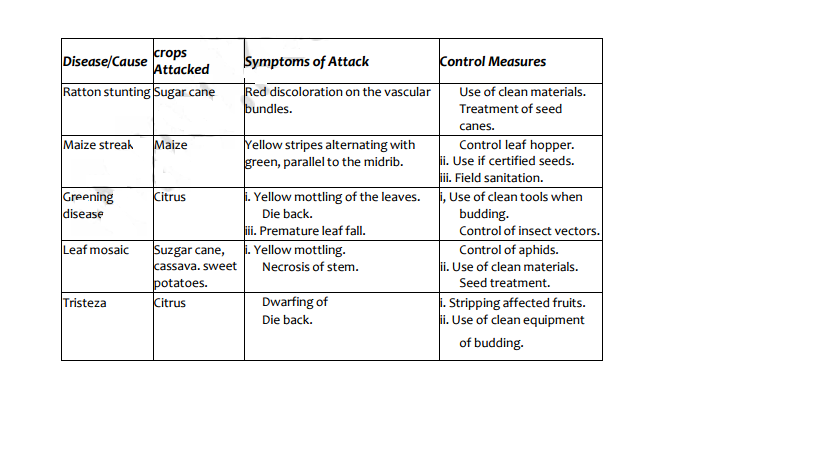
Other Causes of Crop Diseases
Control of Crop Diseases
Legislative Method
Chemical Control
Crop Production VI
(Field Practices ll)
Introduction
There are many crops cultivated in Kenya.
These crops are grown for various uses and require different ecological conditions.
Definitions:
Hybrids —These are crop varieties developed by crossing two pure lines.
Composites - These are crop varieties developed through repeated mass selection.
Cultivars - these are varieties of crops which are cultivated in a given area.
Maize
Main growing areas: Trans-Nzoia, Nakuru, Uasin Gishu, Laikipia districts and others.
> Altitude: Upto 2ooom above sea level.
> Temperature: About 25°C
> Soils: Freely draining, fertile loam soils.
> Rainfall: 750-1250 mm critical at silking and pollination stage.
> High altitude areas: Hybrids 611, 613 and 614C.
> Medium altitude areas: 511,512,622 and 632.
> Marginal rainfall areas: Katumani composite and Makueni composite.
> Coast regions: Coast composite and Katumani composite.
Pest Control
Maize Stalk Borer:
> Nature of damage: Boring the leaves causing windowing effect, boring the stems and cobs.
> Control: Destruction of previous years crop residue, closed season and apply chemicals
Maize Weevils:
> it is a storage pest.
> Damage: Bores holes into the maize grains, eating the contents.
Control: Proper hygiene and sanitation in the stores.
Use of chemicals such as Actellic Super.
Disease Control:
> Cause: Fungus.
> Symptoms: Red or brown pustules on the. leaves.
> Control: Plant resistant varieties and crop rotation.
> Cause: Fungus
> Symptoms: Black sooty mass of spores on maize heads or cobs(ear).
> Control: Crop rotation, growing resistant varieties and destruction of affected plant parts.
> Cause: Virus
> Symptoms: Yellow longitudinal stripes parallel to the midrib.
> Control: Certified seed, early planting and rogueing.
Harvesting
Bulrush Millet
Areas where grown:
Ecological Requirements
Seed Bed Preparations
Planting:
Field Maintenance:
Pest Control
Birds
Disease Control
Ergot
Downy Mildew
Harvesting
Finger Millet
Ecological Requirements
Varieties:
Land Preparations
Field Operations
Planting
Fertilizer Application
Weed Control
Pest Control:
Disease Control
Head blast:
Harvesting
Sorghum
Ecological Requirements
Varieties
Field Operations
Planting
Fertilizer Application
Pest Control
Bird pests: They are the most common sorghum pests.
They include:
They are controlled through;
Disease Control
Common sorghum diseases include:
Smuts are controlled by seed dressing-while the other diseases are controlled by growing resistant varieties.
Harvesting
Beans
Ecological Requirements
Varieties
Varieties for dry beans:
Variety for canning: Mexican 142.
Varieties for French Beans:
Seedbed Preparation
Seed Selection and Treatment
Planting
Field Maintenance
PestControl
Bean-Fly
> Nature of damage: Feeds on the stems causing swelling at the roots.
> This results in wilting and death.
> Control: Dressing of seeds, early planting and spraying with insecticides.
Bean Bruchid (Storage Pest)
> Nature of damage: Make dark circular windows on the grains.
> Control: Clean stores, fumigation, and seed dressing.
Diseases Control
Bean Anthracnose
> Cause‘ Fungus
> Symptoms: Brown or black lesions on the underside of the leaves, pods and stems.
> Control: Growing resistant varieties, crop rotation, destruction of crop residues and spraying with fungicides.
Bean Rust
> Cause: Fungus
> Symptoms: Red brown pustules on the leaves.
> Control: Planting resistant varieties and spraying copper fungicides.
Harvesting
Rice Production
Areas where grown;
Land Preparation
Water Control
Fertilizer Application
Flooding in Rice
Flood water in rice production is important for the following reasons;
Weed Control
Harvesting of Cotton
Stage of harvesting
Method and Procedure
Precautions
Harvesting of Pyrethrum
Stage of harvesting
Methods and Procedure
Precaution
Harvesting Sugarcane
Stage of harvesting;
Methods and Procedures
Precaution
Harvesting of Coffee
Stage of harvesting;
Methods and Procedures;
Precautions
Harvesting Tea
Stage of harvesting
Method and Procedures
Precautions
Forage Crops
Introduction
Classification of Pastures
> Either pure
> Mixe_d stands.
> Low altitude,
> Medium altitude,
> High_altitude pastures
> Natura
> Artificial pastures.
Examples of grasses
Examples of legumes;
Pasture Establishment
Seedbed Preparation
Selection of [planting materials
Treatment of legume seeds
Planting
Methods of sowing are;
Over sowing
Under sowing
Seeds rate depend;
Pasture management
Fertilization of pastures-done by use of manures and nitrogenous fertilizer.
Pasture Utilization
It is utilized through the following methods:
Common fodder Crops
Edible Cana
Napier Grass
Management:
Types of Napier Grass:
Lucerne
Mangolds
Kales
Guatemala Grass
Leaves and stems used as livestock feed.
Sorghum Grass
Two varieties:
Columbus grass Sudan grass.
Established from seeds which are drilled or broadcasted.
Columbus grass should be dried before feeding to animals to avoid hydrocyanic and prussic acid poisoning.
Desmodium (Desmodium spp)
Two varieties;
Agroforestry, trees used as fodder crops include:
Forage Conservation
Forage can be conserved as;
importance of forage conservation:
Methods
Hay Making
Steps in hay making:
Factors Determining Quality of Hay
Silage Making
Steps in silage making:
Factors Affecting the Quality of Silage
Standing Forage
Livestock Health Ill: (Diseases)
Introduction
Livestock diseases are classified according to causative agents as follows:
Protozoan Diseases
East coast Fever
Symptoms
Control and Prevention
Anaplasmosis (gall sickness)
Animals attacked:
Cause:
Symptoms
Control
Coccidiosis
Symptoms
Control
Trypanosomiasis (Nagana)
Symptoms
Control
Bacterial Diseases
Fowl Typhoid
Symptoms
Control
Foot Rot
Symptoms
Control
Contagious Abortion (Brucellosisl Bang's Disease)
Cause: Bacteria
Symptoms
Control
Scours (white Scours)
Symptoms
Control
Black Quarter
Symptoms
Control
Mastitis
Pre-disposing Factors:
Symptoms
Control
Anthrax
Symptoms
Pneumonia
Cause:
Symptoms
Control
Viral Diseases
Rinderpest
Symptoms
Foot and Mouth Disease
Symptoms
Control
New Castle
Symptoms
Control
FowlPox
Symptoms
Control
Gumboro
Symptoms
Control
African Swine Fever
Symptoms
Control
Nutritional Diseases/Disorders
Causes:
Symptoms
Treatment
Note: The animals suffering from milk fever should not be given medicine orally for the following reasons:
Control
Bloat
Symptoms
Control
KCSE Revision Notes Form 1 - Form 4 All Subjects
Kenya Scholarships for Undergraduate Students » Kenya Scholarships for Postgraduate Students » Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyan Students » Kenya Undergraduate Scholarships » Full Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyans » Kenya Postgraduate Scholarships » Scholarships & Grants » Undergraduate Scholarships » Universities in Kenya » Kenya Universities and Colleges Central Placement Service (KUCCPS) » Colleges in Kenya » KASNEB Registration & Results » Secondary Schools Scholarships in Kenya » Undergraduate & Graduate Scholarships for Kenyans
Scholarships for African Students » Undergraduate Scholarships » African Women Scholarships & Grants » Developing Countries Scholarships » Erasmus Mundus Scholarships for Developing Countries » Fellowship Programs » Funding Grants for NGOs » Government Scholarships » LLM Scholarships » MBA Scholarships » PhD and Masters by Research Scholarships » Public Health Scholarships - MPH Scholarships » Refugees Scholarships » Research Grants » Scholarships and Grants
Scholarships in Australia » Scholarships in Belgium » Scholarships in Canada » Scholarships in Germany » Scholarships in Italy » Scholarships in Japan » Scholarships in Korea » Scholarships in Netherlands » Scholarships in UK » Scholarships in USA
a a well labelled diagram of a mouldboard plough advantages and disadvantages. agriculture book 1 notes agriculture book 2 notes agriculture book 3 notes agriculture book 4 notes agriculture exam questions and answers agriculture form 1 notes pdf agriculture form 1 notes pdf download agriculture form 1 pdf agriculture form 1 question papers agriculture form 1 questions agriculture form 1 questions and answers agriculture form 2 agriculture form 2 notes agriculture form 2 notes pdf agriculture form 2 notes pdf download agriculture form 2 question papers agriculture form 3 notes pdf agriculture form 3 notes pdf download agriculture form 3 question papers agriculture form 4 agriculture form 4 notes agriculture form 4 notes pdf agriculture form 4 notes pdf download agriculture form 4 question papers agriculture form 4 schemes of work agriculture form four notes agriculture form four syllabus agriculture form one agriculture form three agriculture form three notes agriculture form two notes agriculture notes agriculture notes class 10 agriculture notes form 1 agriculture notes form 1 - 4 agriculture notes form 1 -4 agriculture notes form 2 agriculture notes form 3 agriculture notes form 4 agriculture notes form four agriculture notes form one agriculture notes form three agriculture notes form two agriculture notes on agroforestry agriculture notes: primary tillage - objectives, mould board plough , disc plough, agriculture pdf download agriculture questions and answers form 2 agroforestry examples agroforestry lecture notes pdf agroforestry pdf basic agriculture books pdf basic agriculture pdf benefits of agroforestry biology form 2 notes biology form 3 notes pdf business studies form 3 notes pdf chemistry form 2 questions and answers pdf chisel plough, subsoiler , components and functions, types, classification of agroforestry systems+pdf cre form two notes pdf diagram of mouldboard plough difference between mould board and disc plow disc plough pdf disc plough wikipedia download geography form 3 notes downloads | agriculture | form four exams | exams downloads | agriculture | form one exams | exams downloads | agriculture | form three exams | exams downloads | agriculture | form two exams | exams draw and label a disc plough form 1 revision papers form 2 agriculture notes pdf form 2 agriculture syllabus form 2 english exam paper with answer form 2 geography notes pdf form 2 mathematics exam paper 2016 form 2 revision papers form 3 agriculture notes form 3 notes of agriculture topic on fish form 3 revision papers form 4 agriculture notes form 4 revision papers form four notes form one agriculture questions form one agriculture syllabus form three agriculture syllabus form two agriculture notes form two chemistry questions and answers free form1,form2,form3 past papers - free kcse past papers functions of disc plough functions of parts of disc plough general agriculture notes pdf geography form 3 notes pdf handbook of agriculture pdf free download history form two notes pdf how do trees help soil? how to pass agriculture questions & answers form 1&2 | text book importance of agroforestry introduction to agriculture notes introduction to agriculture pdf iron plough is agroforestry sustainable? k.l.b agriculture form 3 kcse agriculture notes kcse agriculture notes, syllabus, questions, answers kcse chemistry revision notes klb agriculture book 1 notes klb agriculture book 2 notes klb agriculture book 2 pdf klb agriculture