KCSE Past Papers 2019 Power Mechanics Paper 1
Click Here - Free KCSE Past Papers » KCSE Past Papers 2019 Power Mechanics Paper 1 » Free Downloads » KCSE Papers & Marking Schemes
1. State the purpose of yellow lines in a power mechanics workshop. (1 mark)
(b) State three factors which should be considered when locating an automotive spare parts store. (3 marks)
2. (a) State two safety precautions which should be observed when working with grease and Oils. (2 marks)
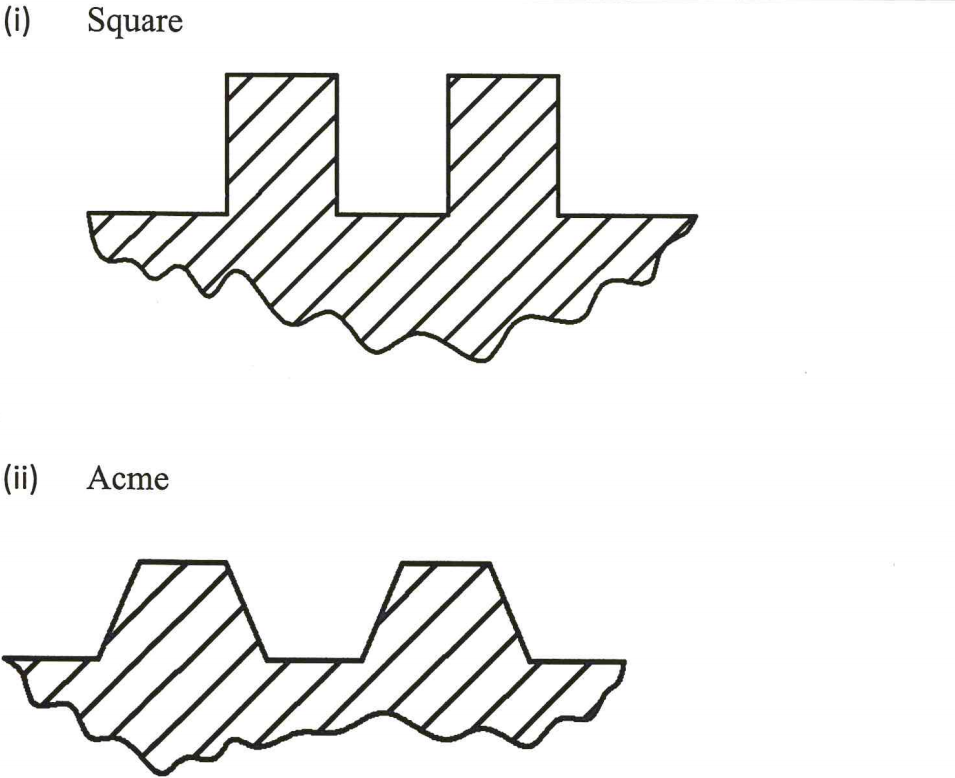
(b) Sketch each of the following types of screw threads.
(i) square (1 marks)
(ii) acme (1 marks)
3. (a) State the purpose of each of the following tools in a motor vehicle garage:
(i) puller (1 mark)
(ii) telescopic gauge (1 mark)
(b) Explain the operational difference between an external circlip and an internal circlip.(2 marks)
4. (a) Describe the energy conversion cycle in a conventional internal combustion engine.(2 marks)
(b) Describe the volumetric efficiency of an engine. (2 marks)
5. (a) Explain one negative effect of high compression ratio in an engine.(2 marks)
(b) State two properties of copper that makes it attractive for use in auto-electrics.(1 marks)
6. (a) State two functions of seals in an engine.(2 marks)
(b) Outline two reasons for carrying out ignition timing.(2 marks)
7. (a)State the effect of:
(i) too small contact breaker points gap (1 marks)
(ii) too big contact breaker points gap (1 marks)
(b) State two methods used by motor vehicle designers to reduce crankshaft whip. (2 marks)
8. (a) Outline two causes of excessive sulphation of a vehicle battery.(2 marks)
(b) State three advantages of brazing over fusion welding.(3 marks)
9. (a) Explain the following terms as used in braking systems:
(i) brake fade(1 marks)
(ii) primary shoe(1 marks)
(b) State the purpose of the safety ridge near the lips of a tyre rim.(1 marks)
10. (a) Name four types of springs used in vehicle suspension systems.(2 marks)
(b) Outline two reasons for having caster angle in steering geometry.(2 marks)
SECTION B (60 marks)
Answer question 11 on A3 paper provided and any other three questions from this section in the spaces provided.
Candidates are advised to spend not more than 25 minutes on question 11.
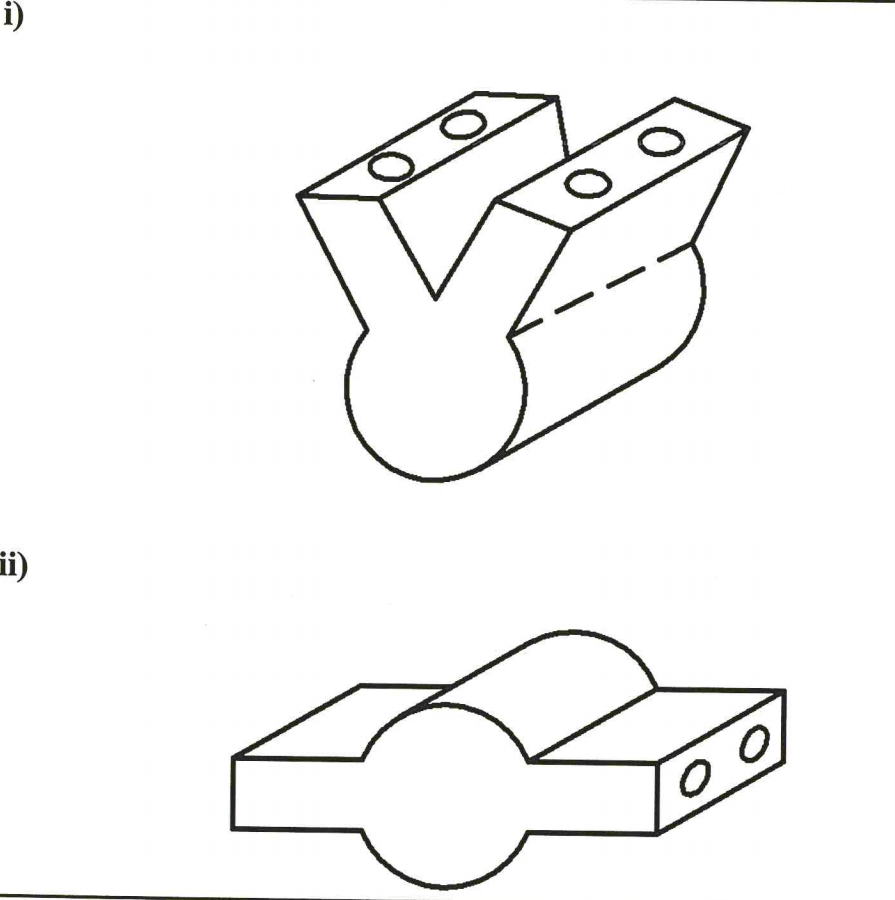
11. Figure 1 shows a machine block drawn in isometric projection.
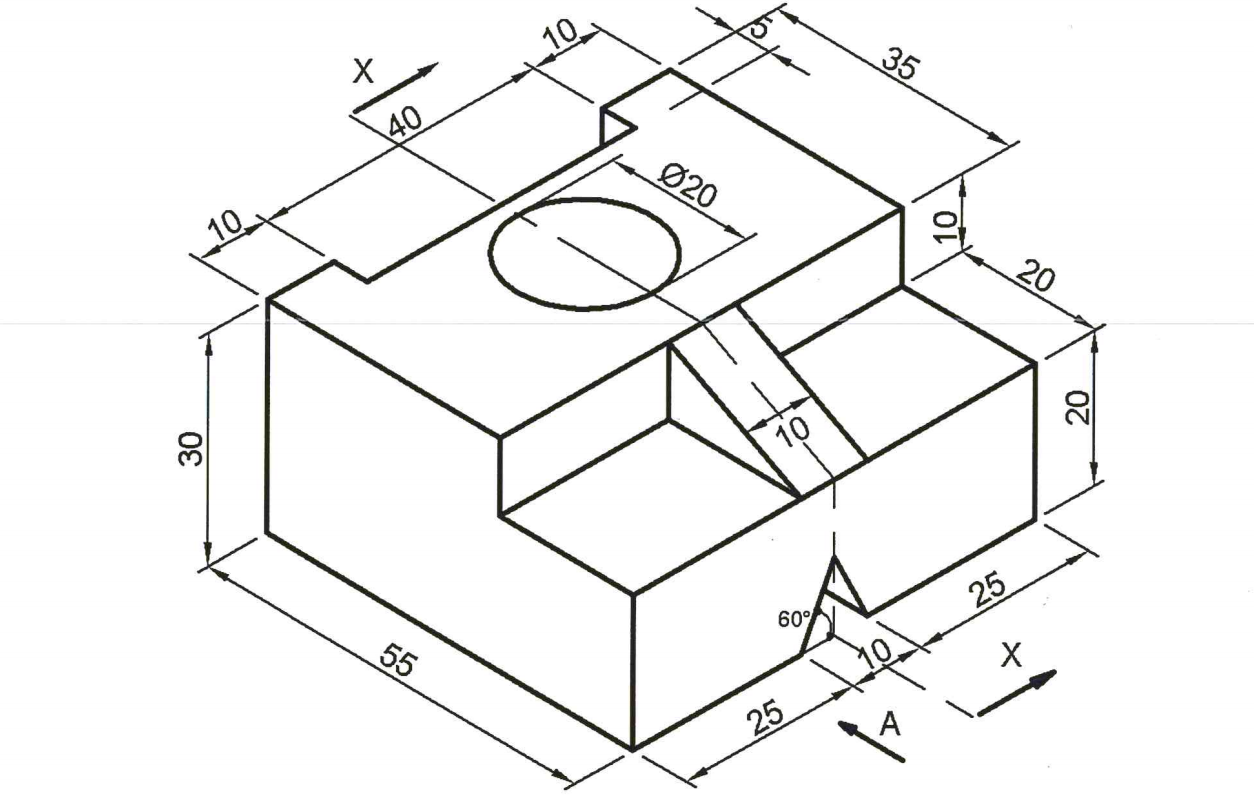
(a) Front elevation in the direction of arrow A;
(b) A sectioned end elevation along the cutting plane x — x.