book 3 pdf klb agriculture book 4 pdf klb agriculture form 1 klb agriculture form 2 klb agriculture form 3 klb agriculture form two klb geography form 3 kusoma chemistry notes kusoma notes geography labelled diagram of a disc plough mould board plough mouldboard plough diagram mouldboard plough parts mouldboard plough parts and their functions mouldboard plough parts and their functions pdf mouldboard plough uses mouldboard plough wikipedia parts of a disc plough and their functions parts of a disc plough and their functions pdf parts of a mouldboard plough and their functions parts of disc plough and their function physics form 2 pdf primary and secondary tillage implements ppt secondary agriculture notes share: this makes the horizontal cut and starts the turning of the furrow slices. types of a plough types of agroforestry types of mould board plough vertical suction of mb plough well labelled diagram of disc plough what are agroforestry practices? what are forest crops? what are silvicultural treatments? what are the benefits of agroforestry? what are the functions of disc plough what are the importance of silviculture? what are the types of agroforestry? what are the types of forestry? what does a silviculturist do? what does urban forestry mean? what is a food forest garden? what is agriculture and forestry? what is agrisilviculture? what is agroforestry system what is agroforestry technology? what is alley cropping system? what is community forest management? what is forest soil? what is indirect deforestation? what is rural forestry? what is selective logging? what is silviculture and its advantages? what is silvopastoral system? what is social forestry and agroforestry? what is the agroforestry? what is the concept of agroforestry? what is the meaning of forest reserve? which trees are found in social forestry? wooden plough www.kusoma notes
"Pdf" Revision Questions Agriculture Form 2 "Pdf" Revision Questions Agriculture Form 3 "Pdf" Revision Questions Agriculture Form 4 "Pdf" Revision Questions Agriculture Form Four "Pdf" Revision Questions Agriculture Form One "Pdf" Revision Questions Agriculture Form Three "Pdf" Revision Questions Agriculture Form Two 1 a a KCSE Past Papers 10th Grade Agriculture Questions and Answers 10th Grade Agriculture Test 11th Ncert Agriculture 12th Class Agriculture Book Free Download 2014 KCSE Marking Schemes 2014 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2015 2015 Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 2016 KCSE Papers 2016 KCSE Prediction Questions 2017 Agriculture Hsc Answers 2017 KCSE Prediction Questions 2018 Agriculture KCSE Leakage 2018 Agriculture KCSE Questions 2018 KCSE Busineness Studies 2018 KCSE Exam 2018 KCSE Leakage 2018 KCSE Prediction Questions 2018 KCSE Questions 2019 Agriculture KCSE Leakage 2019 Agriculture KCSE Questions 2019 KCSE Leakage 2019 KCSE Questions 9th Grade Agriculture Study Guide A a a Agriculture Notes a a a Agriculture Notes! a a a Agriculture Notes! A a KCSE Past Papers A a Well Labelled Diagram of a Mouldboard Plough A Biblical View of Social Justice A Level Agriculture Biological Molecules Questions A Level Agriculture Exam Questions by Topic A Level Agriculture Notes Edexcel A Level Agriculture Notes Xtremepapers A Level Agriculture Past Papers A Level Agriculture Questions and Answers a Level Agriculture Questions and Answers A Level Agriculture Questions and Answers (Pdf) A Level Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf A Level Agriculture Questions by Topic Kidney Questions With Markschemes A Level Agriculture Revision A Level Agriculture Revision Edexcel A Level Agriculture Revision Guide A Level Agriculture Revision Notes A Level Agriculture Revision Notes Pdf A Level Agriculture Textbook Pdf A Level Agriculture Year 1 / as Aqa Exam Questions by Topic A Level Edexcel Notes a* Agriculture aa Agriculture Form 3 Questions and Answers Advance KCSE Past Papers Advance-africa.com KCSE Rev Quiz Advantages and Disadvantages. Agroforestry Examples Agroforestry Lecture Notes Pdf Agroforestry Pdf All Agriculture Essays All Agriculture Notes for Senior Two All KCSE Past Papers Agriculture With Making Schemes All Marking Schemes Questions and Answers All Past K.c.s.e Questions With Answers Alliance Mocks 2017 Ap Bio Quizzes Ap Agriculture 1 Textbook Pdf Ap Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Are Sourced From KNEC. As Level Agriculture Notes Atika Agriculture Notes Atika School Agriculture Notes B/s Book 2 Notes Basic Agriculture Books Pdf basic Agriculture Interview Questions and Answers Pdf Basic Agriculture Interview Questions and Answers Pdf Basic Agriculture Pdf Basic Agriculture Questions and Answers Basic Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Bbc Bitesize Agriculture Ks3 Benefits of Agroforestry Bihar Board Agriculture Objective Answer 2017 Bihar Board Agriculture Objective Answer 2018 Bio Answers Bio Quesions Agriculture 0478 Agriculture 101 Agriculture 12th Agriculture 12th Class Notes Pdf Agriculture 2019 Syllabus Agriculture All KCSE Short Notes Agriculture Answers Agriculture Answers Online Free Agriculture Answers Quizlet Agriculture Bk 2 Notes Agriculture Book 1 Agriculture Book 1 Notes Agriculture Book 2 Agriculture Book 2 Notes Agriculture Book 3 Agriculture Book 3 KLB Agriculture Book 3 Notes Agriculture Book 4 Agriculture Book 4 Notes Agriculture Book 4 Pdf Agriculture Book for Class 11 Agriculture Book Four Agriculture Book Four Notes Agriculture Book One Agriculture Book One Notes Agriculture Book Pdf Free Download Agriculture Book Three Agriculture Book Three Notes Agriculture Book Three Pdf Agriculture Book Two Agriculture Book Two Notes Agriculture Books Form Three Agriculture Bowl Agriculture Study Guide Agriculture Bowl Questions Agriculture Agriculture Bowl Questions Earth Agriculture Agriculture Bowl Questions Math Agriculture Bowl Questions Middle School Agriculture Brekthrough Form Two Notes Agriculture Class 12 Ncert Solutions Agriculture Class 12 Pdf Agriculture Communication Syllabus Agriculture Diagram Software Agriculture Diagrams for Class 11 Agriculture Diagrams for Class 12 Agriculture Diagrams for Class 9 Agriculture Diagrams for Class-10 Agriculture Diagrams in Form 1 Agriculture Diagrams in Form 2 Agriculture Diagrams in Form 3 Agriculture Diagrams in Form 4 Agriculture Diagrams Pdf Agriculture Diagrams to Label Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers 2018 Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Form 1 Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Form 2 Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Form 3 Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Essay Revision Q Agriculture Essays and Answers Agriculture Essays Form One to Form Four Agriculture Essays Form One to Form Three Agriculture Essays KCSE Agriculture Essays Pdf Agriculture Exam 1 Multiple Choice Agriculture Exam 2 Advance Agriculture Exam 2 Test Agriculture Exam 2016 Agriculture Exam Form Four Agriculture Exam Form One Agriculture Exam Form Three Agriculture Exam Form Two Agriculture Exam Practice Test Agriculture Exam Questions Agriculture Exam Questions and Answers Agriculture Exam Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Exam Study Guide Agriculture Exams Agriculture Excretion Notes Agriculture Exercise Form 4 With Answers Agriculture Final Exam Answer Key Agriculture Final Exam Answer Key 2016 Agriculture Final Exam Answer Key 2017 Agriculture Final Exam Answers 2018 Agriculture Final Exam Answers 2019 Agriculture Final Exam Questions and Answers Agriculture Fom 1 Notes Agriculture Fom 2 Notes Agriculture Fom 3 Notes Agriculture Fom 4 Notes Agriculture Form 1 Agriculture Form 1 & 2 and Answers Agriculture Form 1 and 2 Essays Agriculture Form 1 and 2 Essays Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 1 Chapter 1 Agriculture Form 1 Diagrams Agriculture Form 1 Exams Agriculture Form 1 Mid Year Exam Agriculture Form 1 Notes Agriculture Form 1 Notes and Questions Agriculture Form 1 Notes Download Agriculture Form 1 Notes Free Download Agriculture Form 1 Notes GCSE Agriculture Form 1 Notes KCSE-kcse Agriculture Form 1 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 1 Notes Pdf Download Agriculture Form 1 Past Papers Agriculture Form 1 Pdf Agriculture Form 1 Pressure Agriculture Form 1 Question Papers Agriculture Form 1 Questions Agriculture Form 1 Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 1 Quiz Agriculture Form 1 Revision Questions Agriculture Form 1 Summary Notes Agriculture Form 1 Syllabus Agriculture Form 1 Work Agriculture Form 1-4 Notes Agriculture Form 2 Agriculture Form 2 Chapter 1 Agriculture Form 2 Chapter 2 Agriculture Form 2 Diagrams Agriculture Form 2 Exam Paper 2014 Agriculture Form 2 Exams Agriculture Form 2 Notes Agriculture Form 2 Notes and Questions Agriculture Form 2 Notes GCSE Agriculture Form 2 Notes KCSE-kcse Agriculture Form 2 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 2 Notes Pdf Download Agriculture Form 2 Past Papers Agriculture Form 2 Pdf Agriculture Form 2 Question Papers Agriculture Form 2 Questions Agriculture Form 2 Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 2 Quiz Agriculture Form 2 Revision Notes Agriculture Form 2 Salts Agriculture Form 2 Structure and Bonding Agriculture Form 2 Summary Notes Agriculture Form 2 Syllabus Agriculture Form 2 Work Agriculture Form 3 Agriculture Form 3 and 4 Essays Agriculture Form 3 and 4 Essays Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 3 Chapter 3 Agriculture Form 3 Classification Agriculture Form 3 Diagrams Agriculture Form 3 Ecology Agriculture Form 3 Exams Agriculture Form 3 Notes Agriculture Form 3 Notes and Questions Agriculture Form 3 Notes GCSE Agriculture Form 3 Notes KCSE-kcse Agriculture Form 3 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 3 Notes Pdf Download Agriculture Form 3 Notes Topic 1 Agriculture Form 3 Past Papers Agriculture Form 3 Pdf Agriculture Form 3 Question Papers Agriculture Form 3 Questions Agriculture Form 3 Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 3 Questions and Answers Term 3 Agriculture Form 3 Questions and Answers+pdf Agriculture Form 3 Quiz Agriculture Form 3 Revision Notes Agriculture Form 3 Revision Questions Agriculture Form 3 Summary Notes Agriculture Form 3 Syllabus Agriculture Form 3 Syllabus Pdf Agriculture Form 3 Topics Agriculture Form 3 Work Agriculture Form 4 Agriculture Form 4 All Chapter Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 1 Conversion of Units Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 1 Mind Map Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise and Answers Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Experiment Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Formula Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Mind Map Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Momentum Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Paper 2 Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 2 Slideshare Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 3 Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 3 Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 4 Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 4 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 