NB. The Ø 20 mm is a through hole and the 10mm V-trough also goes through the block.(15 marks)
12. (a) Figure 2 shows a component of a vehicle system.
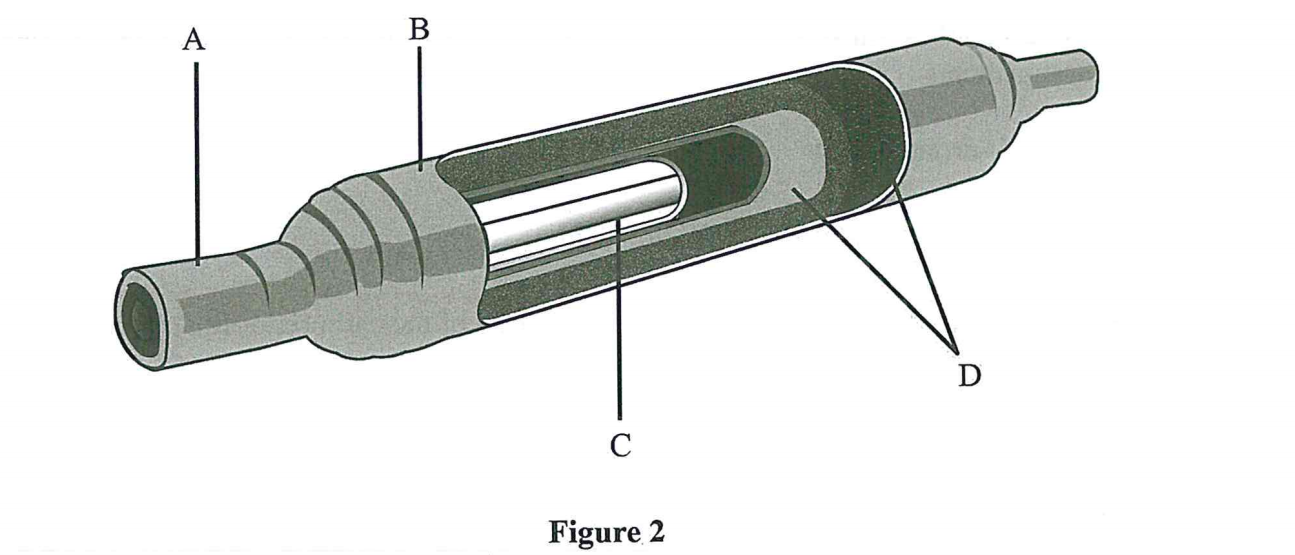
(ii) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (2 marks)
A .....................
B .....................
C .....................
D .....................
(iii) Explain how the component works. (3 marks)
(b) Interpret the meaning of each of the following types of smoky exhausts and in each case, state two possible causes. Complete the table.(9 marks)
| Type of Smoke | Meaning | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Blue | (i) (ii) |
|
| Black | (i) (ii) |
|
| White | (i) (ii) |
(b) Using sketches, illustrate the four-cylinder engines with the following types of cylinder arrangements:
(i) V-arrangement (2 marks)
(ii) horizontally-opposed arrangement (2 marks)
(c) With the aid of a diagram, explain the operation of the carburettor float circuit of a single cylinder engine.(8 marks)
14. (a) List two functions of the crown and pinion assembly of the differential unit. (2 marks)
(b) (i) Sketch a 8uid coupling assembly and label six parts.(7 marks)
(ii) Explain the operation of the coupling when the engine is:
(a) idling (2 marks)
(b) running at low to medium speed (2 marks)
(c) running at medium to high speed (2 marks)
15. (a) State the purpose of each of the following valves in a braking system.
(i) metering valve (1 marks)
(ii) proportionating valve (1 marks)
(b) Outline the procedure of bleeding air out of a braking system. (7 marks)
(c) State two possible causes of each of the following faults in motor vehicle electrical circuits.
(i) Head lights dim when engine is idling (2 marks)
(ii) Wiper fails to operate (2 marks)
(iii) Horn sound is faint (2 marks)
Marking Scheme
KCSE Past Papers 2019 Power Mechanics Paper 1
1. State the purpose of yellow lines in a power mechanics workshop. (1 mark)
(b) State three factors which should be considered when locating an automotive spare parts store. (3 marks)
2. (a) State two safety precautions which should be observed when working with grease and Oils. (2 marks)
(b) Sketch each of the following types of screw threads.
(i) square (1 marks)
(ii) acme (1 marks)
(i) puller (1 mark)
Puller — used for pulling out gears, hubs, bearings, etc.
(ii) telescopic gauge (1 mark)
Telescopic gauge — used together with outside micrometer for measuring diameters of small holes, or widths of slots, grooves, etc.
(b) Explain the operational difference between an external circlip and an internal circlip.(2 marks)
An external circlip fits into a groove on the outside of a shaft and is so made that it tends to contract in diameter.
An internal circlip fits into a groove on the inside of a hole and is so made that it tends to expand and increase its diameter.
4. (a) Describe the energy conversion cycle in a conventional internal combustion engine.(2 marks)
(b) Describe the volumetric efficiency of an engine. (2 marks)
Volumetric efficiency is a measure of an engine’s ability to draw fuel mixture into the cylinders. It is determined by the ratio between what is actually drawn in and what could be drawn in if all the cylinders were completely filled up.
Its formulae
Volumetric efficiency —— Total volume of the charee/ Total cylinders’ volume (displacement)
5. (a) Explain one negative effect of high compression ratio in an engine.(2 marks)
It can lead to engine knocking or detonation, whereby secondary explosion occurs after the spark plug has fired, causing excessive rapid burning of mixture and a pinging or knocking noise. This can damage the engine/con rod cylinder.
(b) State two properties of copper that makes it attractive for use in auto-electrics.(1 marks)
6. (a) State two functions of seals in an engine.(2 marks)
(b) Outline two reasons for carrying out ignition timing.(2 marks)
7. (a)State the effect of:
(i) too small contact breaker points gap (1 marks)
- Induced current will be low and therefore produced spark will be weak. -Advance weak sparks leading into power loss
(ii) too big contact breaker points gap (1 marks)
- May lead to inadequate opening of the points being unable to interrupt current flow in the primary circuit and this may lead to misfiring.
-Retarded/delayed strong sparks leading to engine overheating
(b) State two methods used by motor vehicle designers to reduce crankshaft whip. (2 marks)
8. (a) Outline two causes of excessive sulphation of a vehicle battery.(2 marks)
(b) State three advantages of brazing over fusion welding.(3 marks)
9. (a) Explain the following terms as used in braking systems:
(i) brake fade(1 marks)
Brake fade — refers to loss of frictional properties of the brake lining due to overheating.
(ii) primary shoe(1 marks)
(ii) Primary shoe: refers to the forward or leading brake shoe that moves in the direction of rotation of the drum.
(b) State the purpose of the safety ridge near the lips of a tyre rim.(1 marks)
Its purpose is to prevent the tyres from moving into the drop center of the rim when the tyre blows and thus coming off the wheel.