5 Light Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 4 Chapter 5 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Diagrams Agriculture Form 4 Exam Paper 1 Agriculture Form 4 Exams Agriculture Form 4 Exercise Agriculture Form 4 Exercise Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Module With Answer Agriculture Form 4 Note Agriculture Form 4 Notes Agriculture Form 4 Notes (Pdf) Agriculture Form 4 Notes All Chapter Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Notes and Questions Agriculture Form 4 Notes Chapter 1 Agriculture Form 4 Notes Chapter 2 Agriculture Form 4 Notes Chapter 3 Agriculture Form 4 Notes Download Agriculture Form 4 Notes Free Download Agriculture Form 4 Notes GCSE Agriculture Form 4 Notes KCSE-kcse Agriculture Form 4 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Notes Pdf Download Agriculture Form 4 Paper 2 Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 4 Past Papers Agriculture Form 4 Question Papers Agriculture Form 4 Questions Agriculture Form 4 Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Quiz Agriculture Form 4 Revision Notes Agriculture Form 4 Schemes of Work Agriculture Form 4 Summary Notes Agriculture Form 4 Syllabus Agriculture Form 4 Textbook Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Work Agriculture Form 5 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers Agriculture Form 5 Chapter 1 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 5 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 5 Chapter 2 Slideshare Agriculture Form 5 Chapter 3 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 5 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form Four Book Agriculture Form Four Notes Agriculture Form Four Notes and Questions Agriculture Form Four Notes GCSE Agriculture Form Four Notes Pdf Agriculture Form Four Past Papers Agriculture Form Four Questions Agriculture Form Four Questions and Answers Agriculture Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form Four Quiz Agriculture Form Four Study Notes Agriculture Form Four Syllabus Agriculture Form Four Topic 2 Agriculture Form Four Topic 4 Agriculture Form Four Topics Agriculture Form Four Work Agriculture Form One Agriculture Form One Book Agriculture Form One Book Pdf Agriculture Form One Download Topic 1 Upto 3 Agriculture Form One Exam Agriculture Form One Notes Agriculture Form One Notes and Questions Agriculture Form One Notes GCSE Agriculture Form One Notes Pdf Agriculture Form One Pdf Agriculture Form One Questions Agriculture Form One Questions and Answers Agriculture Form One Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form One Questions and Their Answers Agriculture Form One Quiz Agriculture Form One Revision Question Agriculture Form One Schemes of Work Agriculture Form One Study Notes Agriculture Form One Syllabus Agriculture Form One Term Three Test Agriculture Form One to Three Notes Agriculture Form One Work Agriculture Form Three Agriculture Form Three Book Agriculture Form Three Notes Agriculture Form Three Notes and Questions Agriculture Form Three Notes GCSE Agriculture Form Three Questions and Answers Agriculture Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form Three Quiz Agriculture Form Three Reproduction Agriculture Form Three Reproduction. Agriculture Form Three Study Notes Agriculture Form Three Work Agriculture Form Three-questions and Answers Agriculture Form Two Agriculture Form Two Book Agriculture Form Two Diagrams Agriculture Form Two Notes Agriculture Form Two Notes and Questions Agriculture Form Two Notes GCSE Agriculture Form Two Notes Pdf Agriculture Form Two Notes-pdf Agriculture Form Two Pdf Agriculture Form Two Questions Agriculture Form Two Questions and Answers Agriculture Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form Two Quiz Agriculture Form Two Study Notes Agriculture Form Two Topics Agriculture Form Two Work Agriculture Form Two,schemes of Work Agriculture Form2 Agriculture Form2 Textbook Agriculture Game Form Four Question End Answers Agriculture Grade 10 Exam Papers Agriculture Hsc Pdf Agriculture Human Reproduction Video Agriculture IGCSE Past Papers Xtremepapers Agriculture K.c.s.e 2017 Agriculture KCSE Agriculture KCSE 2016 Agriculture KCSE 2017 Agriculture KCSE 2017 Paper 1 Agriculture KCSE Past Papers Agriculture KCSE Questions Agriculture KCSE Questions and Answer Agriculture KCSE Quizzes & Answers Agriculture KCSE Revision Agriculture KCSE Revision Notes Agriculture KCSE Setting Questions Form One and Two Agriculture Ksce 2015 Agriculture Last Year K.c.s.e Questions Agriculture Lesson Plan Form Two Agriculture Made Familiar Agriculture Mcq for Class 11 Agriculture Mcq for Class 12 Agriculture Mcq for Competitive Exams Agriculture Mcq for Competitive Exams Pdf Agriculture Mcq for Neet Pdf Agriculture Mcq for Ssc Agriculture Mcq Questions With Answers Agriculture Mcq With Answers Pdf Agriculture Mcqs for Class 12 Pdf Agriculture Mcqs With Answers Pdf Agriculture Mid Familia Form One Agriculture Mock Papers Agriculture Module Form 5 Agriculture Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cxc Agriculture Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf Agriculture Note Agriculture Note Form Two All Chapters Agriculture Notes Agriculture Notes and Guestion and Answear Agriculture Notes and Syllabus Agriculture Notes Class 10 Agriculture Notes for Class 11 Pdf Agriculture Notes for Class 12 Pdf Agriculture Notes for High School Students Agriculture Notes for IGCSE 2014 Agriculture Notes Form 1 Agriculture Notes Form 1 4 Agriculture Notes Form 1 Free Download Agriculture Notes Form 1 KLB Agriculture Notes Form 1 Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 1-4 Agriculture Notes Form 1-4(1) Agriculture Agriculture Notes Form 14 Agriculture Notes Form 2 Agriculture Notes Form 2 KLB Agriculture Notes Form 2 Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 2; Agriculture Notes Agriculture Notes Form 3 Agriculture Notes Form 3 KLB Agriculture Notes Form 3 Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 4 Agriculture Notes Form 4 Chapter 2 Agriculture Notes Form 4 KLB Agriculture Notes Form 4 Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 4-pdf Agriculture Notes Form Four Agriculture Notes Form Four KLB Agriculture Notes Form Four Pdf Agriculture Notes Form One Agriculture Notes Form One KLB Agriculture Notes Form One Pdf Agriculture Notes Form One to Form Four Agriculture Notes Form Three Agriculture Notes Form Three KLB Agriculture Notes Form Three Pdf Agriculture Notes Form Two Agriculture Notes Form Two KLB Agriculture Notes Form Two Pdf Agriculture Notes Form2 Agriculture Notes IGCSE Agriculture Notes Kenya Agriculture Notes on Agroforestry Agriculture Notes Pdf Agriculture Notes: Agriculture Objective Answer Agriculture Objective Answer 2018 Agriculture Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Agriculture Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Pdf Agriculture Oral Exam Questions Agriculture Paper 1 Agriculture Paper 1 2018 Marking Rules Agriculture Paper 1 Notes Agriculture Paper 1 Questions Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers Agriculture Paper 1 Topics Agriculture Paper 1 With Answers Agriculture Paper 2 Agriculture Paper 2 2017 Agriculture Paper 2 2018 Marking Rules Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Paper 2 Revision Agriculture Paper 2 Topics Agriculture Paper 2018 Agriculture Paper 3 2018 Marking Rules Agriculture Paper 3 Question and Answer Agriculture Paper 3 Question Paper 2014 KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 Question Paper 2015 KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 Question Paper 2016 KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 Question Paper 2017 KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 Question Paper 2018 KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 Questions and Answers Agriculture Paper One Questions and Answers Agriculture Paper One Topics Agriculture Paper Two Qestions With Answers Agriculture Paper1 Agriculture Paper2 Agriculture Paper3 Agriculture Paper4 Agriculture Past Papers Agriculture Past Papers 2017 Agriculture Past Papers a Level Agriculture Past Papers Form 1 Agriculture Past Papers Form 2 Agriculture Past Papers Form 3 Agriculture Past Papers O Level Agriculture Pdf Download Agriculture Pp1 KCSE 2016 Agriculture Practical Book Class 12 Pdf Agriculture Practical Exam Agriculture Practicals Form One Agriculture Practicals Questions and Answers Agriculture Practice Test 9th Grade Agriculture Practice Test Answers Agriculture Practice Test Questions and Answers Agriculture Practice Test Quizlet Agriculture Predicted Questions This Year KCSE Agriculture Preparation Notes Agriculture Pretest High School Pdf Agriculture Question and Answer With Explanation Agriculture Question and Answers 2019 Agriculture Question and Answers 2020 Agriculture Question and Answers 2021 Agriculture Question and Answers 2022 Agriculture Question and Answers 2023 Agriculture Question and Answers Note Agriculture Questions Agriculture Questions and Answers Agriculture Questions and Answers for High School Agriculture Questions and Answers for High Schools Agriculture Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Agriculture Questions and Answers for Secondary Schools Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 1 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 2 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 3 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 4 Agriculture Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Agriculture Questions and Answers Notes Agriculture Questions and Answers O Agriculture Questions and Answers Online Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf for Class 12 Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf for Competitive Exams Agriculture Questions and Answers-form 2 Agriculture Questions for High School Agriculture Questions for High School Students With Answers Agriculture Questions for Senior 1 Agriculture Questions for Senior 2 Agriculture Questions for Senior 3 Agriculture Questions for Senior 4 Agriculture Questions for Senior 5 Agriculture Questions for Senior 6 Agriculture Questions for Senior Five Agriculture Questions for Senior Four Agriculture Questions for Senior One Agriculture Questions for Senior Six Agriculture Questions for Senior Three Agriculture Questions for Senior Two Agriculture Questions Form One Agriculture Questions Multiple Choice Agriculture Questions Quizlet Agriculture Questions to Ask Your Teacher Agriculture Quetion and Answer Form Four Agriculture Quetion and Answer Form One Agriculture Quetion and Answer Form Three Agriculture Quetion and Answer Form Two Agriculture Quiz for Class 9 Agriculture Quiz for Class 9 Agriculture Agriculture Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Agriculture Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Pdf Agriculture Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 12 Agriculture Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Agriculture Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Pdf Agriculture Quiz Questions and Answers for High School Agriculture Quiz Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Agriculture Quiz Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Quiz Questions for Class 12 Agriculture Quiz Questions for College Students Agriculture Quiz With Answers Agriculture Quiz With Answers Pdf Agriculture Quizlet Agriculture Revision Agriculture Revision a Level Agriculture Revision Agriculture Notes Agriculture Agriculture Revision Exam Agriculture Revision Examination Agriculture Revision Form One Agriculture Revision Notes Agriculture Revision Notes Agriculture Agriculture Revision Notes Form 1 Agriculture Revision Notes Form 2 Agriculture Revision Notes Form 3 Agriculture Revision Notes Form 4 Agriculture Revision Notes IGCSE Agriculture Revision Paper One Agriculture Revision Questions Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form 1 Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form 2 Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form 3 Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form 4 Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form Four Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form One Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form Three Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form Two Agriculture Revision Questions Form 1 Agriculture Revision Questions Form 2 Agriculture Revision Questions Form 3 Agriculture Revision Questions Form 4 Agriculture Revision Questions Form Four Agriculture Revision Questions Form One Agriculture Revision Questions Form Three Agriculture Revision Questions Form Two Agriculture Revision Quiz Agriculture Revision Test Agriculture Secondary School Revision Agriculture Simple Notes Agriculture Spm Notes Download Agriculture Spm Notes Pdf Agriculture Spm Questions Agriculture Study Form 2 Agriculture Study Guide Agriculture Study Guide Answer Key Agriculture Study Guide Answers Agriculture Study Guide Agriculture Questions and Answers Agriculture Study Guide Ib Agriculture Study Guide Pdf Agriculture Study Guides Agriculture Study Notes Agriculture Study Notes Materials Form 1 Pdf Agriculture Study Notes Materials Form 2 3 Pdf Agriculture Study Notes Materials Form 2 Pdf Agriculture Study Notes Materials Form 3 Pdf Agriculture Study Notes Materials Form 4 Pdf Agriculture Syllabus in Kenya Agriculture Syllabus Pdf Agriculture Test 1 Quizlet Agriculture Test Questions Agriculture Test Questions and Answers Agriculture Test Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Topic One Form Four Agriculture Topics Form One Agriculture Unit 1 Quiz Agriculture Vol 3 Agriculture | Revision Agriculture Agriculture,form 4 Agriculture.form Four.topic Three AgricultureExam Form Three Agriculture Module Form 5 Agriculture Notes Agriculture Notes for Class 11 Pdf Agriculture Notes for Class 12 Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 1 Agriculture Notes Form 1 Free Download Agriculture Notes Form 2 Agriculture Notes Form 3 Agriculture Notes Form 3 Pdf Agriculture Notes IGCSE Agriculture Notes Pdf Agriculture Past Papers Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Simple Notes Agriculture Notes Download Agriculture Notes Pdf Agriculture Questions Agriculture Study Guide Answers Agriculture Study Guide Pdf Agriculture Study Guides Blologytextpapers Bridge Agriculture Business Past KCSE Past Papers Business Studies Form 3 Notes Pdf Business Studies Form 4 Notes Pdf C R E Form One KLB C R E Form One Oli Topic C.r.e Form 1 Notes Kenya C.r.e Form 2 Notes Kenya C.r.e Form 3 Notes C.r.e Form 3 Notes Kenya C.r.e Form 3 Pdf C.r.e Form 4 Notes Kenya C.r.e Form One Notes Pdf C.r.e Notes Form 1 C.r.e Revision Notes C.r.e Short Notes Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture 3rd Edition Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture 3rd Edition Plus Cd South Asia Edition Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture Answers Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture Coursebook Pdf Download Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture Practical Workbook Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture Revision Guide Pdf Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture Study and Revision Guide 2nd Edition Pdf Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture Study and Revision Guide Pdf Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture Workbook Free Download Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture Workbook Pdf Cambridge IGCSE® Agriculture Coursebook Caucasian Chalk Circle Essay Questions Chapter 1 Introduction to Agriculture Chapter 1 Introduction to Agriculture Studies Chisel Plough, Subsoiler , Components and Functions, Types, Cie a Level Agriculture Notes 2016 Cie a Level Agriculture Notes Pdf Cie Past Papers Class 10 Agriculture Chapter 1 Mcqs Class 8 Agriculture Notes KCSE-kcse Classification of Agroforestry Systems+pdf College Agriculture Notes College Agriculture Practice Test College Agriculture Quiz College Agriculture Quiz Chapter 1 College Agriculture Quizlet College Agriculture Study Guide College Agriculture Study Guide Pdf College Agriculture Test Questions and Answers College Agriculture Volume 3 Pdf College Agriculture Notes Complete Agriculture for Cambridge IGCSE Complete Agriculture for Cambridge IGCSE Revision Guide Pdf County Mocks 2017 Cse Past Papers Agriculture 2017 Diagram of Mouldboard Plough Difference Between Mould Board and Disc Plow Disc Plough Pdf Disc Plough Wikipedia Dl Agriculture Form 3 Pdf Kusoma Download Agriculture Form 1 Download Agriculture Form 2 Download Agriculture Form 2 Notes Download Agriculture Form 3 Download Agriculture Form 3 Notes Download Agriculture Form 4 Download Agriculture Form Four Download Agriculture Form One Download Agriculture Form Three Download Agriculture Form Two Download Agriculture Notes Form 3 Download Agriculture Notes Form One Download Agriculture Notes Form 3 Download Form Three Agriculture Notes Download Free KCSE Past Papers Agriculture Download Free KCSE Past Papers From KNEC. Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers Download KCSE Revision Notes Download KLB Agriculture Book 2 Download KLB Agriculture Book 3 Download KLB Agriculture Book 4 Download Notes of Agriculture Downloads | Agriculture | Form Four Exams | Exams Downloads | Agriculture | Form One Exams | Exams Downloads | Agriculture | Form Three Exams | Exams Downloads | Agriculture | Form Two Exams | Exams Downloads | KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes | Draw and Label a Disc Plough Dvance KCSE Past Papers Easy Agriculture Questions Edexcel a Level Agriculture B Edexcel a Level Agriculture Notes Pdf Edexcel a Level Agriculture Salters Nuffield Edexcel A2 Agriculture Notes Edexcel as Agriculture Revision Guide Pdf Edexcel Agriculture A2 Revision Notes Pdf Edexcel Agriculture Unit 2 Revision Notes Edexcel GCSE Agriculture Revision Guide Pdf Edexcel IGCSE Agriculture Past Papers Edexcel IGCSE Agriculture Revision Guide Free Pdf Download Edexcel IGCSE Agriculture Revision Guide Pdf Edexcel IGCSE Agriculture Revision Guide Pdf Download Electronics Form Four Notes Energy Questions Agriculture Bowl Essay Questions and Answers KCSE Agriculture Notes Essay Questions and Answers on Betrayal in the City Essay Questions Based on Betrayal in the City Evolving World Agriculture Book 1 Pdf Evolving World Agriculture Book 4 Notes Evolving World Agriculture Book Form 1 Evolving World-history Book 3 Exam Notes for Agriculture 101 Exams KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers F3 Agriculture Test Paper Find Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers Find KCSE Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Form 1 Agriculture Exam Form 1 Agriculture Notes Form 1 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 1 Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form 1 Agriculture Revision Notes Form 1 Agriculture Summurized Revision Pdf Form 1 Agriculture Syllabus Form 1 Agriculture Test Paper Pdf Form 1 Agriculture Topics Form 1 Agriculture Notes Form 1 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 1 AgricultureRevision Notes Form 1 AgricultureSyllabus Form 1 AgricultureTest Paper Pdf Form 1 Past Papers Form 1 Past Papers With Answers Form 1 Revision Papers Form 1 Subjects in Kenya Form 2 Agriculture Exam Form 2 Agriculture Exam Paper Form 2 Agriculture Exam Paper 2016 Form 2 Agriculture Exam Paper Free Download Form 2 Agriculture Exam Paper With Answer Form 2 Agriculture Final Year Exam Paper 2 Form 2 Agriculture Notes Form 2 Agriculture Notes and Revision Questions Form 2 Agriculture Notes Pdf Form 2 Agriculture Past Papers Form 2 Agriculture Questions Form 2 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 2 Agriculture Questions and Answers > Form 2 Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2 Agriculture Revision Notes Form 2 Agriculture Short Notes Form 2 Agriculture Syllabus Form 2 AgricultureExam Paper Form 2 AgricultureExam Paper Free Download Form 2 AgricultureExam Paper With Answer Form 2 AgricultureFinal Year Exam Paper 2 Form 2 Agriculture Past Papers Form 2 AgricultureRevision Notes Form 2 AgricultureShort Notes Form 2 AgricultureSyllabus Form 2 Revision Papers Form 2 Subjects in Kenya Form 3 Agriculture Book Form 3 Agriculture Exam Form 3 Agriculture Exam Paper Form 3 Agriculture Notes Form 3 Agriculture Past Papers Form 3 Agriculture Questions Form 3 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 3 Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3 Agriculture Revision Notes Form 3 Agriculture Syllabus Form 3 AgricultureExam Paper Form 3 Agriculture Notes Form 3 Agriculture Past Papers Form 3 Agriculture Questions Form 3 Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3 AgricultureRevision Notes Form 3 AgricultureSyllabus Form 3 C.r.e Form 3 Notes of Agriculture Topic on Fish Form 3 Past Papers Form 3 Revision Papers Form 3 Subjects in Kenya Form 4 Agriculture Exam Form 4 Agriculture Notes Form 4 Agriculture Notes Pdf Form 4 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 4 Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form 4 Agriculture Revision Notes Form 4 Agriculture Syllabus Form 4 Agriculture Topics Form 4 Agriculture Notes Form 4 AgricultureRevision Notes Form 4 AgricultureSyllabus Form 4 AgricultureTopics Form 4 Exam Papers Form 4 Revision Papers Form 4 Subjects in Kenya Form 5 Agriculture Topics Form 5 AgricultureTopics Form Five Agriculture Notes Form Five Agriculture Notes Form Four Agriculture Book Form Four Agriculture Notes Form Four Agriculture Notes Pdf Form Four Agriculture Questions and Answers Form Four Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form Four Agriculture Revision Questions Form Four Agriculture Syllabus Form Four Agriculture Topics Form Four Agriculture Notes Form Four Agriculture Questions and Answers Form Four Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form Four AgricultureTopics Form Four Notes Form Four Revision Papers Form Four Subjects in Kenya Form One Agriculture Book Form One Agriculture Examination Form One Agriculture First Topic Form One Agriculture Lesson Plan Form One Agriculture Notes Pdf Form One Agriculture Past Papers Pdf Form One Agriculture Questions Form One Agriculture Questions and Answers Form One Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form One Agriculture