10. (a) Name four types of springs used in vehicle suspension systems.(2 marks)
(b) Outline two reasons for having caster angle in steering geometry.(2 marks)
SECTION B (60 marks)
Answer question 11 on A3 paper provided and any other three questions from this section in the spaces provided.
Candidates are advised to spend not more than 25 minutes on question 11.
11. Figure 1 shows a machine block drawn in isometric projection.

(a) Front elevation in the direction of arrow A;
(b) A sectioned end elevation along the cutting plane x — x.
NB. The Ø 20 mm is a through hole and the 10mm V-trough also goes through the block.(15 marks)
Front elevation
4 faces x '/2 = 2
Trough = 1
4 hidden details
Sub-total
End elevation 6 faces x '/2 — 3 2 selected faces 2 x 1 = 2 Quality of hatching = 1 Web (not sectional) 1 Cutting plane xx 1 Subtotal 8 First angle 1 Scale (double size) = 1 Subtotal — 2 Gross Total
12. (a) Figure 2 shows a component of a vehicle system.

(i) State the name and type of the component.
Straight through mufller
(ii) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (2 marks)
A - inlet
B - shell (body)
C - perforated pipe
D - fibre glass
(iii) Explain how the component works. (3 marks)
(b) Interpret the meaning of each of the following types of smoky exhausts and in each case, state two possible causes. Complete the table.(9 marks)
| Type of Smoke | Meaning | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Blue | Water in the system | - Worn piston - Bad valve seal Damaged glow plug - Stuck PVC value Worn Engine - Blown turbo |
| Black | Mixture is too rich | - High speed driving - Fuel pump leakage/faulty - Clogged air cleaner - Stuck jets/fuel needle |
| White | There is steam in exhaust | - coolant leaking into exhaust - worn cylinder head gasket - loose cylinder head bolts |
(b) Using sketches, illustrate the four-cylinder engines with the following types of cylinder arrangements:
(i) V-arrangement (2 marks)
(ii) horizontally-opposed arrangement (2 marks)
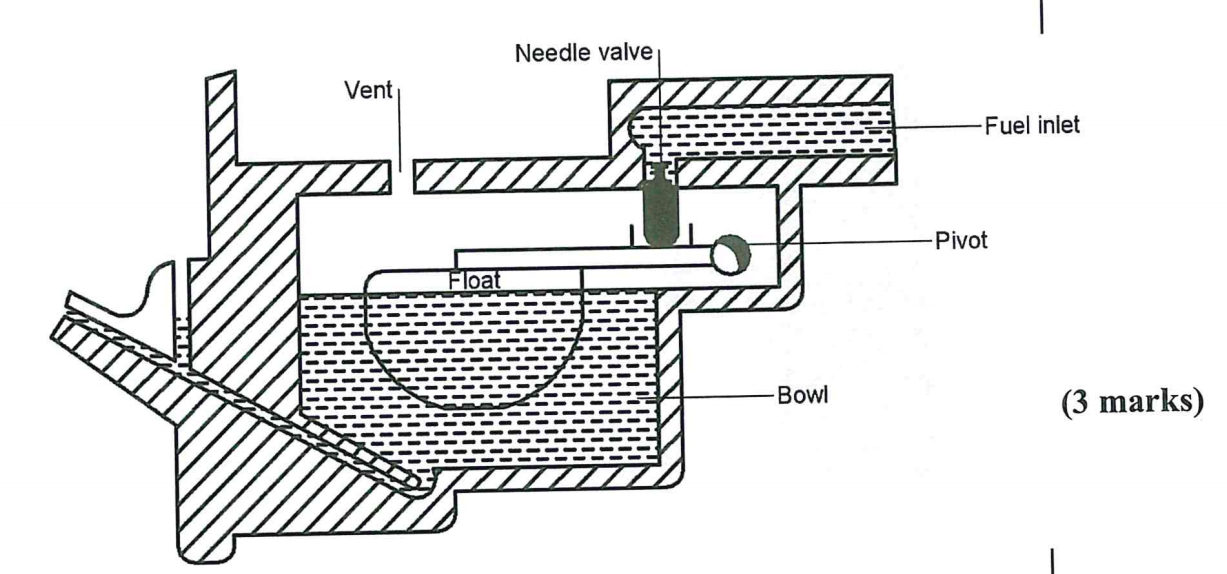
This circuit consists of a float bowl, float and a needle assembly. If the fuel enters the bowl faster than it leaves, the fuel level rises. (Id The rise causes the float to move up and push up the needle valve into a valve seat, closing the fuel inlet to the float bowl.bJ2 When the fuel level drops, the float moves down and releases the needle valve so that fuel inlet opens for fuel to enter the bowl (1) and compensate for the drop. During the engine operation, the float tends to keep the needle valve partly closed so that the fuel flow from the bowl is the same as the fuel flow into the bowl, and therefore a constant level is maintained
14. (a) List two functions of the crown and pinion assembly of the differential unit. (2 marks)
(b) (i) Sketch a fuid coupling assembly and label six parts.(7 marks)
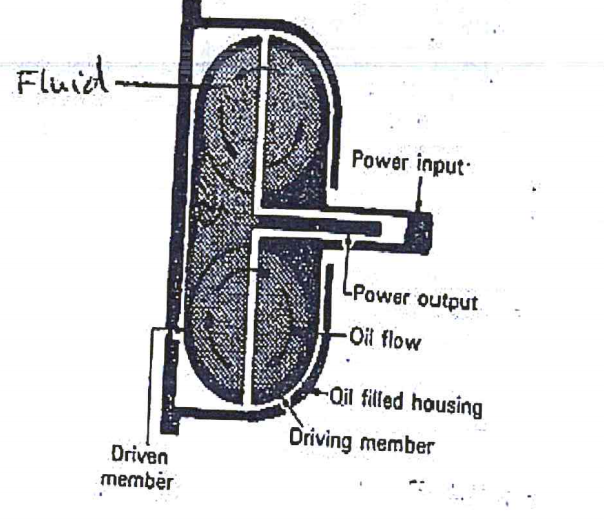
(a) idling (2 marks)