Revision Questions Form One Agriculture Short Notes Form One Agriculture Syllabus Form One Agriculture Topics Form One AgricultureExamination Form One Agriculture Past Papers Pdf Form One Agriculture Questions and Answers Form One Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form One AgricultureTopics Form One Exams Form One Notes of Agriculture Form One Past Papers Form One Subjects in Kenya Form One Term One Agriculture Exam Form One Term One AgricultureExam Form Three Agriculture Book Form Three Agriculture Book Pdf Form Three Agriculture Notes Form Three Agriculture Notes Pdf Form Three Agriculture Questions and Answers Form Three Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form Three Agriculture Revision Questions Form Three Agriculture Syllabus Form Three Agriculture Topics Form Three Agriculture Notes Form Three Agriculture Notes Pdf Form Three Agriculture Questions and Answers Form Three Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form Three AgricultureTopics Form Three Subjects in Kenya Form Two Agriculture Book Form Two Agriculture Cat Form Two Agriculture Examination Form Two Agriculture Notes Form Two Agriculture Notes Pdf Form Two Agriculture Past Papers Form Two Agriculture Questions and Answers Form Two Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form Two Agriculture Revision Questions Form Two Agriculture Syllabus Form Two Agriculture Topics Form Two Agriculture Notes Form Two Agriculture Notes Pdf Form Two Agriculture Questions and Answers Form Two Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form Two AgricultureSyllabus Form Two AgricultureTopics Form Two Notes Form Two Subjects in Kenya Free a-level Agriculture Revision App | Pass Your Agriculture Exams Free Agriculture Form 1 Notes Free Agriculture Notes Form 1 Free Agriculture Notes Pdf Free Agriculture Notes Pdf Free College Agriculture Practice Test Free Form1,form2,form3 Past Papers Free KCSE Past Papers Free KCSE Mocks 2015 Free KCSE Past Papers 2014 Free KCSE Past Papers KCSE Past Free KCSE Past Papers Kenya, Free KCSE Past Papers With Answers Free KCSE Questions and Answers on Agriculture Free KCSE Revision Notes Free Marking Schemes Free Mocks Online KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers Free Revision Papers From Three Notes Topic One KLB Fun Agriculture Questions Functions of Disc Plough Functions of Parts of Disc Plough Funny Agriculture Questions Funny Agriculture Questions and Answers Funny Agriculture Questions to Ask Funny Agriculture Quotes GCSE Agriculture Exam Questions and Answers GCSE Agriculture Past Papers GCSE Agriculture Revision GCSE Agriculture Revision Notes GCSE Agriculture Revision Notes Pdf GCSE Agriculture Revision Notes Pdf 9-1 GCSE Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers GCSE Agriculture Textbook Pdf GCSE Agriculture Topics Pass My Exams: Easy Exam Revision Notes General Agriculture Notes Pdf General Agriculture Practice Test With Answers General Agriculture Quiz General Agriculture Quiz Pdf General Agriculture Test Questions and Answers General Agriculture Test Questions and Answers Pdf General Knowledge in Agriculture Human Body Good Agriculture Questions to Ask GRE Agriculture Practice Test GRE Agriculture Subject Test Pdf Handbook of Agriculture Pdf Free Download Hard Agriculture Questions Hard Agriculture Questions and Answers Hard Agriculture Questions to Ask Your Teacher Hard Agriculture Quiz Questions Hard Form 3 Agriculture Question High School Agriculture Final Exam Doc High School Agriculture Final Exam Pdf High School Agriculture Final Exam Questions High School Agriculture Final Exam Questions and Answers High School Agriculture Notes High School Agriculture Practice Test High School Agriculture Pretest With Answers High School Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf High School Agriculture Study Guide High School Agriculture Test Questions and Answers Pdf High School Agriculture Notes High School Agriculture Study Guide How Do Trees Help Soil? How to Answer KCSE Agriculture Question How to Motivate a Form 4 Student How to Motivate a KCSE Candidate How to Motivate a KCSE Student How to Pass Agriculture Questions & Answers Form 1&2 | Text Book How to Revise Agriculture How to Revise Effectively for KCSE How to Study Agriculture: 5 Study Techniques to Master Agriculture Hsc Agriculture 2018 Hsc Agriculture 2019 Https://www.knec.ac.ke/ Www.knec-portal.ac.ke/ KNEC Portal: Ial Agriculture Notes Ib Agriculture Cold War Notes Ib Agriculture Notes Ib Agriculture Notes Pdf Ib Agriculture of the Americas Notes Ib Agriculture of the Americas Study Guide Ib Agriculture Paper 2 Study Guide Ib Agriculture Question Bank by Topic Ib Agriculture Study Guide Pdf Ict Notes Form 1 IGCSE Agriculture Alternative to Practical Revision IGCSE Agriculture Alternative to Practical Revision Notes IGCSE Agriculture Book IGCSE Agriculture Book Pdf Download IGCSE Agriculture Notes IGCSE Agriculture Notes 2017 Pdf IGCSE Agriculture Notes Edexcel IGCSE Agriculture Paper 2 Notes IGCSE Agriculture Paper 6 Notes IGCSE Agriculture Past Papers IGCSE Agriculture Past Papers 2014 IGCSE Agriculture Past Papers 2017 IGCSE Agriculture Pdf IGCSE Agriculture Pre Release Material 2018 IGCSE Agriculture Resources IGCSE Agriculture Revision Guide IGCSE Agriculture Revision Guide Free Download IGCSE Agriculture Revision Guide Pdf Download IGCSE Agriculture Revision Notes Pdf IGCSE Agriculture Revision Worksheets IGCSE Agriculture Workbook Pdf IGCSE Agriculture Znotes IGCSE Agriculture Past Papers IGCSE Notes Agriculture Importance of Agroforestry indigenous plough Inorganic Agriculture Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf Inorganic Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Interesting Agriculture Questions Interesting Agriculture Questions and Answers Interesting Questions to Ask About Agriculture Intro to Agriculture Quiz Introduction of Agriculture Form One Introduction to Agriculture Introduction to Agriculture Notes Introduction to Agriculture Pdf Introduction to Agriculture Notes Iron Plough Is Agroforestry Sustainable? K.c.s.e Answers Agriculture Paper One 2018 K.c.s.e Agriculture 2017 K.c.s.e Agriculture 2018 K.c.s.e Agriculture Paper 1 2017 K.c.s.e Mocks 2018 K.c.s.e Papers 2015 K.c.s.e Papers 2016 K.c.s.e Past Papers 2014 K.c.s.e.Agriculture Paper 2 Year 2018 K.c.s.e.results 2018 for Busia County K.l.b Agriculture Form 3 K.l.b Agriculture Notes K.l.b Agriculture Notes Kasneb Past Papers for Colleges Agriculture Past Papers KCSE 2010 Marking Scheme KCSE 2010 Past Papers KCSE 2011 Agriculture Paper 1 KCSE 2011 Marking Scheme KCSE 2012 Agriculture Paper 2 Marking Scheme KCSE 2012 Marking Schemes KCSE 2013 Agriculture Paper 1 KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme Pdf KCSE 2014 KCSE 2015 Agriculture Paper 2 KCSE 2015 Agriculture Paper 3 KCSE 2015 Marking Scheme KCSE 2015 Past Papers KCSE 2016 Agriculture Paper 1 KCSE 2016 Agriculture Paper 2 KCSE 2017 Agriculture Paper 1 KCSE 2017 Agriculture Paper 2 KCSE 2017 Hostory Papers With Answers.com KCSE 2017 Marking Scheme KCSE 2017 Papers KCSE 2017 Papers and Marking Scheme KCSE 2017 Papers Pdf KCSE 2017 Past Papers KCSE 2017 Prediction Pdf KCSE 2018 Agriculture and Answers KCSE 2018 Agriculture Prediction KCSE 2018 Leakage KCSE 2018 Marking Scheme KCSE 2018 Papers KCSE 2018 Prediction Pdf KCSE 2018 Predictions KCSE 2018 Questions KCSE 2018 Questions and Answers KCSE 2019 Leakage Agriculture KCSE 2019 Marking Scheme KCSE 2019 Questions KCSE 2019 Questions and Answers KCSE 2020 Questions KCSE 2020 Questions and Answers KCSE Answers KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers Downloads | KCSE Agriculture 2011 KCSE Agriculture 2016 KCSE Agriculture Diagramsbiology Revision Tips KCSE Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers KCSE Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Pdf KCSE Agriculture Essays KCSE Agriculture Essays Pdf KCSE Agriculture Marking Schemes KCSE Agriculture Notes KCSE Agriculture Notes Pdf KCSE Agriculture Notes, Syllabus, Questions, Answers KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2011 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2012 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2013 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2015 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2016 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2017 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2017 Pdf KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2012 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2012 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2015 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2013 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2014 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2015 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2016 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2017 KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 2012 KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 2016 KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 2017 KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 Past Papers KCSE Agriculture Past Papers KCSE Agriculture Past Papers and Answers KCSE Agriculture Past Papers Pdf KCSE Agriculture Practical KCSE Agriculture Practical 2015 KCSE Agriculture Practical 2016 KCSE Agriculture Practical Past Papers KCSE Agriculture Practicals KCSE Agriculture Practicals KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 KCSE Agriculture Question and Answer KCSE Agriculture Questions and Answers KCSE Agriculture Questions and Answers Ap Agriculture KCSE Agriculture Revision KCSE Agriculture Revision Notes KCSE Agriculture Revision Papers KCSE Agriculture Revision Questions KCSE Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers KCSE Agriculture Syllabus KCSE Agriculture Notes KCSE AgriculturePaper 1 KCSE AgriculturePaper 2 KCSE AgriculturePaper 2 Pdf KCSE AgricultureSyllabus KCSE Business Paper 1 2016 KCSE Business Past Papers KCSE Business Studies Past Papers KCSE Essay Questions in Betrayal in the City KCSE Essays KCSE Exam Papers 2018 KCSE Exam Papers Answers KCSE Form 1 Agriculture Revision KCSE Form 2 Agriculture Revision KCSE Form 3 Agriculture Revision KCSE Form 4 Agriculture Revision KCSE Form Four Agriculture Revision KCSE Form One Agriculture Revision KCSE Form Three Agriculture Revision KCSE Form Two Agriculture Revision KCSE KCSE Past Papers KNEC KCSE Leakage KCSE Leakage Agriculture KCSE Made Familiar Agriculture KCSE Made Familiar Agriculture Pdf KCSE Marking Scheme 2016 KCSE Marking Schemes KCSE Marking Schemes 2017 KCSE Marking Schemes Pdf KCSE Mock Exams KCSE Mock Papers 2015 KCSE Mock Papers 2017 KCSE Mock Papers 2018 KCSE Mock Papers Pdf KCSE Mock Papers Pdf 2018 KCSE Mock Papers Pdf KCSE Past Papers KCSE Mocks 2017 KCSE Mocks 2018 KCSE Notes KCSE Online Notes KCSE Online Past Papers KCSE Online Registration KCSE Papers 2015 KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes | Exams KCSE Past Papers KCSE Past Papers 2007 KCSE Past Papers 2009 KCSE Past Papers 2010 KCSE Past Papers 2011 KCSE Past Papers 2011 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2012 KCSE Past Papers 2013 KCSE Past Papers 2013knec KCSE Past Papers 2014 KCSE Past Papers 2014 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2015 KCSE Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes KCSE Past Papers 2015 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2016 KCSE Past Papers 2016 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2017 KCSE Past Papers 2017 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2018 KCSE Past Papers Agriculture KCSE Past Papers Agriculture and Answers KCSE Past Papers Agriculture Pdf KCSE Past Papers Agriculture With Answers KCSE Past Papers Agricultureand Answers KCSE Past Papers Business Studies and Answers KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers Free Mocks Online KCSE Past Papers Marking Scheme KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download KCSE 2013 KCSE Past Papers With Answers KCSE Past Papers Woodwork and Answers KCSE Prediction 2017 KCSE Prediction 2018 KCSE Prediction 2018 Pdf KCSE Prediction Papers 2018 KCSE Prediction Questions KCSE Prediction Questions 2018 KCSE Prediction Questions and Answers KCSE Questions KCSE Questions and Answers KCSE Questions and Answers. KCSE Questions on Agriculture KCSE Results, Online Registration, KCSE Result Slip. KCSE Revision KCSE Revision Notes KCSE Revision Notes Agriculture KCSE Revision Notes Pdf KCSE Revision Papers KCSE Revision Papers 2014 KCSE Revision Papers With Answers KCSE Revision Question for Agriculture KCSE Revision Questions KCSE Revision Questions and Answers KCSE Revision | Secondary School | Text Books | Text Book Centre KCSE Syllabus Pdf KCSE Trial 2017 KCSE Trial Exams 2017 Kenya Secondary School Agriculture Syllabus Kenya Secondary School Agriculture Syllabus Pdf Kenya Secondary School AgricultureSyllabus Pdf Kenya Secondary School Syllabus Pdf Kenya-kcse-christian Religious Education Syllabus Kenyaplex KCSE Past Papers Kenyaplex Past Papers for Secondary KLB Agriculture Book 1 Download KLB Agriculture Book 1 Notes KLB Agriculture Book 1 Pdf KLB Agriculture Book 2 KLB Agriculture Book 2 Notes KLB Agriculture Book 2 Notes Pdf KLB Agriculture Book 2 Pdf KLB Agriculture Book 3 Notes KLB Agriculture Book 3 Pdf KLB Agriculture Book 3 Pdf Download KLB Agriculture Book 4 Notes KLB Agriculture Book 4 Pdf KLB Agriculture Book 4 Pdf Download KLB Agriculture Book 4 Topics KLB Agriculture Book One KLB Agriculture Form 1 KLB Agriculture Form 1 Notes KLB Agriculture Form 1 Pdf KLB Agriculture Form 2 KLB Agriculture Form 2 Book KLB Agriculture Form 2 Notes KLB Agriculture Form 2 Pdf KLB Agriculture Form 2 Pdf Download KLB Agriculture Form 2 Schemes of Work KLB Agriculture Form 3 KLB Agriculture Form 3 Notes KLB Agriculture Form 3 Notes Pdf KLB Agriculture Form 3 Pdf KLB Agriculture Form 3 Pdf Download KLB Agriculture Form 4 KLB Agriculture Form 4 Notes KLB Agriculture Form 4 Pdf KLB Agriculture Form Four KLB Agriculture Form Four Notes KLB Agriculture Form One KLB Agriculture Form One Notes KLB Agriculture Form Three KLB Agriculture Form Three Notes KLB Agriculture Form Two KLB Agriculture Form Two Notes KLB Agriculture Notes KLB Agriculture Notes Form 4 KLB Agriculture Pdf KLB Agriculture Notes KLB Agriculture Notes Form 4 KLB AgriculturePdf KNEC Agriculture Syllabus KNEC Examiners Portal KNEC Website Agriculture Paper 1 All Questions and Answers KNEC Past Papers for Colleges KNEC Past Papers Free Download KNEC Past Papers Free Downloads KNEC Past Papers Pdf KNEC Portal Confirmation KNEC Portal KCSE Results KNEC Portal KNEC Past Papers for Colleges Kasneb Past Papers KNEC Revision Papers KNEC Technical Exams Past Papers Kusoma Agriculture Notes Kusoma Agriculture Notes Pdf Kusoma Notes Agriculture Kusoma.co.ke Kusoma.com Past Papers Labelled Diagram of a Disc Plough Learner Guide for Cambridge IGCSE Agriculture Longhorn Agriculture Book 3 Pdf Made Familiar Agriculture Made Familiar Agriculture Pdf Made Familiar Agriculture Questions Maktaba Tetea Notes Marking Scheme KCSE Agriculture Past Papers Math Form2 Note Mcqs About Gaseous Exchange Middle School Agriculture Bowl Agriculture Questions Mock Past Papers 2017 Mock Past Papers With Answers Mokasa Mock 2017 More Than 1800 Agriculture Questions and Answers to Help You Study Mould Board Plough Mouldboard Plough Diagram Mouldboard Plough Parts Mouldboard Plough Parts and Their Functions Mouldboard Plough Parts and Their Functions Pdf Mouldboard Plough Uses Mouldboard Plough Wikipedia Multiple Choice Questions on Agriculture Necta Agriculture Past Papers Necta Agriculture Practicals Necta Agriculture Past Papers Necta AgriculturePracticals Necta Form Four Past Papers Necta Past Papers Form 4 Necta Past Papers Form 4 2016 Necta Past Papers Form Six Necta Past Papers Form Two Necta Questions and Answers Necta Review Questions Notes Agriculture Form 1 Notes Agriculture Form 2 Notes Agriculture Form 3 Notes Agriculture Form 3 Notes Pdf Notes Agriculture Form 3 Syllabus Notes Agriculture Form 4 Syllabus Notes on Agriculture Studies Notes Za Agriculture 4m 2 Notes Za Agriculture Form One Notes Za Agriculture Form Three O Level Agriculture Practical Experiments O Level Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Orm Three Agriculture Notes Page Navigation Papacambridge Agriculture IGCSE Papers KNEC KCSE Online Past Papers KNEC KCSE Results Past Papers Parts of a Disc Plough and Their Functions Parts of a Disc Plough and Their Functions Pdf Parts of a Mouldboard Plough and Their Functions Parts of Disc Plough and Their Function Past KCSE Papers Past Paper Questions by Topic Agriculture Past Papers 2014 Past Papers in Kenya Pdf Agriculture Form 3 Pdf Agriculture Notes Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 1 Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 2 Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 3 Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 4 Pdf Agriculture Notes Form Four Pdf Agriculture Notes Form One Pdf Agriculture Notes Form Three Pdf Agriculture Notes Form Two Pdf Form 1 Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2 Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3 Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form 4 Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form Four Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form One Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form Three Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Form Two Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Free KCSE Past Papers and Marking Schemes Pdf" Revision Questions Agriculture Form 1 Practical Agriculture Experiments Pdf Practical Agriculture Question and Answer Pdf Pre Mocks 2018 Preliminary Agriculture Primary and Secondary Tillage Implements Ppt Primary Tillage Objectives, Mould Board Plough , Disc Plough, Pte KNEC Past Papers Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form One Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form Two Questions Based to Introduction to Agriculture Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Humans Questions on Introduction to Agriculture Questions to Ask in Agriculture Class Questions to Confuse Your Agriculture Teacher Quizlet Agriculture Test Quizlet Test Questions Qustions in Agriculture and Answers Revision Revision Agriculture Notes and Questions? Revision Quiz for Agriculture for Form Three S.1 Agriculture Questions S.2 Agriculture Questions S.3 Agriculture Questions S.4 Agriculture Questions Sample Essays on Betrayal in the City School Agriculture Notes Secondary Agriculture Notes Secondary Agriculture Notes Pdf Secondary Agriculture Notes Pdf Senior 1 Agriculture Notes Senior 2 Agriculture Notes Senior 3 Agriculture Notes Senior 4 Agriculture Notes Senior 5 Agriculture Notes Senior 6 Agriculture Notes Senior Five Agriculture Notes Senior Four Agriculture Notes Senior One Agriculture Notes Senior Six Agriculture Notes Senior Three Agriculture Notes Senior Two Agriculture Notes Share: This Makes the Horizontal Cut and Starts the Turning of the Furrow Slices. Simple Scientific Questions Smart Questions to Ask a Agriculture Teacher Snab Agriculture Revision Notes Southwest Mock Paper 2 2016 Agriculture Only Spm Agriculture Revision Notes Spm Notes Success Agriculture Spm Pdf Success Agriculture Pdf Summary of Agriculture Form 3 Tahossa Past Papers To Motivate a Form 4 KCSE Student To Motivate a Form 4 Student Topical Revision Material Tricky Agriculture Questions and Answers Tricky Agriculture Questions for Adults Tricky Agriculture Questions With Answers Tricky Agriculture Quiz Questions Two Agriculture Revision Questions University Agriculture Volume 3 Openstax University Agriculture Volume 3 Pdf University Agriculture Volume 4 Pdf Ur Revision Guide IGCSE Agriculture Vertical Suction of Mb Plough Well Labelled Diagram of a Mouldboard Plough Well Labelled Diagram of Disc Plough What Are Agroforestry Practices? What Are Forest Crops? What Are Silvicultural Treatments? What Are the Benefits of Agroforestry? What Are the Functions of Disc Plough What Are the Importance of Silviculture? What Are the Types of Agroforestry? What Are the Types of Forestry? What Are the Types of Gametes What Does a Silviculturist Do? What Does Urban Forestry Mean? What Is a Food Forest Garden? What Is GCSE and Forestry? What Is Agrisilviculture? What Is Agroforestry System What Is Agroforestry Technology? What Is Alley Cropping System? What Is Community Forest Management? What Is Forest Soil? What Is Indirect Deforestation? What Is Rural Forestry? What Is Selective Logging? What Is Silviculture and Its Advantages? What Is Silvopastoral System? What Is Social Forestry and Agroforestry? What Is the Agroforestry? What Is the Concept of Agroforestry? What Is the Meaning of Forest Reserve? What Seven Important Occasions When the Bible Is Used in Kenya Today? Which Trees Are Found in Social Forestry? Wooden Plough Working of Excretory System Www.Agriculture Form One Notes.com Www.Agriculture From One KLB.com Www.form 1 Agriculture.com Www.form 2 Agriculture.com Www.form 3 Agriculture.com Www.form 4 Agriculture.com Www.form Four Agriculture.com Www.form One Agriculture.com Www.form Three Agriculture.com Www.form Two Agriculture.com Www.kusoma Notes Www.kusoma Revision Materials Www.kusoma.co.ke Agriculture Notes Xtremepapers IGCSE Agriculture Year 11 Agriculture Z Notes Agriculture IGCSE Znotes as Agriculture 15 Common Agriculture Questions From Form 1 15 Common Agriculture Questions From Form 2 15 Common Agriculture Questions From Form 3 15 Common Agriculture Questions From Form 4 15 Common Agriculture Questions From Form Four 15 Common Agriculture Questions From Form One 15 Common Agriculture Questions From Form Three 15 Common Agriculture Questions From Form Two 150 Common Agriculture Questions From Form 1 150 Common Agriculture Questions From Form 2 150 Common Agriculture Questions From Form 3 150 Common Agriculture Questions From Form 4 150 Common Agriculture Questions From Form Four 150 Common Agriculture Questions From Form One 150 Common Agriculture Questions From Form Three 150 Common Agriculture Questions From Form Two 2019 KCSE Exams Agriculture Papers 2019 KCSE Exams Papers 2020 KCSE Exams Agriculture Papers 2021 KCSE Exams Agriculture Papers Best Agriculture Books for KCSE Knec Agriculture Agriculture 2 Topic Form Two Agriculture Diagrams