When the engine is idling, there is insufficient centrifugal force for the oil to turn the turbine and so to move the car.
(b) running at low to medium speed (2 marks)
As the engine speeds up, centrifugal force pushes into the turbine and some turning effort is transmitted.
But there is still a large degree of ‘slip’ in the unit; the output shaft therefore rotating more slowly than the input shaft.
(c) running at medium to high speed (2 marks)
Once the engine reaches preset high speed, the force of the oil is sufficient to transmit full power.
This gives in effect a direct drive with the output shaft rotating at about 98% of the speed of the output shaft.
15. (a) State the purpose of each of the following valves in a braking system.
(i) metering valve (1 marks)
Prevents brake fluid movement to the discs until a specified psi has built up in the system. (72 — 125 lbs)
(ii) proportionating valve (1 marks)
limits the amount of pressure to the rear drum brakes to prevent rear wheel lock-up during rapid stops
(b) Outline the procedure of bleeding air out of a braking system. (7 marks)
(c) State two possible causes of each of the following faults in motor vehicle electrical circuits
(i) Head lights dim when engine is idling (2 marks)
(ii) Wiper fails to operate (2 marks)
(iii) Horn sound is faint (2 marks)
Kenya Scholarships for Undergraduate Students » Kenya Scholarships for Postgraduate Students » Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyan Students » Kenya Undergraduate Scholarships » Full Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyans » Kenya Postgraduate Scholarships » Scholarships & Grants » Undergraduate Scholarships » Universities in Kenya » Kenya Universities and Colleges Central Placement Service (KUCCPS) » Colleges in Kenya » KASNEB Registration & Results » Secondary Schools Scholarships in Kenya » Undergraduate & Graduate Scholarships for Kenyans
Scholarships for African Students » Undergraduate Scholarships » African Women Scholarships & Grants » Developing Countries Scholarships » Erasmus Mundus Scholarships for Developing Countries » Fellowship Programs » Funding Grants for NGOs » Government Scholarships » LLM Scholarships » MBA Scholarships » PhD and Masters by Research Scholarships » Public Health Scholarships - MPH Scholarships » Refugees Scholarships » Research Grants » Scholarships and Grants
Scholarships in Australia » Scholarships in Belgium » Scholarships in Canada » Scholarships in Germany » Scholarships in Italy » Scholarships in Japan » Scholarships in Korea » Scholarships in Netherlands » Scholarships in UK » Scholarships in USA
Scholarship 2026/27
Current Scholarships 2026/2027 - Fully Funded
Full Undergraduate Scholarships 2026 - 2027
Fully Funded Masters Scholarships 2026 - 27
PhD Scholarships for International Students - Fully Funded!
Funding Opportunities for Journalists 2026/2027
Funding for Entrepreneurs 2026/2027
***