Agriculture Form 1 and 2 Notes Agriculture Form 1 Download Agriculture Form 1 Notes Online Agriculture Form 1 Notes Revision Agriculture Form 1 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Agriculture Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 1 Revision Notes Agriculture Form 1 Text Book Agriculture Form 1 Text Book Notes Agriculture Form 2 Download Agriculture Form 2 Notes Agriculture Form 2 Notes Online Agriculture Form 2 Notes Revision Agriculture Form 2 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Agriculture Form 2 Pdf Agriculture Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 2 Revision Notes Agriculture Form 2 Text Book Agriculture Form 2 Text Book Notes Agriculture Form 3 Download Agriculture Form 3 Notes Online Agriculture Form 3 Notes Revision Agriculture Form 3 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Agriculture Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 3 Revision Notes Agriculture Form 3 Text Book Agriculture Form 3 Text Book Notes Agriculture Form 4 Download Agriculture Form 4 Notes Online Agriculture Form 4 Notes Revision Agriculture Form 4 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Agriculture Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 4 Revision Notes Agriculture Form 4 Text Book Agriculture Form 4 Text Book Notes Agriculture Form Four Download Agriculture Form Four Notes Online Agriculture Form Four Notes Revision Agriculture Form Four Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Agriculture Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form Four Revision Notes Agriculture Form Four Text Book Agriculture Form Four Text Book Notes Agriculture Form One Download Agriculture Form One Notes Online Agriculture Form One Notes Revision Agriculture Form One Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Agriculture Form One Questions and Answers Agriculture Form One Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form One Revision Notes Agriculture Form One Text Book Agriculture Form One Text Book Notes Agriculture Form Three Download Agriculture Form Three Notes Online Agriculture Form Three Notes Revision Agriculture Form Three Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Agriculture Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form Three Revision Notes Agriculture Form Three Text Book Agriculture Form Three Text Book Notes Agriculture Form Two Download Agriculture Form Two Notes Online Agriculture Form Two Notes Revision Agriculture Form Two Pastpapers and Marking Scheme Agriculture Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form Two Revision Notes Agriculture Form Two Text Book Agriculture Form Two Text Book Notes Agriculture Full Exam Papers Agriculture K.C.S.E Revision Papers Agriculture KCSE Revision Agriculture Notes Book Four Agriculture Notes Book One Agriculture Notes Book Three Agriculture Notes Book Two Agriculture Notes Form 2 Agriculture Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 1 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 2 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 3 Agriculture Short Note for Revising Form 1 Agriculture Short Note for Revising Form 2 Agriculture Short Note for Revising Form 3 Agriculture Short Note for Revising Form 4 Agriculture Short Note for Revising Form Four Agriculture Short Note for Revising Form One Agriculture Short Note for Revising Form Three Agriculture Short Note for Revising Form Two Agriculture Short Notes Form 1 Agriculture Short Notes Form 2 Agriculture Short Notes Form 3 Agriculture Short Notes Form 4 Agriculture Short Notes Form Four Agriculture Short Notes Form One Agriculture Short Notes Form Three Agriculture Short Notes Form Two Agriculture Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Brief Notes Agriculture Form 1 Brief Notes Agriculture Form 2 Brief Notes Agriculture Form 3 Brief Notes Agriculture Form 4 Brief Notes Agriculture Form Four Brief Notes Agriculture Form One Brief Notes Agriculture Form Three Brief Notes Agriculture Form Two Brief Notes Agriculture Form3 Chapter1 Download Book 1 Agriculture Notes Download Book 2 Agriculture Notes Download Book 3 Agriculture Notes Download Book 4 Agriculture Notes Download Book Four Agriculture Notes Download Book One Agriculture Notes Download Book Three Agriculture Notes Download Book Two Agriculture Notes Download Book1 Agriculture Notes Download Book2 Agriculture Notes Download Book3 Agriculture Notes Download Book4 Agriculture Notes Download KCSE Agriculture Study Notes Download Secondary Subjects Download Secondary Subjects in Kenya Download Secondary Subjects KCSE Exams Revision Kenya Exams Revision Kenya KCSE Expected Questions and Answers in Agriculture Form One Form 2 Agriculture Notes Form 2 Agriculture Notes Pdf Form 2 Agriculture Topics Form 3 Agriculture Book Pdf Form Iii Topics of Agriculture Revisios How to Answer Agriculture Paper 1 Questions? How to Answer Agriculture Paper 2 Questions? How to Answer Agriculture Paper 3 Questions? How to Answer KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 Questions? How to Answer KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 Questions? How to Answer KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 Questions? How to Answer Paper 1 Agriculture Questions? How to Answer Paper 2 Agriculture Questions? How to Answer Paper 3 Agriculture Questions? K.C.S.E Revision Papers K.C.S.E Revision Papers Agriculture KCSE Agriculture Essay Questions and Answers Pdf KCSE Agriculture Revisions KCSE Agriculture Study Notes KCSE Free Agriculture Qussions KCSE Free Qussions KCSE Revision Kenya KCSE Revisions Agriculture Form Two Questions Revision Kenya Revision Kenya Kcsse Sammary Note for Agriculture Form 1 Sammary Note for Agriculture Form 2 Sammary Note for Agriculture Form 3 Sammary Note for Agriculture Form 4 Sammary Note for Agriculture Form Four Sammary Note for Agriculture Form One Sammary Note for Agriculture Form Three Sammary Note for Agriculture Form Two Www.last Year KCSE Exams.com A Level Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf All Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf,ppt Agriculture Exam Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 1-4 Pdf Free High School Notes Kenya Free Kcse Revision Notes General Agriculture Test Questions and Answers Pdf High School Agriculture Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf Kcse Agriculture Revision Notes Pdf Kcse Revision Books Pdf Kcse Revision Notes Pdf Kenya Secondary School Notes Pdf Notes of Form 123 and 4 All Subject Agriculture Notes Form 1 Free Download Advice to KCSE Candidates Best Revision Books for KCSE How to Pass an Exam Successfully How to Pass KCSE 2018 How to Pass KCSE 2019 How to Pass KCSE Agriculture Paper How to Pass KCSE Agriculture How to Pass KCSE Agriculture How to Pass KCSE 2019 K.c.s.e Agriculture Paper 1 2017 KCSE 2019 Prediction KCSE Prediction 2019 KCSE Revision Tips KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2018 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2018 KCSE Agriculture Past Papers Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2012 KCSE Past Papers 2017 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2018 KCSE Past Papers of Agriculture Pp2 KCSE Agriculture Past Papers Pdf Agriculture KCSE Papers With Their Marking Schemes Agriculture Paper 1 and Answers KCSE 2017 Papers and Marking Scheme KCSE 2019 Papers and Marking Scheme KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2018 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2019 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2019 Past Papers KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2017 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2018 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2019 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2019 Past Papers KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 2019 Past Papers KCSE Agriculture Past Papers and Answers KCSE Marking Schemes Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes KCSE Past Papers 2019 Marking Schemes KCSE Past Papers Agriculture Paper 1 2019 KCSE Past Papers Agriculture Paper 2 2019 KCSE Past Papers Agriculture Paper 3 2019 Past Papers KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2019 Past Papers KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2019 Past Papers KCSE Agriculture Paper 3 2019 Agriculture Form 1 Questions and Answers Agriculture Paper 1 2018 Agriculture Paper 2 2018 Agriculture Paper 1 2019 Agriculture Paper 2 2019 Agriculture Paper 1 Notes Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 2 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2018 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2018 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2017 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2017 KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2019 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2019 Most Tested KCSE Agriculture Questions 4m1 Notes Viusasa 4m2 Notes Viusasa 4m3 Notes Viusasa 4m4 Notes Viusasa Download on Viusasa - Download Now for Free Elimu - Viusasa Elimu Library | Notes, Exams, Lesson Plans, Schemes Elimu Online High School Notes - Revision Materials for Kenyan Schools Https //www.viusasa.com/elimu Kenya Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 1 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 2 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 3 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 4 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Four Notes Viusasa Elimu Form One Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Three Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Two Viusasa Viusasa Education Viusasa Elimu Viusasa Elimu Class 6 Viusasa Elimu Form 1 Viusasa Elimu Form 1 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 2 Viusasa Elimu Form 2 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 3 Viusasa Elimu Form 3 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form 4 Viusasa Elimu Form 4 Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Four Viusasa Elimu Form Four Notes Viusasa Elimu Form One Viusasa Elimu Form One Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Three Viusasa Elimu Form Three Notes Viusasa Elimu Form Two Viusasa Elimu Form Two Notes Viusasa High School Notes - Revision Materials for Kenyan Schools Viusasa Notes Agriculture Mock Papers Agriculture Paper 1 2019 Agriculture Paper 1 Notes Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Paper 2 Form 3 Agriculture Paper 2 Notes Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Past Papers Agriculture Past Papers Pdf Agriculture Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Pdf Agriculture Revision Questions Pdf Common Exam Questions in Agriculture Paper 1 Common Exam Questions in Agriculture Paper 2 Common Test Questions in Agriculture Paper 1 Common Tested Questions in Agriculture Paper 1 Commonly Tested Questions in Agriculture Paper 1 K.c.s.e.agriculture Questions and Answers KCSE 2019 Agriculture Paper 1 Marking Scheme KCSE 2019 Agriculture Paper 2 KCSE 2019 Agriculture Paper 2 Marking Scheme KCSE 2020 Prediction Questions and Answers KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 2019 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2016 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2017 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2018 KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 2019 KCSE Agriculture Questions and Answers Most Tested Questions in Agriculture Paper 1 Most Tested Questions in Agriculture Paper 2 Mostly Tested Questions in Agriculture Paper 1 Mostly Tested Questions in Agriculture Paper 2 Agriculture Form 4 Agriculture Revision Questions Form 1 Agriculture Notes Form 1 Form 4 Notes High Flyer Series Agriculture Form 1-4 Kcse Past Papers Agriculture With Answers Agriculture Notes Download Secondary Agriculture Notes Pdf Water and Hydrogen Form 1 Notes High Flyer Series KCSE Revision in Agriculture High Flyer Series KCSE Revision Agriculture Form 1-4 Revised A Level Agriculture Notes Uganda Pdf Download Buddo Junior School Holiday Work Agriculture Notes for a Level Pdf Agriculture Notes Form 1 Agriculture Notes Form 3 the Mole Agriculture Notes Form 4 Agriculture Notes O Level Agriculture Notes O Level Uganda Agriculture Notes O Level Uganda Pdf Agriculture Notes Pdf Download Agriculture Notes Form 3 Agriculture Notes Form 3 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form Three Agriculture Syllabus Pdf Gayaza High School Agriculture Notes Gayaza High School Agriculture Notes Pdf Gayaza High School Agriculture Past Papers Gayaza High School Agriculture Past Papers Answers Gayaza High School Agriculture Past Papers Questions and Answers Gayaza High School E Learning Gayaza High School Elearning Platform Gayaza High School Examinations Gayaza High School Holiday Work Gayaza High School Notes Gayaza High School Notes 2021 Gayaza High School Notes 2022 Gayaza High School Notes 2023 Gayaza High School Notes Pdf Gayaza Junior School E Learning Platform Gayaza Junior School Holiday Work Gayaza O Level Agriculture Notes Home › Gayaza High School | Elearning Platform Kabojja Junior School Holiday Work Pdf Klb Agriculture Book 3 Klb Agriculture Form 3 Teachers Guide Klb Agriculture Notes List of Ugandan E-learning Platforms for Students Mirembe Junior School Holiday Work Ntare School Past Papers O Level Agriculture Notes Free Download O Level Agriculture Notes in Uganda O Level Agriculture Notes Pdf O Level Agriculture Notes Uganda Pdf O Level Agriculture Notes Uganda Pdf Download O Level General - Home › Gayaza High School | Elearning S.1 Agriculture Notes | Standard High School Zzana S.3 Agriculture Notes S.4 Agriculture 2 Notes | Standard High School Zzana Seeta High School Elearning Seeta High School Holiday Work Seeta High School Notes Seeta High School Notes Pdf Seeta High School Past Papers Seeta High School Past Papers Pdf Senior 1 Agriculture Notes Senior 1 Agriculture Notes in Uganda Senior 1 Agriculture Notes Uganda Senior 1 Agriculture Questions Senior 1 Exams Senior 1 Work Senior 1 Work 2020 Senior 1 Work 2020 Uganda Senior 2 Agriculture Notes Senior 2 Agriculture Notes in Uganda Senior 2 Agriculture Notes Uganda Senior 2 Agriculture Questions Senior 2 Exams Senior 2 Work Senior 2 Work 2020 Senior 2 Work 2020 Uganda Senior 3 Agriculture Notes Senior 3 Agriculture Notes in Uganda Senior 3 Agriculture Notes Uganda Senior 3 Agriculture Questions Senior 3 Exams Senior 3 Work Senior 3 Work 2020 Senior 3 Work 2020 Uganda Senior 4 Agriculture Notes Senior 4 Agriculture Notes in Uganda Senior 4 Agriculture Notes Uganda Senior 4 Agriculture Questions Senior 4 Exams Senior 4 Work Senior 4 Work 2020 Senior 4 Work 2020 Uganda Senior Four Agriculture Notes Senior Four Agriculture Notes in Uganda Senior Four Agriculture Notes Uganda Senior Four Agriculture Questions Senior Four Exams Senior Four Work Senior Four Work 2020 Senior Four Work 2020 Uganda Senior One Agriculture Notes Senior One Agriculture Notes in Uganda Senior One Agriculture Notes Uganda Senior One Agriculture Questions Senior One Exams Senior One Work Senior One Work 2020 Senior One Work 2020 Uganda Senior Three Agriculture Notes Senior Three Agriculture Notes in Uganda Senior Three Agriculture Notes Uganda Senior Three Agriculture Questions Senior Three Exams Senior Three Work Senior Three Work 2020 Senior Three Work 2020 Uganda Senior Two Agriculture Notes Senior Two Agriculture Notes in Uganda Senior Two Agriculture Notes Pdf Senior Two Agriculture Notes Uganda Senior Two Agriculture Questions Senior Two Exams Senior Two Work Senior Two Work 2020 Senior Two Work 2020 Uganda St Mary's Kitende E Learning Standard High School Notes Standard High School Zana a Level Notes Standard High School Zana Com Notes Standard High School Zana E Learning Standard High School Zana E Learning Platform Standard High School Zana E-learning Platform Standard High School Zana Notes for Senior Two Standard High School Zana Notes Pdf Standard High School Zana Website Standard High Zana Notes Uace Agriculture Notes Uace Agriculture Notes Pdf Uce Agriculture Notes Pdf Uce Agriculture Notes Pdf Download Uce Past Papers Uganda Secondary Schools E-learning Platform Uneb Marking Guides Pdf Uneb Past Papers and Answers Pdf Agriculture Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Download Agriculture Notes Form 1-4 Agriculture Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 1 Agriculture Topical Questions Form 1 Agriculture Exam Paper With Answer Pdf Form 1 Exams 2020 Form 1 Agriculture Past Papers Form 1 Agriculture Revision Papers With Answers Sample Agriculture Test for Form One Exams Ntare School Past Papers Seeta High School Notes Pdf Seeta High School Past Papers Seeta High School Past Papers Pdf St Mary's Kitende Past Papers Uce Agriculture Notes Pdf Uce Past Papers Uneb Marking Guides Pdf Uneb Past Papers and Answers Pdf Agriculture Book 3 Download Agriculture Form 3 Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 3 Syllabus Agriculture Form 3 Topics Agriculture Notes Form 3 Agriculture Notes Form 3 Agriculture Notes Form 3 Agriculture Notes Form Three Agriculture Notes Pdf Download Form 3 Agriculture Exam Form 3 Agriculture Notes on Pdf Revision Agriculture Revision a Level Agriculture Revision Notes - Agriculture S.1-Agriculture-notes S.1-Agriculture-notes Uganda S.2-Agriculture-notes S.2-Agriculture-notes Uganda S.3-Agriculture-notes S.3-Agriculture-notes Uganda S.4-Agriculture-notes S.4-Agriculture-notes Uganda S.5-Agriculture-notes S.5-Agriculture-notes Uganda S.6-Agriculture-notes S.6-Agriculture-notes Uganda S1 Agriculture Notes Term 1 S1 Agriculture Notes Term 2 S1 Agriculture Notes Term 3 S2 Agriculture Notes Term 1 S2 Agriculture Notes Term 2 S2 Agriculture Notes Term 3 S3 Agriculture Notes Term 1 S3 Agriculture Notes Term 2 S3 Agriculture Notes Term 3 S4 Agriculture Notes Term 1 S4 Agriculture Notes Term 2 S4 Agriculture Notes Term 3 Senior 3 Agriculture Notes Senior 3 Agriculture Notes Uganda Senior Three Agriculture Notes Senior Three Agriculture Notes Uganda Agriculture Form 1 the Cell Agriculture Form One Notes Free – Education News Agriculture Notes Form 1-4 Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 1 - Agriculture Form One Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 2 - Agriculture Form Two Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 3 - Agriculture Form Three Agriculture Questions and Answers Form 4 - Agriculture Form Four Agriculture Questions and Answers Senior 1 - Agriculture Senior One Agriculture Questions and Answers Senior 2 - Agriculture Senior Two Agriculture Questions and Answers Senior 3 - Agriculture Senior Three Agriculture Questions and Answers Senior 4 - Agriculture Senior Four Agriculture Topic by Topic Questions and Answers Combined Science Notes Form 1 Form 1 Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form 1 Agriculture Topical Questions Form 1 Revision Papers With Answers Form 2 Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form 3 Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form Four Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form One Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form Three Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Form Two Agriculture Revision Questions and Answers Free Agriculture Form 1 Notes Free Agriculture Notes Introduction to Agriculture Form One Kcse Past Papers: Agriculture Form 1 Kcse Past Papers: Agriculture Form 1 Topical Questions Kcse Past Papers: Agriculture Form 1 Topical Questions and Answers Most Tested Areas in Agriculture Kcse Most Tested Areas in Agriculture Kcse Exams Most Tested Areas in Agriculture Uneb Most Tested Areas in Form 1 in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Form 2 in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Form 3 in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Form 4 in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Form Four in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Form One in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Form Three in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Form Two in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Kcse Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Kcse Agriculture Exams Most Tested Areas in Senior 1 in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Senior 2 in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Senior 3 in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Senior 4 in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Senior Four in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Senior One in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Senior Three in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Senior Two in Agriculture Most Tested Areas in Uneb Agriculture Revision Notes Agriculture Form 1 - Free Kcse Past Papers Who Was Agriculture Champion KCSE 2019 Top 100 Students in Agriculture KCSE 2019 Best 100 Students in Agriculture KCSE 2019 Top Student in Agriculture KCSE Best Student in Agriculture KCSE Who Was Agriculture Champion KCSE 2020 Top 100 Students in Agriculture KCSE 2020 Best 100 Students in Agriculture KCSE 2020 Names of Best Agriculture Students KCSE Names of Top Agriculture Students KCSE High School Agriculture Notes Pdf Best High School Agriculture Notes Pdf Comprehensive High School Agriculture Notes Pdf Klb Agriculture Form 1 Book Pdf Agriculture Form 1 Best Notes Agriculture Form 1 Notes Pdf Agriculture Form 1 Pressure Agriculture Form 1 Questions and Answers Agriculture Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Download Agriculture Form 2 Best Notes Agriculture Form 3 Best Notes Agriculture Form 4 Best Notes Agriculture Form Four Best Notes Agriculture Form One Best Notes Agriculture Form Three Best Notes Agriculture Form Two Best Notes Agriculture Notes Form 1 to 4 Agriculture Notes Pdf The Type of Soil Erosion That Can Occur Without Its Effects Being Easily Noticed Is Sheet Erosion Gully Erosion Rill Erosion Splash Erosion What Are the Main Types of Erosion What Are the Two Types of Soil Erosion What Is Soil Erosion What Causes Soil Erosion
Scholarship 2026/27
Current Scholarships 2026/2027 - Fully Funded
Full Undergraduate Scholarships 2026 - 2027
Fully Funded Masters Scholarships 2026 - 27
PhD Scholarships for International Students - Fully Funded!
Funding Opportunities for Journalists 2026/2027
Funding for Entrepreneurs 2026/2027
***
